Summary
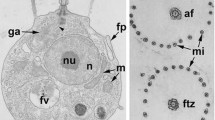
Cells ofScherffelia dubia regenerate flagella with a complete scale covering after experimental flagellar amputation. Flagellar regeneration was used to study Golgi apparatus (GA) activity during flagellar scale production. By comparing the number of scales present on mature flagella with the flagellar regeneration kinetics, it is calculated that each cell produces ca. 260 scales per minute during flagellar regeneration. Flagellar scales are assembled exclusively in the GA and abstricted from the rims of thetrans-most GA cisternae into vesicles. Exocytosis of scales occurs at the base of the anterior flagellar groove. The central portion of thetrans-most cisterna, containing no scales, detaches from the stack of cisternae and develops a coat to become a coated polygonal vesicle. Scale biogenesis involves continuous turnover of GA cisternae, and scale production rates indicate maturation of four cisternae per minute from each of the cells two dictyosomes. A possible model of membrane flow routes during flagellar regeneration, which involves a membrane recycling loop via the coated polygonal vesicles, is presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balch, W. A., Dunby, W. G., Braell, W. A., Rothman, J. E., 1984 a: Reconstitution of the transport of protein between successive compartments of Golgi measured by the coupled incorporation of N-acetylglucosamine. Cell39, 405–416.
—,Glick, B. S., Rothmann, J. E., 1984 b: Sequential intermediates in the pathway of intercompartmental transport in a cell-free system. Cell39, 525–536.
Bowles, D. J., Northcote, D. H., 1974: The amounts and rates of export of polysaccharides found within the membrane system of maize root cells. Biochem. J.142, 139–144.
Braell, W. A., Balch, W. E., Dobbertin, D. C., Rothmann, J. E., 1984: The glycoprotein that is transported between successive compartments of the Golgi in a cell-free system resides in stacks of cisternae. Cell39, 511–524.
Brown, R. M., 1969: Observations on the relationship of the Golgi apparatus to wall formation in the marine Chrysophyceaen algaPleurochrysis scherffelii Pringsheim. J. Cell. Biol.41, 109–123.
—, 1974: The Golgi apparatus and endomembrane system: its role in the biosynthesis, transport, and secretion of cell wall constituents inPleurochrysis. Port. Acta Biol.14, 369–384.
—,Herth, W., Franke, W. W., Romanovic, D., 1973: The role of the Golgi apparatus in the biosynthesis of a cellulosic glycoprotein inPleurochrysis: a model system for synthesis of structural polysaccharides. In: Biogenesis of Plant Cell Wall Polysaccharides (Loewus F., ed.), pp. 207–257. New York: Academic Press.
Dunphy, W. G., Brands, R., Rothman, J. E., 1985: Attachment of terminal N-acetylglucosamine to asparagine-linked oliogosaccharides occurs in central cisternae of the Golgi stack. Cell40, 463–472.
Farquhar, M. G., 1978: Traffic of products and membranes through the Golgi complex. In: Transport of Molecules in Cellular Systems (Silverstein, S., ed.), pp. 341–362. Berlin: Dahlemkonferenzen.
—,Palade, G. E., 1981: The Golgi apparatus (complex)-(1954–1981)-from artifact to center stage. J. Cell Biol.91, 77s-103s.
Franke, W., W., Kartenbeck, J., 1976: Some principals of membrane differentiation. In: Progress in Differentiation Research (Müller-Berat, N., ed.), pp. 213–243. Amsterdam: North Holland Publishers.
—,Morré, D. J., Deumling, B., Cheetham, R. D., Kartenbeck, J., Jarasch, E. D., Zentgraf, H. W., 1971: Synthesis and turnover of membrane protein in rat liver: an examination of the membrane flow hypothesis. Z. Naturforsch.26b, 1031–1039.
Jamieson, J. D., Palade, G. E., 1967: Intracellular transport of secretory proteins in the pancreatic exocrine cell I. Role of the peripheral elements of the Golgi complex. J. Cell Biol.34, 577–596.
Kies, L., 1967: Über Zellteilung und Zygotenbildung beiRoya obtusa (Bre.) West et West. Mitt. Staats, allg. Bot. Hamburg12, 35–42.
McFadden, G. I.,Preisig, H.,Melkonian, M., 1986: Golgi apparatus activity and membrane flow during scale biogenesis in the green flagellateScherffelia dubia (Prasinophyceae) II: Cell wall secretion and assembly. Protoplasma (in preparation).
—,Wetherbee, R., 1985: Flagellar regeneration and associated scale deposition inPyramimonas gelidicola (Prasinophyceae, Chlorophyta). Protoplasma128, 31–37.
Meldolesi, J. N., Borgese, P., de Camilli, P., Ceccarelli, B., 1978: Cytoplasmic membranes and the secretory process. In: Membrane Fusion (Poste, G., Nicolson, G. L., eds.), pp. 509–627. Amsterdam: Elsevier/North-Holland Biomedical Press.
Melkonian, M., 1975: The fine structure of zoospores ofFritschiella tuberosa Iyeng (Chaetophorineae, Chlorophyceae) with special reference to the flagellar apparatus. Protoplasma86, 391–404.
—, 1982: Effect of divalent cations on flagellar scales in the green flagellateTetraselmis cordiformis. Protoplasma111, 227–233.
-Preisig, H., 1986: A light and electron microscopic study ofScherffelia dubia, a new member of the scaly green flagellates (Prasinophyceae). Nord. J. Bot. (in press).
—,Reize, I. B., McFadden, G: I., 1985: Flagellar scales in the green flagellateTetraselmis striata: isolation, characterization and biogenesis. Eur. J. Cell Biol.36, 44 (abstract).
Moestrup, Ø., 1982: Flagellar structure in algae. A review with new observations in theChrysophyceae, Phaeophyceae (Fucophyceae), Euglenophyceae, and inReckertia. Phycologia21, 427–528.
Mollenhauer, H. H., 1971: Fragmentation of mature dictyosome cisternae. J. Cell Biol.49, 212–214.
Morré, D. J., 1975: Membrane biogenesis. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol.26, 447–487.
—, 1980: Flow differentiation of membranes: pathways and mechanisms. In: Cell Compartmentation and Metabolic Chanelling (Nover, L., Lynen, F., andMothes, K., eds.), pp. 47–61. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
—,Kartenbeck, J., Franke, W. W., 1979: Membrane flow and interconversions among endomembranes. Biochim. biophys. Acta559, 71–152.
—,Keenan, T. W., Huang, C. M., 1974: Membrane flow and differentiation: origin of Golgi apparatus membrane from endoplasmic reticulum. In: Advances in Cytopharmacology (Ceccarelli, B., Clementi, F., Meldolesi, J., eds.), pp. 107–125. New York: Raven Press.
—,Mollenhauer, H. H., Bracker, C. E., 1971: The origin and continuity of Golgi apparatus. In: Results and Problems in Cell Differentiation II. Origin and Continuity of Cell Organelles (Reinert, J., Ursprung, H., eds.), pp. 82–126. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer.
Novikoff, A. B., 1976: The endoplasmic reticulum: A cytochemists view (A review). Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.93, 2781–2787.
Orci, L., Halban, P., Amherdt, M., Ravazzola, M., Vassali, J. D., Perrelet, A., 1984: A clathrin-coated, Golgi-related compartment of the insulin secreting cell accumulates proinsulin in the presence of monensin. Cell39, 39–47.
Palade, G. E., 1975: Intracellular aspects of the process of protein synthesis. Science189, 347–358.
Phillips, J. H., Burridge, K., Wilson, J. P., Kirshner, N., 1983: Visualization of the exocytosis/endocytosis secretory cycle in cultured adrenal chromaffin cells. J. Cell. Biol.97, 1906–1917.
Quader, H., Glas, R., 1984: Geißelregeneration beiChlamydomonas reinhardtii. Biologie in unserer Zeit14, 125–127.
Robenek, H., Melkonian, M., 1979: Rhizoplast-membrane associations in the flagellateTetraselmis cordiformis Stein (Chlorophyceae) revealed by freeze-etching and thin sections. Arch. Protistenk.122, 340–351.
Robinson, D. G., 1981: Membrane flow in relation to secretion in higher plant cells: new results and concepts. In: Cell Walls 1981 (Robinson, D. G., Quader, H., eds.), pp. 43–52. Stuttgart: Wissenschaftliche Verlagsges.
—,Kristen, U., 1982: Membrane flow via the Golgi apparatus of higher plant cells. Int. Rev. Cytol.77, 89–127.
Rothman, J. E., 1981: The Golgi apparatus: two organelles in tandem. Science214, 1212–1219.
—,Lenard, J., 1984: Membrane traffic in animal cells. Trends Biochem. Sci.9, 176–178.
Salisbury, J. L., Baron, A., Surek, B., Melkonian, M., 1984: Striated flagellar roots: isolation and partial characterization of a calcium-modulated contractile organeile. J. Cell Biol.99, 962–970.
—,Swanson, J. A., Floyd, G. L., Hall, R., Maihle, N. J., 1981: Ultrastructure of the flagellar apparatus of the green algaTetraselmis subcordioformis with special considerations given to the function of the rhizoplasts and rhizancora. Protoplasma107, 1–12.
Tartakoff, A. M., 1982: Simplifying the complex Golgi. Trends Biochem. Sci.7, 174–176.
—, 1983: The confined function model of the Golgi complex: center for ordered processing of biosynthetic products of the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Int. Rev. Cytol.85, 221–252.
—,Vassali, P., 1983: Lectin-binding sites as markers of Golgi subcompartments: proximal-distal maturation of oligosaccharides. J. Cell. Biol.97, 1243–1248.
Whaley, W. G., 1975: The Golgi apparatus. Cell Biology Monographs2, 1–190.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McFadden, G.I., Melkonian, M. Golgi apparatus activity and membrane flow during scale biogenesis in the green flagellateScherffelia dubia (Prasinophyceae). I: Flagellar regeneration. Protoplasma 130, 186–198 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01276600
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01276600