Summary
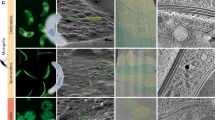
An electron microscope study of a variety of invertebrate and vertebrate cell types has supported the postulate that the microtubule is a universal cellular organelle. Microtubules of similar dimensions have been observed in the flagellum and beneath the plasma membrane of Trypanosoma lewisi, in the flagellum, manchette and mitotic spindle of the earthworm (Lumbricus terrestris) spermatid; and in fibroblasts, proximal convoluted and collecting tubule cells of the hypertrophying rat kidney. The specific occurrence and organization of the microtubules in cells undergoing morphological and developmental changes have suggested that these organelles are contractile and that they effectively contribute to the maintenance of cellular form. The possibility that microtubules may function as an intracellular transport system is also suggested.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, W. A.: Ultrastructure of the flagellum and pellicle of Trypanosoma lewisi. J. Cell Biol. 23, 5A (1965).
Auber, J.: Mode d'accroissement des fibrilles au cours de la nymphose de Calliphora erythrocephala. C. R. Acad. Sci. (Paris) 254, 4074–4075 (1962).
Behnke, O.: A preliminary report on “Microtubules” in differentiated and undifferentiated vertebrate cells. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 11, 139–146 (1964).
Bouck, G. B., and J. Cronshaw: The fine strucure of differentiating sieve tube elements. J. Cell Biol. 25, 79–96 (1965).
Burgos, M. H., and D. W. Fawcett: Studies on the fine structure of the mammalian testis. I. Differentiation of the spermatid in the cat, (Felis domestica). J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 1, 287–299 (1955).
Byers, B., and K. R. Porter: Oriented microtubules in elongating cells of the developing lens rudiment after induction. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 52, 1091–1099 (1964).
de-Thé, G.: Cytoplasmic microtubules in different animals cells. J. Cell Biol. 23, 265–275 (1964).
Fahrenbach, W. H.: The morphology of some simple photoreceptors. Z. Zellforsch. 66, 233–254 (1965).
Finley, H. E., C. A. Brown, and W. A. Daniel: Electron microscopy of the ectoplasm and infraciliature of Spirostomum ambiguum. J. Protozool. 11, 264–280 (1964).
Gatenby, J. B., and A. J. Dalton: Spermiogenesis in Lumbricus herculeus. An electron microscope study. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 6, 45–51 (1959).
Gibbons, I. R., and A. V. Grimstone: On flagellar structure in certain flagellates. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 7, 697–715 (1960).
Grimstone, A. V., and L. R. Cleveland: The fine structure and function of the contractile axostyles of certain flagellates. J. Cell Biol. 24, 387–400 (1965).
Kane, R. E.: The mitotic apparatus. Fine structure of the isolated unit. J. Cell Biol. 15, 279–287 (1962).
Ledbetter, M. C., and K. R. Porter: A microtubule in plant cell fine structure. J. Cell Biol. 19, 239–250 (1963).
Palay, S.: Synapses in the central nervous system. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol., Suppl. 2, 193–201 (1956).
Philpott, C. W.: The comparative morphology of the chloride secreting cells of three species of Fundulus as revealed by the electron microscope. Anat. Rec. 142, 267–268 (1962).
Porter, K. R., M. C. Ledbetter, and S. Badenhauser: The microtubule in cell fine structure as a constant accompanyment of cytoplasmic movements. Proc. 3rd Eur. Reg. Conf. on Electron Microscopy, Prague 1964, p. 119.
Reynolds, E. S.: The use of lead citrate as an electron dense stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 17, 208–212 (1963).
Rhodin, J. A. G.: Structure of the kidney. In: Diseases of the kidney (M. B. Strauss and L. G. Welt, eds.), p. 22. Boston (Mass.): Little Brown & Co. 1963.
Rudzinska, M.: The fine structure and function of the tentacle in Tokophrya infusionum. J. Cell Biol. 25, 459–477 (1965).
Sandborn, E., P. F. Koen, J. D. [scMcNabb, and G. Moore: Cytoplasmic microtubules in mammalian cells. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 11, 123–138 (1964).
Silviera, M., and K. R. Porter: The spermatozoids flatworms and their microtubular systems Protoplasma (Wien) 59, 240–265 (1964).
Slautterback, D. B.: Cytoplasmic microtubules. 1. Hydra. J. Cell Biol. 18, 367–388 (1963).
Steinert, M., and A. B. Novikoff: The existence of a cytostome and the occurrence of pinocytosis in the trypanosome Trypanosoma mega. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 8, 563–569 (1960).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by grants CA-04046, GM-08380, and K 3-AM-4932 from the U. S. Public Health Service.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anderson, W.A., Weissman, A. & Ellis, R.A. A comparative study of microtubules in some vertebrate and invertebrate cells. Zeitschrift für Zellforschung 71, 1–13 (1966). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00339826
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00339826