Abstract
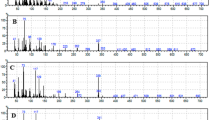
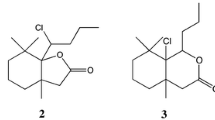
When carbon-14-labeled HEOD (dieldrin) is injected into the American cockroach, German cockroach, and house fly, metabolism takes place forming radioactive metabolites which have been isolated and identified by thin-layer chromatographic methods. The major metabolite of dieldrin in the American cockroach iscis-aldrindiol. This is the first report ofcis-aldrindiol being formed as a dieldrin metabolite and possible mechanisms for its formation are given. Other dieldrin metabolites identified or characterized indicate that both hydrolytic and oxidative systems are important in the metabolism of dieldrin by the three insect species studied. Thein vitro metabolism of HEOD-14C by the fat body from the American cockroach also supports the above conclusion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bieniek, D., and F. Korte: Beiträge zur okologischen chemie XXIII (1) Synthese eines dieldrin metaboliten durch photo-isomerisierung. Tetrahedron Letters46, 4059 (1969).
Brooks, G. T., and A. Harrison: Hydration of HEOD (dieldrin) and heptachlor epoxides by microsomes from the livers of pigs and rabbits. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxical.4, 352 (1969).
—— Relation between structure, metabolism and toxicity of the cyclodiene insecticides. Nature198, 1169 (1963).
Chau, A. S. Y., and W. P. Cochrane:Cis-opening of dieldrin oxirane ring. Chem. Ind. (London)20, 1568 (1970).
Cohen, A. J., and J. N. Smith: Fate of aldrin and dieldrin in locusts. Nature189, 600 (1961).
Damico, J. N., Jo-Yun T. Chen, C. E. Costello, and E. O. Haenni: Structure of Klein's metabolites of aldrin and of dieldrin. J. Ass. Offic. Anal. Chem.51, 48 (1968).
Feil, V. J., R. D. Hedde, R. G. Zaylskie, and C. H. Zacharison: Dieldrin-14C metabolism in sheep. Identification oftrans — 6,7-dihydroxydihydroaldrin and 9-(syn-epoxy) hydroxy-1,2,3,4,10,10-hexachloro-6,7-epoxy-1,4,4a,5,6,7,8,8a-octahydro-1,4-endo-5, 8-exo-dimenthano naphthalene. J. Agr. Food Chem.18, 120 (1970).
Gerolt, P.H.: The fate of dieldrin in insects. J. Econ. Entomol.58, 849 (1965).
Khan, M. A. Q., J. D. Rosen, and D. J. Sutherland: Insect metabolism of photoaldrin and photodieldrin. Science164, 318 (1969).
Klein, A. K., J. D. Link, and N. F. Ives: Isolation and purification of metabolites found in the urine of male rats fed aldrin and dieldrin. J. Ass. Offic. Anal. Chem.51, 895 (1968).
Korte, F., and H. Arent: Metabolism of insecticides. IX (1) Isolation and identification of dieldrin metabolites from urine after oral administration of dieldrin-14C. Life Sci.4, 135 (1965).
——, G. Ludwig, and J. Vogel: Umwandlung von aldrin (14C) und dieldrin (14C) durch mikroorganismen, leberhomogenate, und moskito-larven. Ann. der Chem.656, 135 (1962).
Lichtenberg, J. J., J. W. Eichelberger, R. C. Dressman, and J. E. Longbottom: Pesticides in surface waters of the United States: A 5-year summary 1964–68. Pesticide Monit. J.4, 71 (1970).
Matsumura, F., J. M. Telford, and M. Hayashi: Effect of sesamex upon dieldrin resistence in the German cockroach. J. Econ. Entomol.60, 942 (1967).
——, and M. Hayashi: Dieldrin resistence: Biochemical mechanisms in the German cockroach. J. Agr. Food Chem.17, 231 (1969).
——, G. M. Boush, and Akira Tai: Breakdown of dieldrin in the soil by a micro-organism. Nature219, 965 (1968).
——, K. C. Patil, and G. M. Boush: Formation of “photodieldrin” by micro-organisms. Science170, 1206 (1970).
Matthews, H. B. (PhD thesis): Dieldrin metabolism in mammals. University of Wisconsin (1968).
——, and F. Matsumura: Metabolic fate of dieldrin in the rat. J. Agr. Food Chem.17, 845 (1969).
Nakatsugawa, T., and P. A. Dahm: Activation of Guthion by tissue preparations from the American cockroach. J. Econ. Entomol.55, 594 (1962).
Oonnithan, E. S., and R. Miskus: Metabolism of C14-dieldrin by dieldrin-resistantCulex pipens quinquefasciatas mosquitoes. J. Econ. Entomol.57, 425 (1964).
Plapp, F. W., Jr., and R. F. Hoyer: Insecticide resistence in the housefly: resistence spectra and preliminary genetics of resistence in eight strains. J. Econ. Entomol.60, 768 (1967).
Richardson, A., M. Baldwin, and J. Robinson: Metabolites of dieldrin (HEOD) in the urine and feces of rats. Chem Ind. (London)18, 588 (1968).
Sellers, L. G., and F. E. Guthrie: Distribution and metabolism of14C-dieldrin in the resistant and susceptible housefly. J. Econ. Entomol.65, 378 (1972).
Schonbrod, R. D., M. A. Q. Khan, L. C. Terriere, and F. W. Plapp, Jr.: Microsomal oxidases in the housefly: a survey of fourteen strains. Life Sci.7, 681 (1968).
Tomlin, A. D.:Trans-aldrin glycol as a metabolite of dieldrin in larvae of the southern house mosquito. J. Econ. Entomol.61, 855 (1968).
Tsukamoto, M., and J. E. Casida: Albumin enhancement of oxidative metabolism of methylcarbamate insecticide chemicals by the house fly microsome-NADPH2 system. J. Econ. Entomol.60, 617 (1967).
Wedemeyer, G.: Partial hydrolysis of dieldrin byAerobacter aerogenes. Appl. Microbiol.16, 661 (1968).
Winteringham, F. P. W., and A. Harrison: Mechanisms of resistence of adult houseflies to the insecticide dieldrin. Nature184, 608 (1959).
Yamasaki, T., and T. Narahashi: The effects of potassium and sodium ions on the resting and action potentials of the cockroach giant axon. J. Insect Physiol.3, 146 (1959).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nelson, J.O., Matsumura, F. Dieldrin (HEOD) metabolism in cockroaches and house flies. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1, 224–244 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01985746
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01985746