Abstract
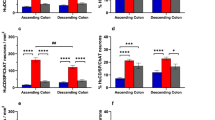
Enkephalin (ENK) immunoreactivity was localised in different neuronal subpopulations of the myenteric plexus in the guinea-pig gastric fundus using immunohistochemistry for neurone-specific enolase (NSE), ENK, choline acetyltransferase (ChAT), substance P (SP), neuropeptide Y (NPY), calretinin (CALRET), and somatostatin (SOM). NADPH-diaphorase staining was used to label nitric oxide synthase (NOS)-containing neurones. ENK was observed in 44% of the myenteric neurones. The major ENK-positive subpopulations were ChAT/ENK (35% of ENK-positive neurones), ChAT/SP/ENK (26%), NOS/NPY/ENK (22%) and ChAT/SP/ENK/CALRET (9%). The projection pathways of these ENK-positive subpopulations to the circular muscle and the mucosa were determined using retrograde labelling with DiI in organ culture followed by immunohistochemistry. Of myenteric neurones retrogradely labelled from the mucosa and the circular muscle, 13% and 48% exhibited ENK immunoreactivity, respectively. Three major ENK-positive subpopulations innervating the mucosa or circular muscle were identified: ascending ChAT/SP/ENK (7% of all mucosa neurones; 24% of all circular muscle neurones), ascending ChAT/ENK (4%; 15%) and descending NOS/NPY/ENK (1%; 8%) neurones. Only very few CALRET- or SOM-positive neurones projected to the mucosa or circular muscle. ChAT/SP/ENK and ChAT/ENK neurones might function as ascending excitatory muscle motor neurones, whereas NOS/NPY/ENK neurones are most likely descending inhibitory muscle motor neurones. The relatively few ENK-positive mucosa neurones do not favour a major involvement of ENK-positive myenteric neurones in the control of gastric mucosa activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 25 February 1998 / Accepted: 2 June 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pfannkuche, H., Reiche, D., Firzlaff, U. et al. Enkephalin-immunoreactive subpopulations in the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig fundus project primarily to the muscle and not to the mucosa. Cell Tissue Res 294, 45–55 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004410051155
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004410051155