Summary
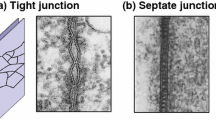
In previous works it was demonstrated that the monolayer of MDCK cells behaves as a leaky epithelium where the electrical resistance across reflects the sealing capacity of the occluding junction. In the present work we study whether this sealing capacity can be modified by temperature and whether this is accompanied by changes in the structure of the occluding junction. Monolayers were prepared on disks of nylon cloth coated with collagen and mounted as a flat sheet between two Lucite chambers. The changes in resistance elicited by temperature were large (306% between 3 and 37°C), fast (less than 2 sec), and reversible. An Arrhenius plot of conductance versus the inverse of temperature shows a broken curve (between 22 and 31°C), and the activation energies calculated (3.2 and 4.0 kcal·mol−1) fall within the expected values for processes of simple diffusion. The morphology of the occuluding the number of evaluated in freeze-fracture replicas by counting the number of strands and the width of the band occupied by the junction every 133 nm. In spite of the change by 306% of the electrical resistance and the phase transition, we were unable to detect any appreciable modification of the morphology of the occluding junction. Since the freeze-fracture replicas also show a density of intramembrane particles (IMP) different in the apical from that in the basolateral regions of the plasma membrane, as well as differences between faceE and faceP, we also investigated whether this is modified by temperature. Cold increases the population of IMP, but does not affect their polarization with the incubation time it takes to elicit changes in electrical resistance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, C.R., Cull-Candy, S.G., Miledi, R. 1977. Potential dependent transition temperature of the ionic channels induced by glutamate in locust muscle.Nature (London) 268:663–665
Barry, P.H., Diamond, J.M. 1971. A theory of ion permeation through membranes with fixed neutral sides.J. Membrane Biol. 4:295–330
Barry, P.H., Diamond, J.M., Wright, E.M. 1971. The mechanism of cation permeation in rabbit gallbladder: Dilution potentials and biionic potentials.J. Membrane Biol. 4:358–394
Bentzel, C.J., Hainau, B., Ho, S., Hui, S.W., Edelman, A. Anagnostopoulos, T., Benedetti, E.L. 1980. Cytoplasmic regulation of tight junctions permeability: Effect of plant cytokinins.Am. J. Physiol. 239:C75-C89
Borovjagin, V., Vergara, J., McIntosh, T. 1982. Morphology of the intermediate structures in membrane fusion process and bilayer to hexagonal HII transitions.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 645:262–269
Bullivant, S. 1982. Tight junction structure and development.In: The Paracellular Pathway. S.E. Bradley and E.F. Purcell, editors. pp. 13–35. Josiah Macy, Jr., Foundation, New York
Cereijido, M., Stefani, E., Chávez de Ramírez, B. 1982. Occluding junctions of theNecturus gallbladder.J. Membrane Biol. 70:15–25
Cereijido, M., Meza, I., Martínez-Palomo, A. 1981. Occluding junctions in cultured epithelial monolayers.Am. J. Physiol. 240:C96-C102
Cereijido, M. Robbins, E.S., Dolan, W.J., Rotunno, C.A., Sabatini, D.D. 1978a. Polarized monolayers formed by epithelial cells on a permeable and translucent support.J. Cell Biol. 77:853–880
Cereijido, M., Rotunno, C.A., Robbins, E.S., Sabatini, D.D. 1978b. Polarized epithelial membrane producedin vitro. Membrane transport processes, Vol. 1. pp. 433–461. J.F. Hoffman, editor. Raven, New York
Cereijido, M., Stefani, E., Martínez-Palomo, A. 1980. Occluding junctions in a cultured transporting epithelium: Structural and functional heterogeneity.J. Membrane Biol. 53:19–32
Claude, P. 1978. Morphological factors influencing, transepithelial permeability: A model for the resistance of the Zonula Occludens.J. Membrane Biol. 39:219–232
De Camilli, P., Peluchetti, D., Meldolesi, J. 1974. Structural difference between luminal and lateral plasmalemma in pancreatic acinar cells.Nature (London) 248:245–246
Dreyer, F., Müller, K.D., Peper, K., Sterz, R. 1976. Temperature dependence of ionic channel properties of ACH-receptors at frog and mouse neuromuscular junctions.Pfluegers Arch. 365:R36
Duffey, M., Hainau, B., Ho, S., Bentzel, C. 1981. Regulation of epithelial tight junction permeability by cyclic AMP.Nature (London) 294:451–453
Fischbach, G.D., Lass, Y. 1978. A transition temperature for acetylcholine channel conductance in chick myoballs.J. Physiol. (London) 280:527–536
Fischer, A., Stoeckenius, W. 1977. Freeze-fractured purple membrane particles: Protein content.Science 197:72–74
Griepp, E.B., Dolan, W.J., Robbins, E.S., Sabatini, D.D. 1983. Participation of plasma membrane proteins in the formation of tight junctions by cultured epithelial Cells.J. Cell Biol. 96(3):693–702
Hoi Sang, U., Saier, M.H., Jr., Ellisman, M.H. 1979. Tight junction formation is closely linked to the polar redistribution of intramembraneous particles in aggregating MDCK epithelia.Exp. Cell Res. 122:384–392
Hoi Sang, U., Saier, M. H., Ellisman, M. H. 1980. Tight junction formation in the establishment of intramembranous particle polarity in aggregating MDCK cells.Exp. Cell Res. 128:223–235
Hong, K., Hubbell, W.L., 1972. Preparation and properties of phospholipid bilayers containing rhodopsin.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 69:2617–2621
Hope, M.J., Walker, D.C., Cullis, P.R. 1983. Ca2+ and pH induced fusion of small unilamillar vesicles consisting of phophatidylethanolamine and negatively charged phospholipids: A freeze-fracture study.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 110(1):15–22
Hudspeth, A.J. 1975. Establishment of tight junctions between epithelial cells.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 72(7):2711–2713
Humbert, F., Montesano, R., Perrelet, A., Orci, L. 1976. Junctions in developing human and rat kidney: A freeze-fracture study.J. Ultrastruct. Res. 56:202–214
Jähnig, F., Bramhall, J. 1982. The origin of a break in Arrhenius plots of membrane processes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 690:310–313
Kachar, B., Pinto da Silva, P. 1981. Rapid massive assembly of tight junction strands.Science 213:541–544
Kachar, B., Reese, T. 1982. Evidence for the lipidic nature of tight junction strands.Nature (London) 296:64–66
Kniffki, R.O., Siemen, D., Vogel, W. 1981. Development of sodium permeability inactivation in nodal membranes.J. Physiol. (London) 313:37–48
Lagarde, S., Elias, E., Wade, J., Boyer, L. 1981. Structural heterogeneity of hepatocyte “tight” junctions: A quantitative analysis.Hepatology,1:193–203
Leech, C.A., Stanfield, P.K. 1981. Inward rectification in frog skeletal muscle fibers and its dependence on membrane potential and external potassium.J. Physiol. (London) 319:295–309
Luzzati, V., Husson, F. 1962. The structure of the liquid crystalline phases of lipid water systems.J. Cell Biol. 12:207–219
Madin, S.H., Darby, N.B. 1958.As catalogued in: American Type Culture Collection Catalogue of Strains. Vol. 2, pp 574–576. R. Hay et al., editors. Rockville, Maryland
Margolios, L., Neyfakh, A., Bergelson, L., Vasiliev, J. 1982. Interaction of solid liposomes with epithelial cells.Cell Biol. Int. Rep. 6(2):131–136
Martínez-Palomo, A., Erlij, D. 1975. Structure of tight junctions in epithelia with different permeability.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 72:4487–4491
Martínez-Palomo, A., Meza, I., Beaty, G., Cereijido, M. 1980. Experimental modulation of occluding junctions in a cultured transporting epithelium.J. Cell Biol. 87:736–745
Meldolesi, J., Castiglioni, G., Parma, R., Nassivera, N., De Camilli, P. 1978. Ca++-dependent disassembly and reassemby of occluding junctions in guinea pig pancreatic acinar cells: Effect of drugs.J. Cell Biol. 79:156–172
Misfeldt, D.S., Hamamoto, S.T., Pitelka D.K. 1976. Transepithelial transport in cell culture.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 73:1212–1216
Møllgård, K., Malinowska, D.H., Saunders, N.R. 1976. Lack of correlation between tight junction morphology and permeability properties in developing choroid plexus.Nature (London) 264:293–294
Montesano, R., Friend, D.S., Perrelet, A., Orci, L. 1975.In vivo assembly of tight junctions in fetal rat liver.J. Cell Biol. 67:310–319
Moreno, J.H., Diamond, J.M. 1975. Nitrogenous cations as probes of permeation channels.J. Membrane Biol.,21:197–259
Morgan, G., Wooding, F.B. 1982. A freeze-fracture study of tight junction structure in sheep mammary gland epithelium during pregnancy and lactation.J. Dairy Res. 49:1–11
Murphy, C., Swift, J., Mukherjee, T., Rogers, A. 1982a. The structure of tight junctions between uterine luminal epithelial cells at different stages of pregnancy in the rat.Cell Tissue Res. 223:281–286
Murphy, C., Swift, J., Need, J., Mukherjee, T., Roger, A. 1982b. A freeze-fracture electron microscopic study of tight junction of epithelial cells in the human uterus.Anat. Embryol. 163:367–370
Mutoh, H. 1981. Freeze replica observation of the junction structures in the guinea-pig liver after bile duct ligation and recanalization.Arch. Histol. Jpn. 44(4):345–367
Ojakian, G.K. 1981. Tumor promoter-induced changes in the permeability of epithelial cell tight junction.Cell 23:95–103
Pinto da Silva, P., Kachar, B. 1982. On tight junction structure.Cell 28:441–450
Pitelka, D.R., Hamamoto, S.T., Duafala, J.G., Nemanic, M.K. 1973. Cell contacts in the mouse mammary gland: I. Normal gland in postnatal development and the secretory cycle.J. Cell Biol. 56:797–818
Pitelka, D.R., Taggart, B.N. 1983. Mechanical tension induces lateral movement of intramembrane components of the tight junction: Studies on mouse mammary cells in culture.J. Cell Biol. 96:606–612
Pitelka, D.R., Taggart, B.N., Hamamoto, S.T. 1983. Effects of extracellular calcium depletion on membrane topography and occluding junctions of mammary epithelial cells in cultureJ. Cell Biol. 96(3):613–624
Polak-Charcon, S., Shoham, J., Ben-Shaul, Y. 1978. Junction formation in trypsinized cells of human adenocarcinoma cell line.Exp. Cell. Res. 116:1–13
Rabito, C.A., Tchao, R., Valentich, J., Leighton, J. 1978. Distribution and characteristics of the occluding junctions in a monolayer of a cell line (MDCK) derived from canine kidney.J. Membrane Biol. 43:351–365
Schiller, A., Taugner, R. 1982. Heterogeneity of tight junctions along the collecting duct in the renal medulla: A freeze-fracture study in rat and rabbit.Cell Tissue Res. 223:603–614
Schwarz, W. 1979. Temperature experiments on nerve and muscle membranes of frogs: Indications for a phase transition.Fluegers Arch. 382:27–34
Stefani, E., Cereijido, M. 1983. Electrical properties of cultured epithelioid cells (MDCK).J. Membrane Biol. 73:177–184
Suzuki, F., Nagano, T. 1979. Morphogenesis of tight junctions in the peritoneal mesothelium of the mouse embryo.Cell Tissue Res. 198:247–260
Tadvalkar, G., Pinto da Silva, P., 1983.In vitro rapid assembly of gap junctions is induced by cytoskeleton disruptors.J. Cell Biol. 96:1279–1287
Tice, L.W., Carter, R.L., Cahill, M.C. 1977. Tracer and freeze-fracture observations on developing tight junctions in fetal rat thyroid.Tissue Cell. 9(3):395–417
Van Deurs, B., Luft, J.H. 1979. Effects of glutaraldehyde fixation on the structure of tight junctions: A quantitative freeze-fracture analysis.J. Ultrastruc. Res. 68:160–172
Van Venetie, R., Verkleij, A.J. 1981. Analysis of the Hexagonal II phase and its relations to lipidic particles and the lamellar phase: A freeze-fracture study.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 645:262–269
Verkleij, A., Van Echteld, C., Gerristen, W., Cullis, P., De Kriuff, B. 1980. The lipidic particle as an intermediate structure in membrane fusion processes and bilayer to hexagonalH II transitions.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 645:262–269
Wade, J.B., Karnovsky, M.J. 1974. Fracture faces of osmotically disrupted zonulae occludentes.J. Cell Biol. 62:344–350
Wright, E.M., Barry, P.H., Diamond, J.M. 1971. The mechanism of cation permeation in rabbit gallbladder.J. Membrane Biol. 4:331–357
Yancey, S.B., Caster, D., Revel, J. 1979. Cytological changes in gap junctions during liver regeneration.J. Ultrastruct. Res. 67:229–242
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
González-Mariscal, L., Chávez de Ramírez, B. & Cereijido, M. Effect of temperature on the occluding junctions of monolayers of epithelioid cells (MDCK). J. Membrain Biol. 79, 175–184 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01872121
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01872121