Summary
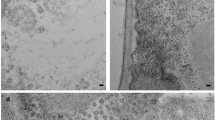
Wheat roots from germinating seedlings of Chinese spring wheatTriticum aestivum grown for 36 hours at 20°C were examined by conventional thin-section electron microscopy. Virus-like particles were seen inside a large cytoplasmic intrusion into the nucleus having the appearence of a nucleolar vacuole. The particles were isometric and about 50 nm in diameter with a membrane-like coat and a small core. The cytoplasmic intrusion was bounded by nuclear envelope with pores apparent where it abutted nucleoplasm. The particles are similar to previously reported solitary particles “S bodies” from a range of plants but are also similar in size and morphology to the retroposon particles associated with copia like elements in other organisms. The position of the virus-like particles in the young wheat roots is discussed in relation to interactions with components of the cell skeleton.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anton-Lamprecht I (1967) Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen an Plasmaabänderungen von Epilobium-Bastarden. I. Cytologische Untersuchungen zur Feinstruktur und Häufigkeit bisher unbekannter Partikeln in den Abänderungen der Irregulare-Gruppe und einigen anderen Plasmatypen. Protoplasma 64: 276–296
Burgess J, Motoyoshi F, Flemming EN (1974) Structural and autoradigraphic observation of the infection of tobacco protoplasts with pea enation mosaic virus. Planta 119: 247–256
Dörr I, Kollmann R (1974) Strukturelle Grundlage des Parasitismus beiOrobanche. I. Wachstum der Haustorialzellen im Wirtsgewebe. Protoplasma 80: 245–259
Esau K, Hoefert LL (1971) Cytology of beet yellow virus infection inTetragonia. 1. Parenchyma cells in infected leaf. Protoplasma 72: 255–273
— — 1972: Development of infection with beet western yellow virus in sugar beet. Virology 48: 724–738
Falk H (1976) Chromoplasts ofTropaeolum majus L.: structure and development. Planta 128: 15–22
Francki RIB, Milne RG, Hatta T (1985) Atlas of plant viruses, vol I. CRC Press, Florida, p 222
Garfinkel DJ, Boeke JD, Fink GR (1985) Ty element transposition: reverse transcriptase and virus-like particles. Cell 42: 507–517
Goff LJ (1976) Solitary bodies (S-bodies) in the parasitic red algaHarveyella mirabilis (Choreocolaceae, Cryptonemiales). Protoplasma 89: 189–195
Heine CW, Kelly DC, Avery RJ (1980) The detection of intracellular retrovirus-like entities inDrosophilia melanogaster cell cultures. J Gen Virol 49: 385–395
Hoefert LL (1984) Beet western yellow virus in phloem of Pennycress. J Ultrastruct Res 88: 44–54
Ie TS (1972) Cytoplasmic particles inTropaeolum majus. Planta 106: 227–236
Jordan EG (1976) Nuclear structure inDaucus carota L. Cytobiologie 14: 171–177
— (1984) Nucleolar nomenclature. J Cell Science 67: 217–220
—,Cooper PJ, Martini G, Bennet MD, Flavell RB (1985) The effect of temperature and ageing on root apical meristems during seedling growth ofTriticum aestivum L.: a specific effect of temperature. Plant Cell and Env 8: 325–331
—,McGovern JM (1981) The quantitative relationship of the fibrillar centres and other nucleolar components to changes in growth conditions, serum deprivaton and low doses of Actinomycin D in cultured diploid human fibroblasts (strain MRC-5). J Cell Sci 52: 373–389
Kim KS, Shock TL, Goodman RM (1978) Infection ofPhaseolus vulgaris by Bean Golden Mosaic Virus: ultrastructural aspects. Virology 89: 22–33
—,Ramsdell DC, Gillet JM, Fulton JP (1981) Virions and ultrastructural changes associated with Blueberry red ring spot disease. Phytopathology 71: 673–678
Kuff EL, Wivel WA, Luders KK (1968) The extraction of intracisternal A-particles from a mouse plasma-cell tumor. Cancer Res 28: 2137–2148
Matthews RF (1982) Classification and nomenclature of viruses. (Fourth report of the International Committee on taxonomy of viruses). Karger, Basel, p 199
Shiba T, Saigo K (1983) Retrovirus-like particles containing RNA homologous to the transposable elementcopia inDrosophilia melanogaster. Nature 302: 119–124
Sigee DC (1974) Structure and function in the ligule ofSelaginella kraussiana I. Fine structure and development. Protoplasma 79: 359–375
Sjolund RD, Shih CY (1970) Virus like particles in nuclei of cultured plant cells which have lost the ability to differentiate. Proc Natl Acad Sci 66: 25–31
Shikata E, Maramorosch K (1966) Electron microscopy of pea enation mosaic virus in plant cell nuclei. Virology 30: 439–454
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jordan, E.G., Cooper, P.J. Cytoplasmic virus-like particles associated with the nucleolus in wheat, similar to “S bodies” and retroposon particles. Protoplasma 133, 160–164 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01304631
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01304631