Summary
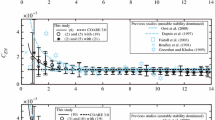
In a recent review on the drag coefficient, Garrat ([5], p. 915) pointed to the fact that “The effect (if any) of the fetch, wind duration and unsteadyness remains obscure in this experimental data scatter”. The present paper makes an attempt to analyse, in the light of a fetch dependency, data which have been accumulated on the Lake of Geneva. Postulated is a possible functional relationship between the local drag coefficient,C 10, and a fetch Reynolds number, (U 10 F)/ν, with a dimensionless roughness,F/y 0, as parameter. Subsequently, a possible relationship between the roughness parameter and the sea state (expressed presently with the significant wave) is discussed.
The present study should be considered as preliminary in as much as it served to establish another field programme on Lake Geneva.
Zusammenfassung
In einem Artikel von Garrat ([5], S. 915), der sich zusammenfassend und kritisch mit der jüngsten Forschung über die aerodynamische Reibung über einer Wasseroberfläche auseinandersetzt, heißt es: “Die Auswirkungen des Fetches, der Dauer und der Unstetigkeit eines Windes sind unbekannt und verstecken sich wohl hinter der Streuung der experimentellen Resultate”. In unserem Artikel ist ein Versuch unternommen worden, vorhandene Resultate von Experimenten am Genfersee auf eine Fetchabhängigkeit zu untersuchen. Dabei wird eine funktionelle Beziehung zwischen dem lokalen Reibungs- oder Widerstandskoeffizienten,C 10, und einer Fetch-Reynoldszahl, (U 10 F)/ν, mit einer dimensionslosen Rauhigkeit,F/y 0, als Parameter vorgeschlagen. Weiter wird gezeigt, daß eine Beziehung zwischen dem Rauhigkeitsparameter und dem Seegang (ausgedrückt als signifikante Welle,H 1/3) möglich ist.
Diese Studie sollte als Vorstudie angesehen werden; sie diente unter anderem als Grundlage für ein größeres aerodynamisches Projekt am Genfersee.
Résumé
Dans un article récent sur le coefficient de frottement, Garrat ([5], p. 915) laisse supposer que «les effets du fetch, de la durée et de la variabilité du vent s'ils existent, demeurent obscurs dans la dispersion des données expérimentales». Dans cet article, on essayera d'analyser l'éventuelle dépendance du fetch sur les données obtenues au cours des campagnes de mesures sur le Léman. On admettra qu'une relation entre le coefficient de frottement local,C 10, et le nombre de Reynolds de fetch,(U 10 F)/ν, existe, avec la rugosité adimensionelle,F/y 0, comme paramètre. Puis on discutera de l'éventuelle relation entre le paramètre de rugosité et l'état de surface du lac (exprimé ici en fonction de la vague significative).
Cette étude est à considérer plutôt comme un travail préliminaire à l'établissement d'un nouveau programme expérimental projeté sur le Léman.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boullery, B.: Etude expérimentale du coefficient de frottement pour un fetch court et en régime de vent faible. Bull. Dir. Etudes et Rech. Electricité de France, No. 1, Série A, 1977.
Davidson, K. L.: Observational Results on the Influence of Stability and Wind-Wave Coupling on Momentum Transfer and Turbulent Fluctuations Over Ocean Waves. Bound. Layer Met.6, 305–331 (1974).
Donelan, M. A., Birch, K. N., Beesley, D. C.: Generalized Profiles of Wind Speed, Temperature and Humidity. Proc. 17th Conf. Great Lakes Res., 1974.
Dunckel, M., Hasse, L., Krügermeyer, L., Schriever, D., Wucknitz, J.: Turbulent Fluxes of Momentum, Heat and Water Vapor in the Atmospheric Surface Layer at Sea During ATEX. Bound. Layer Met.6, 81–106 (1974).
Garratt, J. R.: Review of Drag Coefficient Over Oceans and Continents. Mon. Weath. Rev.105, 915–929 (1977).
Graf, W. H., Perrinjaquet, C., Bauer, S. W., Prost, J.-P., Girod, H.: Measuring on Lake Geneva. In: Hydrodynamics of Lakes (Graf, W. H., Mortimer, C. H., eds.). Amsterdam: Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company 1979.
Hsu, S. A.: A Dynamic Roughness Equation and Its Application to Wind Stress at the Air-Sea Interface. J. Phys. Oceanogr.4, 116–120 (1974).
Kitaigorodskii, S. A.: The Physics of Air-Sea Interaction, Vol. 15. Israel Prog. Scient. Translations, Jerusalem, 1973.
Kondo, J., Fujinawa, Y., Natto, G.: High Frequency Components of Ocean Waves and Their Relation to the Aerodynamic Roughness. J. Phys. Oceanogr.3, 197–202 (1973).
Kondo, J.: Air-Sea Bulk Transfer Coefficients in Diabatic Conditions. Bound. Layer Met.9, 91–112 (1975).
Kraus, E. B.: What Do We Know About the Sea-Surface Wind Stress? Bull. Amer. Met. Soc.49, 247–253 (1968).
Krügermeyer, L., Grünewald, M., Dunckel, M.: The Influence of Sea Waves on the Wind Profile. Bound. Layer Met.14, 403–414 (1978).
Plate, E. J., Wengefeld, P.: Exchange Processes at the Water Surface. In Hydrodynamics of Lakes (Graf, W. H., Mortimer, C. H., eds.). Amsterdam: Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company 1979.
Schlichting, H.: Boundary Layer Theory. New York: McGraw Hill 1968.
Stewart, R. W.: The Air-Sea Momentum Exchange. Bound. Layer Met.6, 151–167 (1974).
Taylor, P. A., Gent, P. R.: A Numerical Investigation of Variations in the Drag Coefficient for Flow Above Water Waves. Quart. J. R. Met. Soc.104, 979–988 (1978).
U. S. Army Coastal Engineering Research Center: Shore Protection Manual, Vol. 1. Dept. of the Army Corps of Engineers, 1975.
Wiegel, R. L.: Oceanographical Engineering. Englewood Cliffs, N. J.: Prentice Hall, Inc. 1964.
Wu, J.: Wind Stress and Surface Roughness at Air-Sea Interface. J. Geophys. Res.74, 444–455 (1969).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
With 11 Figures
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Graf, W.H., Prost, J.P. Aerodynamic drag and its relation to the sea state: With data from Lake Geneva. Arch. Met. Geoph. Biokl. A. 29, 67–87 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02247734
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02247734