Abstract
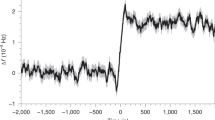
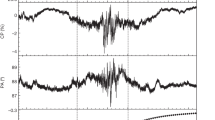
THE rotation rate of a pulsar is thought to decrease with time according to a simple power law, with a 'braking index' equal to 3 if rotational energy is lost through radiation from a dipolar magnetic field1–3. The age of the pulsar can accordingly be determined simply by measuring the current rotation rate, and its current rate of change. Here we report an analysis of the rotation rate of the Vela pulsar as observed over 25 years. We find that the braking index is 1.4 ± 0.2, suggesting that the braking cannot be attributed entirely to radiation from a constant magnetic dipole but is probably due to a changing, magnetic moment or effective moment of inertia. Taken at face value, the result implies that the Vela pulsar may be much older than previously thought, and that inferred velocities of the supernova ejecta4 and an X-ray jet from the pulsar5 are correspondingly reduced. If other young pulsars associated with supernova remnants have similarly low braking indices, then they too may be much older than believed, thereby reducing their estimated velocities.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pacini, F. Nature 219, 145–146 (1968).
Ostriker, J. P. & Gunn, J. E. Astrophys. J. 157, 1395–1417 (1969).
Goldreich, P. & Julian, W. H. Astrophys. J. 157, 869–880 (1969).
Strom, R., Johnston, H. M., Verbunt, F. & Aschenbach, B. Nature 373, 590–592 (1995).
Markwardt, C. B. & Ögelman, H. Nature 375, 40–42 (1995).
Lyne, A. G., Pritchard, R. S. & Smith, F. G. Mon. Not. R. astr. Soc. 265, 1003–1012 (1993).
Boyd, P. T. et al. Astrophys. J. 448, 365–368 (1995).
Kaspi, V. M., Manchester, R. N., Siegman, B., Johnston, S. & Lyne, A. G. Astrophys. J. 422, L83–L86 (1994).
Baym, G., Pethick, C., Pines, D. & Ruderman, M. Nature 224, 872–874 (1969).
Alpar, M. A., Chau, H. F., Cheng, K. S. & Pines, D. Astrophys. J. 409, 345–359 (1993).
Cordes, J. M., Downs, G. S. & Krause-Polstorff, J. Astrophys. J. 330, 847–869 (1988).
Chau, H. F., McCulloch, P. M., Nandkumar, R. & Pines, D. Astrophys. J. 413, L113–L116 (1993).
Manchester, R. N. & Taylor, J. H. Pulsar (Freeman, San Francisco, 1977).
Aschenbach, B., Egger, R. & Trümper, J. Nature 373, 587–590 (1995).
Bailes, M., Manchester, R. N., Kesteven, M. J., Norris, R. P. & Reynolds, J. E. Astrophys J. 343, L53–L55 (1989).
Blandford, R. D. & Romani, R. W. Mon. Not. R. astr. Soc. 234, 57P–60P (1988).
Alpar, M. A. & Pines, D. in Isolated Pulsars (eds Van Riper, K. A., Epstein, R. & Ho, C.) 17–27 (Cambridge Univ. Press, 1993).
Lyne, A. G. in The Lives of the Neutron Stars (eds Alpar, A., Kiziloğlu, Ü. & van Paradis, J.) 167–176 (NATO ASI Ser., Kluwer, Dordrecht, 1995).
Frail, D. A., Goss, W. M. & Whiteoak, J. B. Z. Astrophys. J. 437, 781–793 (1994).
Frail, D. A. & Kulkarni, S. R. Nature 352, 785–787 (1991).
Lyne, A. G. & Lorimer, D. R. Nature 369, 127–129 (1994).
Downs, G. S. & Reichley, P. E. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 53, 169–240 (1983).
Downs, G. S. & Krause-Polstorff, J. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 62, 81–107 (1986).
Flanagan, C. S. in The Lives of Neutron Stars (eds Alpar, A., Kiziloğlu, Ü. & van Paradis, J.) 181–184 (NATO ASI Ser., Kluwer, Dordrecht, 1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lyne, A., Pritchard, R., Graham-Smith, F. et al. Very low braking index for the Vela pulsar. Nature 381, 497–498 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/381497a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/381497a0
This article is cited by
-
A study of microglitches in Hartebeesthoek radio pulsar
Astrophysics and Space Science (2016)
-
Rotational evolution of young pulsars due to superfluid decoupling
Nature Physics (2012)
-
New phase-coherent measurements of pulsar braking indices
Astrophysics and Space Science (2007)
-
Two decades of pulsar timing of Vela
Astrophysics and Space Science (2007)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.