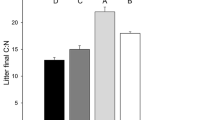
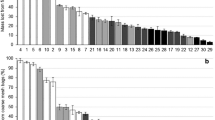
Abstract
The strength and generality of the relationship between decomposition rates and detritus carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus concentrations was assessed by comparing published reports of decomposition rates of detritus of photosynthetic organisms, from unicellular algae to trees. The results obtained demonstrated the existence of a general positive, linear relationship between plant decomposition rates and nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations. Differences in the carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus concentrations of plant detritus accounted for 89% of the variance in plant decomposition rates of detritus orginating from photosynthetic organisms ranging from unicellular microalgae to trees. The results also demonstrate that moist plant material decomposes substantially faster than dry material with similar nutrient concentrations. Consideration of lignin, instead of carbon, concentrations did not improve the relationships obtained. These results reflect the coupling of phosphorus and nitrogen in the basic biochemical processes of both plants and their microbial decomposers, and stress the importance of this coupling for carbon and nutrient flow in ecosystems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aber JD, Melillo JM, McClaugherty CA (1990) Predicting longterm patterns of mass loss, nitrogen dynamics, and soil organic matter formation from initial fine litter chemistry in temperate forest ecosystems. Can J Bot 68:2201–2208
Aerts R (1989) Aboveground biomass and nutrient dynamics ofCalluna vulgaris andMolinia caerulea in a dry heathland. Oikos 56:31–38
Aizaki M, Takamura N (1991) Regeneration of nutrient and detritus formation from aerobic decomposition of natural Phytoplankton. Jpn J Limnol 52:83–94
Albright LJ, Chocair J, Masuda K, Valdés M (1980) In situ degradation of the kelpsMacrocystis integrifolia andNereocystis luetkeana in British Columbia coastal waters. Nat Can 107:3–10
Andersen FØ (1978) Effects of nutrient level on the decomposition ofPhragmites communis. Trin Arch Hydrobiol 84:42–54
Atchley WR, Anderson D (1978) Ratios and the analysis of biological data. Syst Zool 27:71–78
Azam F, Fenchel T, Field JG, Meyer-Reil LA, Thingstad F (1983) The ecological role of water-column microbes in the sea. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 10:257–263
Bastardo H (1979) Laboratory studies on decomposition of littoral plants. Polskie. Arch Hydrobiol 26:267–299
Bayley SE, Zoltek J Jr, Hermann AJ, Dolan TJ, Tortora L (1985) Experimental manipulation of nutrients and water in a freshwater marsh: Effects on biomass decomposition, and nutrient accumulation. Limnol Oceanogr 30:500–512
Benner R, Fogel ML, Sprague EK (1991) Diagenesis of belowground biomass ofSpartina alterniflora in salt-marsh sediments. Limnol Oceanogr 36:1358–1374
Berg B, Ekbohm G (1991) Litter mass-loss rates and decomposition patterns in some needle and leaf litter types. Long-term decomposition in a Scots pine forest VII. Can J Bot 69:1449–1456
Berg B, Tamm CO (1991) Decomposition and nutrient dynamics of litter in long-term optimum nutrition experiments. Scand J For Res 6:305–321
Berg B, Wessen B, Ekbohm G (1982) Nitrogen level and decomposition in Scots pine needle litter. Oikos 38:291–296
Best EPH, Dassen JHA, Boon JJ, Wiegers G (1990) Studies on decomposition ofCeratophyllum demersum litter under laboratory and field conditions: losses of dry mass and nutrients, qualitative changes in organic compounds and consequences for ambient water and sediments. Hydrobiologia 194:91–114
Biddanda BA (1988) Microbial aggregation and degradation of phytoplankton-derived detritus in seawater. II. Microbial metabolism. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 42:89–95
Birch PB, Gabrielson JO, Hamel KS (1983) Decomposition of Cladophora. I. Field studies in the Peel-Harvey estuarine system, Western Australia. Bot Mar 26:165–171
Bockheim JG, Jepsen EA, Heisey DM (1991) Nutrient dynamics in decomposing leaf of four tree species on a sandy soil in northwestern Wisconsin. Can J For 21:803–812
Breteler RJ, Teal JM (1981) Trace element enrichments in decomposing litter ofSpartina alterniflora. Aquat Bot 11:111–120
Briggs SV, Maher MT, Tongway DJ (1985) Dry matter and nutrient loss from decomposingVallisneria spiralis L. Aquat Bot 22:387–392
Brock TCM (1984) Aspects of the decomposition ofNymphoides peltata (Gmel.) O. Kuntze (Menyantheceae). Aquat Bot 19:131–156
Brock TCM, De Lyon MJH, Van Laar EMJM, Van Loon EMM (1985) Field studies on the breakdown ofNuphar lutea (L.) SM. (Nymphaeaceae), and a comparison of three mathematical models for organic weight loss. Aquat Bot 21:1–22
Chapin FS III (1980) The mineral nutrition of wild plants. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 11:233–260
Chapin FS III, Bloom AJ, Field CB, Waring RH (1987) Plant responses to multiple environmental factors. BioScience 37:49–57
Chayes F (1971) Ratio correlations. University of Chicago Press, Chicago
Coley PD, Bryant JP, Chapin FS III (1985) Resource availability and plant antiherbivore defense. Science 230:895–899
Davis SM (1991) Growth, decomposition, and nutrient retention ofCladium jamaicense Crantz andTypha dominguensis Pers. in the Florida Everglades. Aquat Bot 40:203–224
De Busk TA, Dierberg FE (1984) The effect of nitrogen and fiber content on the decomposition of the water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) Solms.). Hydrobiologia 118:199–204
Draper NR, Smith H (1966) Applied regression analysis. Wiley
Duarte CM (1990) Seagrass nutrient concentration. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 67:201–207
Duarte CM (1992) Nutrient concentration of aquatic plants: Patterns across species. Limnol Oceanogr 37: 882–889
Escudero A, Sanz SE, Del Arco JM, Garrido MV (1991) Leaf litter decomposition in a mountain stream. Verh Int Ver Limnol 24: 1987–1993
Fahey TJ, Stevens PA, Hornung M, Rowland P (1991) Decomposition and nutrient release from logging residue following conventional harvest of Sitka spruce in North Wales. Forestry 64: 289–301
Findlay WPK (1934) Studies in the physiology of wood-decay fungi. I. The effect of nitrogen content upon the rate of decay. Ann Bot 46: 109–117
Findlay S, Howe K, Austin HK (1990) Comparison of detritus dynamics in two tidal freshwater wetlands. Ecology 71: 288–295
Gabrielson JO, Birch PB, Hamel KS (1983) Decomposition of Cladophora. II. In vitro studies of nitrogen and phosphorus regeneration. Bot Mar 26: 173–179
Garber JH (1984) Laboratory study of nitrogen and phosphorus remineralization during the decomposition of coastal plankton and seston. Estuarine Coastal Shelf Sci 18: 685–702
Garten CT Jr (1976) Correlation between concentrations of elements in plants. Nature 261: 686–688
Gessner MO, Meyer E, Schwoerbel J (1991) Rapid processing of fresh leaf litter in an upland stream. Verh Int Verein Limnol 24: 1846–1850
Godshalk GL, Wetzel RG (1978a) Decomposition of aquatic angiosperms. II. Particulate components. Aquat Bot 5: 301–327
Godshalk GL, Wetzel RG (1978b) Decomposition of aquatic angiosperms. III.Zostera marina L. and a conceptual model of decomposition. Aquat Bot 5: 329–354
Goldman JC, Caron DA, Dennett MR (1987) Regulation of gross growth efficiency and ammonium regeneration in bacteria by substrate C:N ratio. Limnol Oceanogr 32: 1239–1252
Golterman HL (1972) The role of phytoplankton in detritus formation. Mem Ist Ital Idrobiol 29: 89–103
Gosz JR, Likens GE, Bormann FH (1973) Nutrient release from decomposing leaf and branch litter in the Hubbard Brook Forest, New Hampshire. Ecol Monogr 43: 173–191
Haines EB, Hanson RB (1979) Experimental degradation of detritus made from the salt marsh plantsSpartina alterniflora Loisel,Salicornia virginica L., andJuncus roemerianus Scheele. 1979. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 40: 27–40
Harrison PG (1982) Control of microbial growth and of amphipod grazing by water soluble compounds from leaves ofZostera marina. Mar Biol 67: 225–230
Harrison PG (1989) Detrital processing in seagrass systems: a review of factors affecting decay rates, remineralization and detritivory. Aquat Bot 23: 263–288
Hemminga MA, Buth GJC (1991) Decomposition in salt marsh ecosystems of the S.W. Netherlands: the effects of biotic and abiotic factors. Vegetatio 92: 73–83
Hemminga MA, Nieuwenhuize J (1991) Transport, deposition and “in situ” decay of seagrasses in a tropical mudflat area (Banc D'Arguin, Mauritania). Neth J Sea Res 27: 183–190
Hill BH (1979) Uptake and release of nutrients by aquatic macrophytes. Aquat Bot 7: 87–93
Iversen TM (1973) Decomposition of autumn-shed beech leaves in a springbrook and its significance for the fauna. Arch Hydrobiol 72: 305–312
Joergensen RG (1991) Organic matter and nutrient dynamics of the litter layer on a forest rendzina under beech. Biol Fertil Soils 11: 163–169
Joergensen RG, Meyer B (1990) Nutrient changes in decomposing beech leaf litter assessed using a solution flux approach. J Soil Sci 41: 279–293
Kenworthy WJ, Thayer GW (1984) Production and decomposition of the roots and rhizomes of seagrasses,Zostera marina andThalassia testudinum, in temperate and subtropical marine ecosystems. Bull Mar Sci 35: 364–379
Lee SY (1989) The importance of sesarminae crabsChiromanthes spp. and inundation frecuency on mangrove (Kandelia candel (L.) Druce) leaf litter turnover in a Hong Kong tidal shrimp pond. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 131: 23–43
Mattson WJ Jr (1980) Herbivory in relation to plant nitrogen content. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 11: 119–161
McClaugherty CA, Pastor J, Aber JD (1985) Forest litter decomposition in relation to soil nitrogen dynamics and litter quality. Ecology 66: 266–275
Melillo JM, Aber JD, Muratore JM (1982) Nitrogen and lignin control of hardwood leaf litter decomposition dynamics. Ecology 63: 621–626
Mitchell DT, Coley PGF, Webb S, Allsopp N (1986) Litterfall and decomposition processes in the coastal fynbos vegetation, South-Western Cape, South Africa. J Ecol 74: 977–993
Neely RK, Davis CB (1985) Nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization ofSparganium eurycarpum Engelm. andTypha glauca Godr. Stands. II. Emergent plant decomposition. Aquat Bot 22: 363–375
Nelson WJ, Kadlec JA, Murkin HR (1990) Seasonal comparison of weight for two types ofTypha glauca Godr. leaf litter. Aquat Bot 37: 299–314
Newell RC, Lucas MI, Linley EAS (1981) Rate of degradation and efficiency of conversion of phytoplankton debris by marine micro-organisms. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 6: 123–136
Newell SY, Fell JW, Statzell-Tallman A, Miller C, Cefalu R (1984) Carbon and nitrogen dynamics in decomposing leaves of three coastal marine vascular plants of the subtropics. Aquat Bot 19: 183–192
Newell SY, Fell JW, Miller C (1986) Deposition and decomposition of Turtlegrass leaves. Int Rev Ges Hydrobiol 71: 363–369
O'Connell AM (1987) Litter dynamics in Karri (Eucalyptus diversicolor) forest of South-Western Australia. J Ecol 75: 781–796
O'Connell AM (1988) Nutrient dynamics in decomposing litter in karri (Eucalyptus diversicolor F. Muèll.) forests of South-Western Australia. Journal of Ecology 76: 1186–1203
Olson JS (1963) Energy storage and the balance of producers and decomposers in ecological systems. Ecology 44: 327–332
Otsuki A, Hanya T (1972) Production of dissolved organic matter from dead green algal cells. I. Aerobic microbial decomposition. Limnol Oceanogr 17: 248–257
Palm CA, Sanchez PA (1990) Decomposition and nutrient release patterns of the leaves of three tropical legumes. Biotropica 22: 330–338
Peduzzi P, Herndl GJ (1991) Decomposition and significance of seagrass leaf litter (Cymodocea nodosa) for the microbial food web in coastal waters (Gulf of Trieste, Northern Adriatic Sea). Mar Ecol Prog Ser 71: 163–174
Pellikaan GC (1982) Decomposition processes of eelgrass,Zostera marina L. Hydrobiol Bull 16: 83–92
Pellikaan GC (1984) Laboratory experiments on eelgrass (Zostera marina) decomposition. Neth J Sea Res 18: 360–383
Persson T, Bååth E, Clarholm M, Lundkvist H, Söderström B, Sohlenius B (1980) Trophic structure, biomass dynamics and carbon metabolism of soil organisms in a Scots pine forest. Ecol Bull 32: 419–462
Reddy KR, DeBusk WF (1991) Decomposition of water hyacinth detritus in eutrophic lake water. Hydrobiologia 211: 101–109
Robertson AI, Daniel PA (1989) Decomposition and the annual flux of detritus from fallen timber in tropical mangrove forest. Limnol Oceanogr 34: 640–646
Rogers KH, Breen CM (1982) Decomposition ofPotamogeton crispus L.: The effects of drying on the pattern of mass and nutrient loss. Aquat Bot 12: 1–12
Romero J, Pergent G, Pergent-Martini C, Mateo MA, Regnier C (1992) The detritic compartment in aPosidonia oceanica meadow: litter features, decomposition rates and mineral stocks. Mar Ecol PSZNI 13: 69–83
Rublee PA, Roman MR (1982) Decomposition of turtlegrass (Thalassia testudinum Koning) in flowing sea-water tanks and litterbags: compositional changes and comparisons with natural particulate matter. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 58: 47–58
Schlesinger WH (1985) Decomposition of chaparral shrub foliage. Ecology 66: 1353–1359
Seastedt TR (1988) Mass, nitrogen and phosphorus dynamics in foliage and root detritus of tallgrass prairie. Ecology 69: 59–65
Sharma E, Ambasht RS (1987) Litterfall, decomposition and nutrient release in an age sequence ofAlnus nepalensis plantation stands in the eastern Himalaya. J Ecol 75: 997–1010
Swift MJ, Heal OW, Anderson JM (1979) Decomposition in terrestrial ecosystems (Studies in Ecology Vol. 5) Blackwell, Oxford
Tanaka Y (1991) Microbial decomposition of reed (Phragmites communis) leaves in a saline lake. Hydrobiologia 220: 119–129
Taylor BR, Parkinson D, Parsons WFJ (1989) Nitrogen and lignin content as predictors of litter decay rates: a microcosm test. Ecology 70: 97–104
Tenny FG, Waksman SA (1929) Composition of natural organic materials and their decomposition in the soil. IV. The nature and rapidity of decomposition of the various organic complexes in the different plant materials, under aerobic conditions. Soil Sci 28: 55–84
Tezuka Y (1990) Bacterial regeneration of ammonium and phosphate as affected by the carbon: nitrogen: phosphorus ratio of organic substrates. Microb Ecol 19: 228–238
Thayer GW (1974) Identity and regulation of nutrients limiting phytoplankton production in the shallow estuaries near Beaufort, N. C. Oecologia 14: 75–92
Twilley RR, Blanton LR, Brinson MM, Davis GJ (1985) Biomass production and nutrient cycling in aquatic macrophyte communities of the Chowan River, North Carolina. Aquat Bot 22: 231–252
Twilley RR, Ejdung G, Romare P, Kemp M (1986) A comparative study of decomposition, oxygen consumption and nutrient release for selected aquatic plants occurring in an estuarine environment. Oikos 47: 190–198
Upadhyay VP, Singh JS, Meentemeyer V (1989) Dynamics and weight loss of leaf litter in Central Himalayan forests: abiotic versus litter quality influences. J Ecol 77: 147–161
Valiela I, Wilson J, Buchsbaum R, Rietsma C, Bryant D, Foreman K, Teal J (1984) Importance of chemical composition of salt marsh litter on decay rates and feeding by detritivores. Bull Mar Sci 35: 261–269
Vadstern O, Olsen Y (1989) Chemical composition and phosphate uptake kinetics of limnetic bacterial communities cultures in chemostats under phosphorus limitation. Limnol Oceanogr 34: 939–946
Van der Valk AG, Attiwill PM (1984) Decomposition of leaf and root litter ofAvicennia marina at Westernport bay, Victoria, Australia. Aquat Bot 18: 205–221
Van der Valk AG, Rhymer JM, Murkin HR (1991) Flooding and the decomposition of litter of four emergent plant species in a prairie wetland. Wetlands 11: 1–16
Wahbeh MI, Mahasneh AM (1985) Some aspects of decomposition of leaf litter of the seagrass Halophila stipulacea from the Gulf of Aqaba (Jordan). Aquat Bot 21: 237–244
Walsh I, Dymond J, Collier R (1988) Rates of recycling of biogenic components of settling particles in the ocean derived from sediment trap experiments. Deep-Sea Res 35: 43–58
Williams WA, Jones MB, Demment MW (1990) A concise table for path analysis statistics. Agron J 82: 1022–1024
Yavitt JB, Fahey TJ (1986) Litter decay and leaching from the forest floor inPinus contorta (Lodgepole pine) ecosystems. J Ecol 74: 525–545
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was funded through a grant of CICYT (MAR91-0503) to C.M.D.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Enríquez, S., Duarte, C.M. & Sand-Jensen, K. Patterns in decomposition rates among photosynthetic organisms: the importance of detritus C:N:P content. Oecologia 94, 457–471 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00566960
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00566960