Abstract.
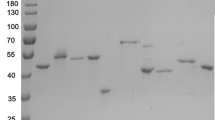
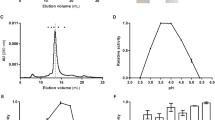
Acetobacter diazotrophicus SRT4 secretes a constitutive levansucrase (LsdA) (EC 2.4.1.10) that is responsible for sucrose utilization. Immunogold electron microscopical studies revealed that LsdA accumulates in the periplasm before secretion. The periplasmic and extracellular forms of the enzyme were purified to homogeneity. Both proteins exhibited similar physical and biochemical characteristics indicating that LsdA adopts its final conformation in the periplasm. The N-terminal sequence of mature LsdA was pGlu-Gly-Asn-Phe-Ser-Arg as determined by PSD-MALDI-TOFMS (post-source decay—matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization—time-of-flight mass spectrometry). Comparison of this sequence with the predicted precursor protein revealed the cleavage of a 30-residue typical signal peptide followed by the formation of the pyroglutamic acid (pGlu) residue. Thus, in contrast with other Gram-negative bacteria, A. diazotrophicus secretes levansucrase by a signal-peptide-dependent mechanism.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 24 March 1999 / Accepted: 30 April 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hernández, L., Arrieta, J., Betancourt, L. et al. Levansucrase from Acetobacter diazotrophicus SRT4 Is Secreted via Periplasm by a Signal-Peptide-Dependent Pathway. Curr Microbiol 39, 146–152 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002849900436
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002849900436