Abstract.
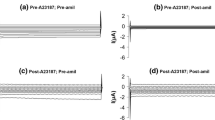
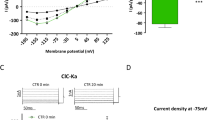
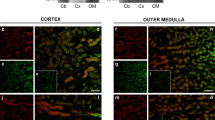
It has previously been shown that osmotic cell shrinkage activates a nonselective cation (NSC) channel in M-1 mouse cortical collecting duct cells [54] and in a variety of other cell types [20]. In the present study we further characterized the shrinkage-activated NSC channel in M-1 cells and its mechanism of activation using whole-cell current recordings. Osmotic cell shrinkage induced by addition of 100 mm sucrose to the bath solution caused a 20-fold increase in whole-cell inward currents from −10.8 ± 1.5 pA to −211 ± 10.2 pA (n= 103). A similar response was observed when cell shrinkage was elicited using a hypo-osmotic pipette solution. This indicates that cell shrinkage and not extracellular osmolarity per se is the signal for current activation. Cation substitution experiments revealed that the activated channels discriminate poorly between monovalent cations with a selectivity sequence NH4 (1.2) ≥ Na+ (1) ≈ K+ (0.9) ≈ Li+ (0.9). In contrast there was no measurable permeability for Ca2+ or Ba2+ and the cation-to-anion permeability ratio was about 14. The DPC-derivatives flufenamic acid, 4-methyl-DPC and DCDPC were the most effective blockers followed by LOE 908, while amiloride and bumetanide were ineffective. The putative channel activator maitotoxin had no effect. Current activation was dependent upon the presence of intracellular ATP and Mg2+ and was inhibited by staurosporine (1 μm) and calphostin C (1 μm). Moreover, cytochalasin D (10 μm) and taxol (2 μm) reduced the current response to cell shrinkage. These findings suggest that the activation mechanism of the shrinkage-activated NSC channel involves protein kinase mediated phosphorylation steps and cytoskeletal elements.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 3 May 2000/Revised: 6 July 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koch, JP., Korbmacher, C. Mechanism of Shrinkage Activation of Nonselective Cation Channels in M-1 Mouse Cortical Collecting Duct Cells. J. Membrane Biol. 177, 231–242 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002320010006
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002320010006