Abstract
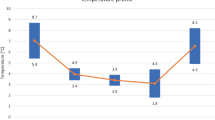
Activities of erythrocyte aldose reductase were compared in 34 normal subjects, 45 diabetic patients, and nine young men following immersion in water at 25, 39, and 42° C. Mean basal enzyme activity was 1.11 (SEM 0.12) U/g Hb and 2.07 (SEM 0.14) U/g Hb in normal controls and diabetic patients, respectively (P<0.0001). Activities of the enzyme showed a good correlation with hemaglobin A1 (HbA1) concentrations (P<0.01) but not with fasting plasma glucose concentrations. After immersion at 42° C for 10 min, enzyme activity was increased by 37.6% (P<0.01); however, the activity decreased by 52.2% (P<0.005) after immersion for 10 min at 39° C and by 47.0% (P<0.05) at 25° C. These changes suggest that heat stress might aggravate diabetic complications, and body exposure to hot environmental conditions is not recommended for diabetic patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agishi Y (1985) Endocrine and metabolic aspects of balneotherapy. Biometeorology 10 (Suppl to 29):89–103
Bagnasco SM, Uchida S, Balaban RS, Kador PF (1987) Induction of aldose reductase and sorbitol in renal inner medullary cells by elevated extracellular NaCl. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:1718–1720
Beutler E, West C, Blume RV (1976) The removal of leukocytes and platelets from whole blood. J Lab Clin Med 88:328–333
Cheng HM, Gonzalez RG (1986) The effect of high glucose and oxidative stress on lens metabolism, aldose reductase, and senile cataractogenesis. Metabolism 35 (Suppl 1):10–14
Crabbe MJ, Peckar CO, Halder AB, Cheng H (1980) Erythrocyte glyceraldehyde reductase levels in diabetics with retinopathy and cataract. Lancet 1:1268–1270
Das B, Srivastava SK (1985) Activation of aldose reductase from human tissues. Diabetes 34:1145–1151
Finegold D, Lattimer SA, Nolle S, Bernstein M, Greene DA (1983) Polyol pathway activity and myo-inositol metabolism. Diabetes 32:988–992
Hamada Y, Kitoh R, Raskin P (1991) Crucial role of aldose reductase and plasma glucose level in sorbitol accumulation in erythrocytes from diabetic patients. Diabetes 40:1233–1240
Hotta N, Kakuta H, Fukasawa H, Kimura M, Koh N, Ida M, Terashima H, Morimura T, Sakamoto N (1985) Effects of a fructose-rich diet and the aldose reductase inhibitor, ONO-2235, on the development of diabetic neuropathy in streptozotocin-treated rats. Diabetologia 28:176–180
Hotta N, Kakuta H, Koh N, Fukasawa H, Yasuma T, Awaya S, Sakamoto N (1991) In vitro retinal and erythrocyte polyol pathway regulation by hormones and an aldose reductase inhibitor. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 14:29–36
Kador P, Kinoshita JH (1985) Role of aldose reductase in the development of diabetes-associated complications. Am J Med (Suppl. 5A) 79:8–12
Lyons PA, Gould S, Wise PH, Palmer TN (1991) Activation of erythrocyte aldose reductase in man in response to glycemic challenge. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 14:9–14
Malone JI, Knox G, Benford S, Tedesco TA (1980) Red cell sorbitol. An indicator of diabetic control. Diabetes 29:861–864
Malone JI, Leavengood H, Peterson MJ, O'brien MM, Page MG, Aldinger CE (1984) Red blood cell sorbitol as an indicator of polyol pathyway activity. Inhibition by sorbinil in insulin-dependent diabetic subjects. Diabetes 33:45–49
Ohtsuka Y, Yabunaka N, Fujisawa H, Watanabe I, Agishi Y (1994) Effect of thermal stress on glutathione metabolism in human erythrocytes. Eur J Appl Physiol 68:87–91
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohtsuka, Y., Yabunaka, N., Watanabe, I. et al. Thermal stress and diabetic complications. Int J Biometeorol 38, 57–59 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01270659
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01270659