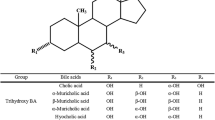
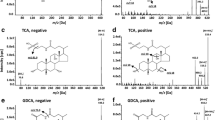
Summary
In order to analyse bile acids in biological matrices, e.g. rat bile and human serum, high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) was coupled to continuous-flow fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry (CFFAB-MS). A gradient elution system which had already proved to be well suited for the quantitative determination of conjugated bile acids in bile was modified to allow HPLC-CFFAB-MS-coupling. Due to the sensitivity of this coupling method it is possible to obtain more information about the biliary bile acid pattern and species-specific secondary bile acids. Furthermore, we were able to identify obviously unknown bile acid species in rat bile which most likely classify as mono-oxo and di-oxo-taurocholates (MW 513 Da, 511 Da) and mono-oxo-glycocholates (MW 463 Da). In the present study we show that using this system it is possible to determine both conjugated and unconjugated as well as sulfated bile acids, without time consuming group separation and derivatization, from rat bile and human serum. In addition, it is suggested that the method presented here should be considered for use in routine analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HPLC:
-
High Performance Liquid Chromatography
- CFFAB:
-
Continuous Flow Fast Atom Bombardment
- MS:
-
Mass Spectrometry
- LC:
-
Liquid Chromatography
- HPTLC:
-
High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography
- GC:
-
glycocholate
- TC:
-
taurocholate
- GCDC:
-
glycochenodeoxycholate
- TCDC:
-
taurochenodeoxycholate
- GDC:
-
glycodeoxycholate
- TDC:
-
taurodeoxycholate
- GLC:
-
glycolithocholate
- TLC:
-
taurolithocholate
- GUDC:
-
glycoursodeoxycholate
- TUDC:
-
tauroursodeoxycholate
- GHC:
-
glycohyocholate
- THC:
-
taurohyocholate
- GHDC:
-
glycohyodeoxycholate
- THDC:
-
taurohyodeoxycholate
- α-GM:
-
α-glycomuricholate
- α-TM:
-
α-tauromuricholate
- β-GM:
-
β-glycomuricholate
- β-TM:
-
β-tauromuricholate
- ω-GM:
-
ω-glycomuricholate
- ω-TM:
-
ω-tauromuricholate
References
R. Colman, Biochem. Soc. Transactions15, 68 (1987).
I. M. Arias, W. B. Jacoby, H. Popper, D. Schachter, D. A. Shafritz, “The Liver in Biology and Pathobiology”, Raven Press, New York (1988).
R. Balducci, A. Roda, R. S. Pearlman, J. Solution Chem.18, 355 (1989).
K. Miyasaka, A. Funakoshi, F. Shikado, K. Kitani, Gastroenterology102, 598 (1992).
P. H. E. Groot, N. J. Pearce, K. E. Suckling, S. Eisnberg, Biochim. Biophys. Acta1123, 76 (1992).
O. Hernell, J. E. Staggers, M. C. Carey, Biochemistry29, 2041 (1990).
J. E. Staggers, O. Hernell, R. J. Stafford, M. C. Carey, Biochemistry29, 2028 (1990).
M. C. Bateson, Brit. Med. J.284, 1 (1992).
J. M. Street, D. J. H. Trafford, H. L. J. Makin, J. Lipid Res.24, 491 (1983).
H. R. Almond, Z. R. Vlahcevic, C. C. Bell, D. H. Gregory, L. Swell, N. Engl. J. Med.289, 1213 (1973).
G. E. Muller, H. Bockhorn, R. Fleischmann, G. H. Muller, Transplant. Proc.13, 845 (1981).
D. Labbé, M. F. Gerhardt, A. Myara, C. Vercambre, F. Trivin, J. Chromatogr.490, 275 (1989).
K. Shimada, Y. Komine, K. Mitamura, J. Chromatogr.565, 111 (1991).
S. Yoshida, H. Murai, S. Hirose, T. Takeda, J. Chromatogr.431, 27 (1988).
J. Goto, Y. Teraya, T. Nambara, J. Chromatogr.585, 281 (1991).
J. Goto, H. Murai, M. Inada, T. Nambara, T. Nagakura, H. Suzuki, J. Chromatogr.452, 119 (1988).
C. Eckers, N. J. Haskins, T. Large, Biomed. Environ. Mass Spectrometry18, 702 (1989).
C. Eckers, P. B. East, N. J. Haskins, Biol. Mass Spectrometry20, 731 (1991).
K. D. R. Setchell, C. H. Vestal, J. Lipid Res.30, 1459 (1989).
B. L. Ackermann, J. Coutant, T.-M. Chen, in “Continuous Flow Fast Atom Bombardment Mass Spectrometry”, R. M. Caprioli, Ed., Wiley, Chichester (1990), p. 160.
J. E. Evans, A. Ghosh, B. A. Evans, M. R. Natowicz, Biol. Mass Spectrometry22, 331 (1993).
B. M. Warrack, G. C. DiDonnato, Biol. Mass. Spectrometry22, 101 (1993).
M. Kindel, H. Ludwig-Koehn, B. Lembcke, J. Chromatogr.497, 139 (1989).
L. Lepri, D. Heimler, P. G. Desideri, J. Chromatogr.288, 461 (1984).
S. Müllner, R. Hofmann, K. Saar, B. Karbe-Thönges, J. Planar Chromatogr.5, 408 (1992).
A. Rivas-Nass, S. Müllner, J. Planar Chromatogr.7, 278 (1994).
R. E. Levitt, J. C. Touchstone, J. High Resolut. Chromatogr. Commun.2, 588 (1979).
K. L. Busch, J. Planar Chromatogr.2, 355 (1989).
K. D. R. Setchell, A. Matsui, Clin. Chim. Acta127, 1 (1983).
K. D. R. Setchell, J. Worthington, Clin. Chim. Acta125, 135 (1982).
J. M. Street, D. J. H. Trafford, H. L. J. Makin, J. Chromatogr.343, 259 (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dax, C., Vogel, M. & Müllner, S. HPLC-continuous-flow fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry (HPLC-CFFAB) — a convenient method for the analysis of bile acids in bile and serum. Chromatographia 40, 674–679 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02315136
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02315136