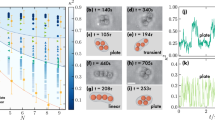
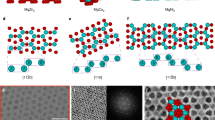
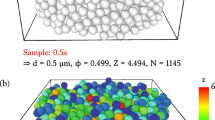
Abstract
THE attention which J. D. Bernal1 has directed to the importance of geometrical models for representing the structure of liquids has elicited considerable recent interest in the packing of spheres2–7. While previous investigations were often concerned with the dense random state8,9, some of the more recent work has been devoted to looser states3,4,6. Both Scott3 and MacRae and Gray4 obtained loose deposits of spheres by a rolling procedure, while Rutgers6, in common with Leva et al.10 some years earlier, obtained a loose packing by dumping or pouring. Porosities thus reported, though significantly higher than those found in the dense random state, are nevertheless still lower than those obtained either by rapidly inverting a cylinder11 or by gradually diminishing to zero the gas (or liquid) flow through a fluidized bed12,13. It is the latter porosities which correspond to those observed in both moving packed14 and incipiently fluidized13 beds.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernal, J. D., Nature, 183, 141 (1959).
Mangelsdorf, P. C., and Washington, E. L., Nature, 187, 930 (1960).
Scott, G. D., Nature, 188, 908 (1960).
MacRae, J. C., and Gray, W. A., Brit. J. App. Phys., 12, 164 (1961).
Parrish, J. R., Nature, 190, 800 (1961).
Rutgers, R., Nature, 193, 465 (1962).
Smalley, I. J., Nature, 194, 1271 (1962).
Mott, R. A., Some Aspects of Fluid Flow, Paper 14 (Edward Arnold, London, 1951).
Denton, W. H., A.E.R.E. E/R 1095 (Harwell, 1953).
Leva, M., et al., U.S. Bur. Mines Bull., 504, 22 (1951).
Oman, A. O., and Watson, K. M., Refinery Management and Petroleum Chem. Tech., 36, R-795 (1944).
Ergun, S., and Orning, A. A., Indust. Chem. Eng., 41, 1179 (1949).
Leva, M., Fluidization, 21 (McGraw-Hill, 1959).
Happel, J., Indust. Eng. Chem., 41, 1161 (1949).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
EPSTEIN, N., YOUNG, M. Random Loose Packing of Binary Mixtures of Spheres. Nature 196, 885–886 (1962). https://doi.org/10.1038/196885a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/196885a0
This article is cited by
-
Effect of surface texture, size ratio and large particle volume fraction on packing density of binary spherical mixtures
Granular Matter (2020)
-
Melt segregation from silicic crystal mushes: a critical appraisal of possible mechanisms and their microstructural record
Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology (2018)
-
Orthopyroxene oikocrysts in the MG1 chromitite layer of the Bushveld Complex: implications for cumulate formation and recrystallisation
Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology (2018)
-
Crystal settling and convection in the Shiant Isles Main Sill
Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology (2017)
-
Geometrical parameters of binary granular mixtures with size ratio and volume fraction: experiments and DEM simulations
Granular Matter (2016)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.