Abstract
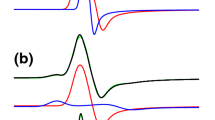
Vibrational assignments for the Fe-OH unit of ferric alkaline forms of two deletion derivatives of Rhizobium meliloti FixL, FixL*, a functional O2-sensing heme kinase, and FixLN, which contains only the heme domain, are made. Appearance of 2H- and 18O-sensitive Raman bands indicates that the heme group of FixL binds hydroxide as a distal ligand to form a six-coordinate complex. The alkaline FixLs are distributed between high- and low-spin states. The high- and low-spin bands corresponding to the ν (Fe-OH) modes occur at 479 and 539 cm–1, respectively. Low temperature favors formation of the low-spin complex, indicative of a thermal spin-state equilibrium. The ν (Fe-OH) frequencies of FixLN and FixL* are 11 to 18 cm–1 lower than those observed for the respective vibrations in alkaline myoglobin and hemoglobin. The weaker Fe-OH bond in the FixLs is attributed to a lack of hydrogen bonding on the distal side of the heme pocket.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 20 November 1997 / Accepted: 2 March 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lukat-Rodgers, G., Rodgers, K. Spin-state equilibria and axial ligand bonding in FixL hydroxide: a resonance raman study. JBIC 3, 274–281 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007750050232
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007750050232