Summary
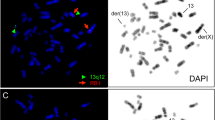
Retinoblastoma (Rb) occurs in hereditary, non-hereditary, and chromosomal deletion forms and the locus for the Rb gene (Rb-1) is closely linked to the locus for esterase D (ESD) assigned to the chromosome 13q14.11. We describe a patient who was predicted to have Rb from the genetic analysis of the chromosome and ESD phenotype. Furthermore, the gene for lymphocyte cytosol polypeptide with molecular weight of 64,000 (LCP1: McKusick catalogue No. 15343, 1983) was assigned to chromosome 13 by deletion mapping. A 3-month-old female had many characteristics of chromosome 13q-syndrome, including dolichocephaly, epicanthus, ptosis, depressed nasal bridge, micrognathia, short webbed neck, and short fifth fingers with clinodactyly and single crease. The karyotype of the patient was 46,XX,del(13) (q14.1–q32), though both the parents had normal karyotypes. As expected, the phenotype of ESD derived from one of the parents, the father in this case, was not detected in peripheral blood lymphocytes by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (two-DE), indicating that ESD from the father was deleted in the abnormal chromosome 13. The possibility of paternity was calculated to be 0.996 based on the data using 22 genetic markers. Bilateral retinoblastomas could be diagnosed by ophthalmologic examinations before the manifestation of any clinical signs of the tumor and immediately intensive care was taken. In addition, the phenotype of LCP1 derived from the father was not expressed in the lymphocyte proteins from the patient. These data indicate that the gene for LCP1 (LCP1) is located in the region q14.1–q32 of chromosome 13 and may be a useful genetic marker for preclinical diagnosis of Rb.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hamaguchi H, Yamada M, Noguchi A, Fujii K, Shibasaki M, Mukai R, Yabe T, Kondo I (1982) Genetic analysis of human lymphocyte proteins by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. II. Genetic polymorphism of lymphocyte cytosol 64k polypeptide. Hum Genet 60:176–180
Hopkinson DA, Mertine MA, Cortner J, Harris H (1973) Esterase D: a new human polymorphism. Ann Hum Genet 37:119–137
Ikeuchi T (1984) Inhibitory effect of ethidium bromide on mitotic chromosome concentration and its application to high-resolution chromosome banding. Cytogenet Cell Genet 38:56–61
Kondo I, Yamamoto T, Yamakawa K, Harada S, Oishi H, Nishigaki I, Hamaguchi H (1984a) Genetic analysis of human lymphocyte proteins by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. VI. Identification of esterase D in the two-dimensional gel electrophoresis pattern of cellular proteins. Hum Genet 66:248–251
Kondo I, Nishigaki I, Yamakawa K, Hamaguchi H (1984b) The esterase D polymorphism: analysis of esterase D 7 by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Jinrui Idengaku Zasshi 29:27–30
Kondo I, Hamaguchi H (1985) Evidence for the close linkage between lymphocyte cytosol polypeptide with molecular weight of 64,000 (LCP1) and esterase D. Am J Hum Genet (in press)
Lowry DH, Rosenbrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Maynard-Smith S, Penrose LS (1955) Monozygotic and dizygotic twin diagnosis. Ann Hum Genet 19:273–289
McKusick VA (1983) No. 15343 Lymphocyte cytosol polypeptide, molecular weight 64,000 (LCP1). In: Mendelian inheritance in man, 6th edn. The Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore London, p 338
Merril CR, Goldman D, Sedman SA, Ebert MH (1981) Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science 211:1437–1438
Niebuhr E (1977) Partial trisomies and deletions of chromosome 13. In: Yunis JJ (ed) New chromosomal syndromes. Academic Press, New York London, pp 273–299
O'Farrell PH (1975) High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem 250:4007–4021
Sparkes RS, Murphree AL, Lingue RW, Sparkes MC, Leight Field L, Funderburk SJ, Benedict W (1983) Gene for hereditary retinoblastoma assigned to human chromosome 13 by linkage to esterase D. Science 219:971–973
Vogel F (1979) Genetics of retinoblastoma. Hum Genet 53:1–54
Ward P, Packman S, Loughman W, Sparkes M, Sparkes R, McMahon A, Gregory T, Ablin A (1984) Location of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene(s) and the human esterase D locus. J Med Genet 21:92–95
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kondo, I., Shin, K., Honmura, S. et al. A case report of a patient with retinoblastoma and chromosome 13q deletion: assignment of a new gene (gene for LCP1) on human chromosome 13. Hum Genet 71, 263–266 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00284588
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00284588