Abstract
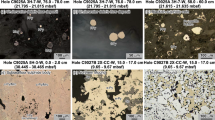
THE hydrothermal circulation of sea water through permeable ocean crust results in rock–water interactions that lead to the formation of massive sulphide deposits. These are the modern analogues of many ancient ophiolite-hosted deposits1–4, such as those exposed in Cyprus. Here we report results obtained from drilling a series of holes into an actively forming sulphide deposit on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. A complex assemblage of sulphide–anhydrite–silica breccias provides striking evidence that such hydrothermal mounds do not grow simply by the accumulation of sulphides on the sea floor. Indeed, the deposit grows largely as an in situ breccia pile, as successive episodes of hydrothermal activity each form new hydrothermal precipitates and cement earlier deposits. During inactive periods, the collapse of sulphide chimneys, dissolution of anhydrite, and disruption by faulting cause brecciation of the deposit. The abundance of anhydrite beneath the present region of focused hydrothermal venting reflects the high temperatures ( > 150 °C) currently maintained within the mound, and implies substantial entrainment of cold sea water into the interior of the deposit. These observations demonstrate the important role of anhydrite in the growth of massive sulphide deposits, despite its absence in those preserved on land.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Spooner, E. T. C. in Deep Drilling Results in the Atlantic Ocean: Ocean Crust (eds Talwani, M., Harrison, C. G. & Hayes, D. E.) 429–431 (Am. Geophys. Un., Washington DC., 1978).
Spooner, E. T. C. Geol. Ass. Canada Spec. Pap. 20, 685–704 (1980).
Rona, P. A. & Scott, S. D. Econ. Geol. 88, 1935–1975 (1993).
Herzig, P. M. & Hannington, M. D. Ore Geol. Rev. (in the press).
Rona, P. A. et al. Econ. Geol. 18, 1989–2017 (1993).
Rona, P. A. et al. J. geophys. Res. 98, 9715–9730 (1993).
Rona, P. A., Klinkhammer, G., Nelsen, T. A., Trefry, J. H. & Elderfield, H. Nature 321, 33–37 (1986).
Lalou, C. et al. Earth planet. Sci. Lett. 97, 113–128 (1990).
Lalou, C. et al. J. geophys. Res. 98, 9705–9713 (1993).
Humphris, S. E., Kleinrock, M. C. & Deep-TAG Team (abstr.) Eos 75, 660 (1994).
Thompson, G., Humphris, S. E., Schroeder, B., Sulanowska, M. & Rona, P. A. Can. Mineralogist 26, 697–711 (1988).
Tivey, M. K., Humphris, S. E., Thompson, G., Hannington, M. D. & Rona, P. A. J. geophys. Res. 100, 12527–12555 (1995).
Campbell, A. C. et al. Nature 335, 514–519 (1988).
Edmond, J. M., Campbell, A. C., Palmer, M. R. & German, C. R. (abstr.) Eos 71, 1650–1651 (1990).
Edmond, J. M. et al. in Hydrothermal Vents and Processes (eds Parson, L. M., Walker, C. L. & Dixon, D. R.) 77–86 (Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ., London, 1995).
Franklin, J. M., Lydon, J. W. & Sangster, D. F. Econ. Geol. 75, 485–627 (1981).
Strens, M. R. & Cann, J. R. Tectonophysics 122, 307–324 (1986).
Strens, M. R. & Cann, J. R. Geophys. J. R. astr. Soc. 71, 225–240 (1982).
Adamides, N. G. thesis, Univ. Leicester (1984).
Constantinou, G. in Proc. Int. Ophiolite Symp. on Ophiolites (ed. Panayioutou, A.) 663–674 (Cyprus Geol. Surv. Dept., Nicosia, 1980).
Lydon, J. W. Geol. Surv. Can. Pap. 84–1A, 601–610 (1984).
Constantinou, G. Geol. Ass. Can. Spec. Pap. 14, 187–210 (1976).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Humphris, S., Herzig, P., Miller, D. et al. The internal structure of an active sea-floor massive sulphide deposit. Nature 377, 713–716 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/377713a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/377713a0
This article is cited by
-
Sulfide metallogenic model for the ultraslow-spreading Southwest Indian Ridge
Science China Earth Sciences (2023)
-
Trace metal and sulfur cycling in a hydrothermally active arc volcano: deep-sea drilling of the Brothers volcano, Kermadec arc, New Zealand
Mineralium Deposita (2023)
-
Iron isotopes constrain sub-seafloor hydrothermal processes at the Trans-Atlantic Geotraverse (TAG) active sulfide mound
Communications Earth & Environment (2022)
-
Mineral-scale variation in the trace metal and sulfur isotope composition of pyrite: implications for metal and sulfur sources in mafic VMS deposits
Mineralium Deposita (2022)
-
Low-temperature silica-rich gold mineralization in mafic VMS systems: evidence from the Troodos ophiolite, Cyprus
Mineralium Deposita (2021)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.