Abstract
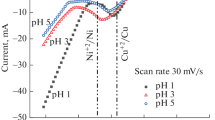
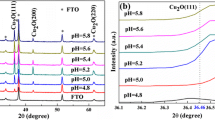
The surface area (nanoscale roughness) of copper coatings deposited from electroless plating solutions containing Quadrol, L(+)- and DL(∓)-tartrate as Cu(II) ion ligands was measured using underpotential deposition thallium monolayer formation. Surface roughness of Cu coatings depends on the plating solution pH and the Cu(II) ligand, and varies over a wide range. In L(+)-tartrate and Quadrol solutions (pH 12.5–13.3) the roughness factor R f is low and is equal to 2–3 and 4–6, respectively (substrate: electrodeposited Cu; R f=2.2). Cu coatings of higher surface area are obtained in DL(∓)-tartrate (pH 12.3–12.7) and Quadrol (pH 12.0) solutions: R f reaches 20–30. The correlation between R f and Cu deposition rate was found in L(+)-tartrate solution. The Cu surface area changes are discussed in terms of partial electrochemical reactions of the autocatalytic Cu deposition process, and the decisive role of cathodic Cu(II) reduction from adsorbed Cu(II) complex species.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 2 November 1999 / Accepted: 22 February 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Norkus, E., Vaškelis, A. & Stalnioniene, I. Changes of the Cu electrode real surface area during the process of electroless copper plating. J Solid State Electrochem 4, 337–341 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s100080000129
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s100080000129