Abstract
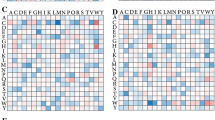
Two types of distributions for the frequencies of occurrence of amino acids in each position of hypervariable regions CDR-1 and CDR-2 were obtained for 2,000 immunoglobulins. The results show that some positions fit an inverse power-law distribution, while others fit an exponential-type distribution. As a result of comparison with structural data in the literature it is proposed that sites in which the frequency distribution fits the inverse power law are critical to maintaining canonical shapes of the recognition regions or are involved in modulating these canonical conformations, while those sites where the distribution fits the exponential law are those which should be exclusively involved in the recognition mechanism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alt FW, Blackwell TK, Yancopoulos GD (1987) Development of the primary antibody repertoire. Science 238:1079–1087
Bolger, MB, Sherman MA (1991) Computer modeling of combining site structure of anti-hapten monoclonal antibodies. Methods Enzymol 203:21–45
Chothia C, Lesk AM (1987) Canonical structures for the hypervariable regions of immunoglobulins. J Mol Biol 186:651–663
Chothia C, Lesk AM, Gherardi E, Tomlinson IM, Walter G, Marks JD, Llewelyn MB, Winter G (1992) Structural repertoire of the human VH segments. J Mol Biol 227:799–817
Gilman JJ (1991) Research management today. Phys Today March: 42–49
Gutsche CD (1992) Supramolecular chemistry. In: Parker SP (eds) Encyclopedia of chemistry, 2nd ed. McGraw Hill, Inc., NY
Grantham R (1974) Amino acid difference formula to help explain protein evolution. Science 185:862–864
Kabat EA (1978) The structural basis of antibody complementarity. Adv Protein Chem 32:1–75
Kabat EA, Wu TT (1971) Attempts to locate complementarity determining residues in the variable portions of light and heavy chains. Ann NY Acad Sci 190:382–393
Kabat EA, Wu TT, Bilofsky H (1977) Unusual distributions of amino acids in complementarity-determining (hypervariable) segments of heavy and light chains of immunoglobulins and their possible roles in specificity of antibody-combining sites. J Biol Chem 252:6609–6616
Kabat EA, Wu T, Perry HM, Gottesman KS, Foeller C (1991) In: Sequences of proteins of immunological interest, 5th ed. National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD
Lara-Ochoa F, Vargas E, Jimenez-Montano MA, Almagro JC (1994) Patterns in the complementarity determining regions of immunoglobulins (CDRs). Biosystems 32:1–9
Lehn JM (1990) Perspectives in supramolecular chemistry, from molecular recognition towards molecular information processing and self-organization. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 29:1304–1319
Lewis AR (1991) Clefts and binding sites in protein receptors. Methods Enzymol 202:126–156
Lim WA, Sauer RT (1989) Alternative packing arrangement in the hydrophobic core of proteins. Nature 339:31–36
Mandelbrot BB (1977) Fractals: form, chance, and dimension. Freeman, San Francisco
Meijer PHE, Mountain RD, Souler Jr RJ, eds (1981) Sixth International Conference on Noise in Physical Systems. National Bureau Standards, Washington, DC, Special Publication No. 614
Mian IS, Bradwell AR, Olson AJ (1991) Structure, function and properties of antibody binding sites. J Mol Biol 217:133–151
Miyata T, Miyasawa S, Yasunaga T (1979) Two types of amino acid substitution in protein evolution. J Mol Evol 12:219–223
Montroll E, Badger WW (1974) Introduction to quantitative aspects of social phenomena. Gordon and Breach Science Pub
Montroll EW, Schlesinger MF (1982) On 1/f noise and other distributions with long tails. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:3380–3383
Montroll E, Shlesinger MF (1983) Maximum entropy formalism, fractals, scaling phenomena, and 1/f noise: a tale of tails. J Statist Phys 32:209–230
Nicolis JS (1986) Chaotic dynamics as applied to information processing. Rep Prog Phys 49:1109–1187
Nicolis JS (1987) Chaotic dynamics of logical paradoxes. In: Bothe, Ebeling, Kurzhanski, Peschel, (eds) Dynamical systems and environmental models. Academic-Verlag, pp 105–113
Ohno S, Mori N, Matsunaga T (1985) Antigen-binding specificities of antibodies are primarily determined by seven residues of Vh. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:2945–2949
Padlan EA (1994) Anatomy of the antibody molecule. Mol Immunol (in press)
Schroeder M (1991) Fractals, chaos, power laws. WH Freeman and Company, New York, p 35
Sneath PHA (1966) Relation between chemical structure and biological activity in peptides. J Theor Biol 12:157–195
Tonegawa S (1983) Somatic generation of antibody diversity. Nature 302:575–581
Vargas-Madrazo E, Lara-Ochoa F, Jimenez-Montano M (1994) A skewed distribution of amino acids at recognition sites of the hypervariable region of immunoglobulins. J Mol Evol 38:100–104
West BM (1985) An essay on the importance of being non-linear. Lectures notes in biomathematics, 62, Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Wu TT, Kabat EA (1970) An analysis of the sequences of the variable regions of Bence Jones proteins and myeloma light chains and their implications for antibody complementarity. J Exp Med 132:211–250
Zipf GK (1949) Human behavior and the principle of least effort. Addison-Wesley, Cambridge
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to: F. Lara-Ochoa
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lara-Ochoa, F., Vargas-Madrazo, E. & Almagro, J.C. Distributions of the use frequencies of amino acids in the hypervariable regions of immunoglobulins. J Mol Evol 41, 98–103 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00174045
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00174045