Summary
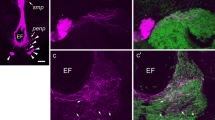
The histochemical fluorescence method of Falck and Hillarp was used to locate monoamine-containing neurones in the nervous system ofStrophocheilus, a Brazilian land snail. Green-fluorescing (catecholamines) cell bodies were found only in cerebral ganglia. Neuropiles of all ganglia contained many green-fluorescing fibers most of which appeared to enter from the periphery. Giant (up to 500 μ) non-fluorescing cells were seen in most ganglia of the suboesophageal mass. Green-fluorescing fibers surrounded, and apparently ended on, their axon hillocks and proximal segments of axons. Green-fluorescing sensory cells were seen in the eyeless tentacles. Cells fluorescing yellow (5-hydroxytryptamine) or yellow fading to green on exposure to ultraviolet light were found in cerebral, visceral and right palliai ganglia. Ligature of the cardiac nerve for 24 hrs resulted in an accumulation of yellow or “yellow green”-fluorescing masses in axons proximal to the constriction. The distribution of monoamine-containing neurones inStrophocheilus is rather similar to that found in other pulmonate molluscs such asHelix.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becquaert, J. C.: Monograph on the Strophocheilidae. A neotropical family of terrestrial mollusks. Bull. Mus. Comp. Zool. Harv.100, 210 pp. (1948).
Cardot, J.: Mise en évidence de monoamines dans les fibres nerveuses du coeur des MollusquesHelix pomatia Linné etArchachatina marginata Swainson par l'histochimie de fluorescence. C. R. Acad. Sci. (Paris)269, 345–347 (1969).
Corrodi, H., Jonsson, G.: The formaldehyde fluorescence method for the histochemical demonstration of biogenic monoamines. J. Histochem. Cytochem.15, 65–78 (1967).
Cottrell, G. A.: Direct postsynaptic responses to stimulation of serotonin-containing neurones. Nature (Lond.)225, 1060–1062 (1970).
- Osborne, N. N.: Localization and mode of action of cardioexcitatory agents in molluscan hearts. In: F. V. McCann (ed.), Comparative physiology of the heart: current trends. Experientia (Basel) Suppl.15 (1969).
— —: Subcellular localization of serotonin in an identified serotonin-containing neurone. Nature (Lond.)225, 470–472 (1970).
Dahl, E., Falck, B., Mecklenburg, C. von, Myhrberg, H.: Adrenergic sensory neurons in invertebrates. Gen. comp. Endocr.3, 693 (1963a).
— — — —: An adrenergic nervous system in sea anemones. Quart. J. micr. Sci.104, 531–534 (1963b).
— — — —, Rosengren, E.: Neuronal localization of dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine in some Mollusca. Z. Zellforsch.71, 489–498 (1966).
Dawson, A. B.: Evidence for the termination of neurosecretory fibers within the pars intermedia of the hypophysis of the frogRana pipiens. Anat. Rec.115, 63–69 (1953).
Falck, B.: Observations on the possibilities of the cellular localization of monoamines by a fluorescence method. Acta physiol. scand.56, Suppl. 197 (1962).
—, Hillarp, N. -A., Thieme, G., Torp, A.: Fluorescence of catecholamines and related compounds condensed with formaldehyde. J. Histochem. Cytochem.10, 348–354 (1962).
—, Owman, C.: A detailed methodological description of the fluorescence method for the cellular demonstration of biogenic monoamines. Acta Univ. Lund., Section II, N.7, 1–23 (1965).
Hamberger, B., Malmfors, T., Sachs, C.: Standardization of paraformaldehyde and of certain procedures for the histochemical demonstration of catecholamines. J. Histochem. Cytochem.13, 147 (1965).
Jaeger, C. P.: Physiology of Mollusca. II. Action of serotonin and other amines on the heart ofStrophocheilus oblongus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.6, 243–245 (1962).
—: Neuroendocrine regulation of cardiac activity in the snailStrophocheilus oblongus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.17, 409–415 (1966).
Kerkut, G. A., French, M. C., Walker, R. J.: The location of axonal pathways of identifiable neurones ofHelix aspersa using the dye Procion yellow M-4R. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.32, 681–690 (1970).
—, Sedden, C. B., Walker, R. J.: Uptake of DOPA and 5-hydroxytryptophan by monoamine-forming neurones in the brain ofHelix aspersa. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.23, 159–162 (1967).
Marsden, C., Kerkut, G. A.: The occurrence of monoamines inPlanorbis corneus: a fluorescence microscopic and microspectrometric study. Comp. Gen. Pharmacol.1, 101–116 (1970).
Myhrberg, H. E.: Monoaminergic mechanisms in the nervous system ofLumbricus terrestris (L.). Z. Zellforsch.81, 311–343 (1967).
Nisbet, R. H.: Some aspects of the structure and function of the nervous system ofArchachatina (Calachatina) marginata (Swainson). Proc. roy. Soc. B154, 267–287 (1961).
Rude, S.: Monoamine-containing neurons in the nerve cord and body wall ofLumbricus terrestris. J. comp. Neurol.128, 397–412 (1966).
Sakharov, D. A., Zs.-Nagy, I.: Localization of biogenic monoamines in cerebral ganglia ofLymnaea stagnalis L. Acta biol. Hung.19, 145–157 (1968).
Sedden, C. B., Walker, R. J., Kerkut, G. A.: The localization of dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine in neurones ofHelix aspersa. Symp. zool. Soc. Lond. No22, 19–32 (1968).
Sidman, R. L., Mottla, P. A., Feder, N.: Improved polyester wax embedding for histology. Stain Technol.36, 279–284 (1961).
Stretton, A. O. W., Kravitz, E. A.: Neuronal geometry: determination with a technique of intracellular dye injection. Science162, 132–134 (1968).
Sweeney, D. C.: The anatomical distribution of monoamines in a fresh-water bivalve mollusc,Sphaerium sulcatum (L.). Comp. Biochem. Physiol.25, 601–613 (1968).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The authors are eager to acknowledge the constant interest of Dr. Sonia Rude while the experiments were taking place. This work was jointly supported by OAS, Capes (Brazil), U. F. R. G. S. (Brazil), and Grant No. NB 00623 (USPHS).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jaeger, C.P., Jaeger, E.C. & Welsh, J.H. Localization of monoamine-containing neurones in the nervous system ofStrophocheilus oblongus (Gastropoda). Z.Zellforsch 112, 54–68 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00665621
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00665621