Abstract
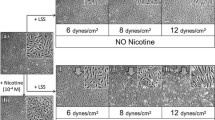
This study evaluates the toxicity of lead in the presence or absence of cadmium on the maintenance of a monolayer of cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells. It was histologically shown that lead at 50 μM or less induced a slight formation of de-endothelialized areas on the monolayer after a 24-h incubation. Although lead accumulated in endothelial cells in a dose-dependent manner, the cytotoxicity (evaluated by the [3H]adenine release assay) was not detected. However, cadmium (1.0 or 2.0 μM)-induced de-endothelialized areas on the monolayer was considerably larger in the presence of lead at 10 μM; the cytotoxicity of cadmium was significantly enhanced by lead. It was concluded that vascular endothelial cell monolayer is severely destroyed by a greater cytotoxicity of combination of cadmium with lead.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blazka ME, Shaikh ZA (1991) Differences in cadmium and mercury uptakes by hepatocytes: role of calcium channels. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 110:355–363
Jewell SA, Bellomo G, Thor H, Orrenius S, Smith MT (1982) Bleb formation in hepatocytes during drug metabolism is caused by disturbances in thiol and calcium ion homeostasis. Science 217:1257–1259
Kaji T, Yamamoto C, Sakamoto M (1991) Effect of lead on the glycosaminoglycans metabolism of bovine aortic endothelial cells in culture. Toxicology 68:249–257
Kaji T, Mishima A, Yamamoto C, Sakamoto M, Koizumu F (1992a) Effect of cadmium on the monolayer maintenance of vascular endothelial cells in culture. Toxicology 71:267–276
Kaji T, Fujiwara Y, Koyanagi E, Yamamoto C, Mishima A, Sakamoto M, Kozuka H (1992b) Protective effect of copper against cadmium cytotoxicity on cultured vascular endothelial cells. Toxicol Lett 63:13–20
Kaji T, Yamamoto C, Sakamoto M, Kozuka H (1992c) Inhibitory effect of lead on the release of tissue plasminogen activator from human vascular endothelial cells in culture. Toxicology 73:219–227
Kaji T, Mishima A, Yamamoto C, Sakamoto M, Kozuka H (1993) Zinc protection against cadmium-induced destruction of the monolayer of cultured vascular endothelial cells. Toxicol Lett 66:247–255
Kissane JM, Robins E (1958) The fluorometric measurement of deoxyribonucleic acid in animal tissue with special reference to the central nervous system. J Biol Chem 233:184–188
Lutton JD, Ibraham NG, Friedland M, Levere RD (1984) The toxic effects of heavy metals on rats bone marrow in vitro erythropoiesis: Protective role of hemin and zinc. Environ Res 35:97–103
Mahaffey KR, Capar SG, Gladen BC, Fowler BA (1981) Concurrent exposure to lead, cadmium, and arsenic. J Lab Clin Med 98:463–481
Nakashima Y, Sueishi K, Tanaka K (1988) Thrombin enhances production and release of tissue plasminogen activator from bovine venous endothelial cells. Fibrinolysis 2:227–234
Onosaka S, Tanaka K, Doi M, Okahara K (1978) A simplified procedure for determination of metallothionein in animal tissue. Eisei Kagaku 24:128–131
Revis NW, Zinsmeister AR, Bull R (1981) Atherosclerosis and hypertension induction by lead and cadmium ions: An effect prevented by calcium ion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:6494–6498
Ross R, Glomset JA (1976) The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: II. N Engl J Med 295:420–425
Suzuki KT (1981) Heavy metals and metallothionein. J Syn Org Chem Japan 39:1073–1082
Yamamoto C, Kaji T, Sakamoto M, Kozuka H (1993) Cadmium stimulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 release from human vascular endothelial cells in culture. Toxicology 83:215–223
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaji, T., Suzuki, M., Yamamoto, C. et al. Severe damage of cultured vascular endothelial cell monolayer after simultaneous exposure to cadmium and lead. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 28, 168–172 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00217612
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00217612