Abstract
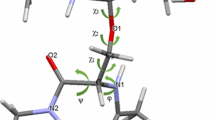
The attachment of a virus to the host cell surface is influenced by enthalpic and entropic factors. A detailed evaluation of all possible energetic interactions including the effects of solvent molecules seems to be a promising way to gain deeper insights in the overall process of binding. Here we performed intensive molecular dynamics studies to compare the conformational space available for the unbound sialyllactose in aqueous solution and when complexed with influenza A hemagglutinin and the murine polyoma virus. In general the conformational freedom of sialyllactose is considerably reduced compared to the free state. Remarkably, two different conformations of the Siaα(2-3)Galβ glycosidic linkages are preferred (which are both populated in the free state) when complexed with either protein.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 3 July 1997 / Accepted: 30 July 1997 / Published: 2 October 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frank, M., von der Lieth, CW. Comparison of the Conformational Behavior of Sialyllactose Complexed with the two Viral Attachment Proteins Influenza A Hemagglutinin and the Murine Polyomavirus. J Mol Med 3, 408–414 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s008940050058
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s008940050058