Abstract.
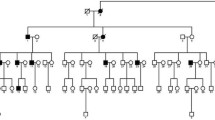
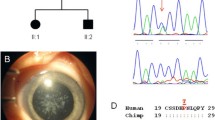
A seven-generation family with 30 members affected by highly variable autosomal dominant zonular pulverulent cataracts has been previously described. We have localized the cataracts to a 19-cM interval on chromosome 2q33-q35 including the γ-crystallin gene cluster. Maximum lod scores are 4.56 (θ=0.02) with D2S157, 3.66 (θ=0.12) with D2S72, and 3.57 (θ=0.052) with CRYG. Sequencing and allele-specific oligonucleotide analysis of the pseudo γE-crystallin promoter region from individuals in the pedigree suggest that activation of the γE-crystallin pseudo gene is unlikely to cause the cataracts in the family. In addition, base changes in the TATA box but not the Sp1-binding site have been found in unaffected controls and can be excluded as a sole cause of cataracts. In order to investigate the underlying genetic mechanism of cataracts in this family further, exons of the highly expressed γC- and γD-crystallin genes have been sequenced. The γD-crystallin gene shows no abnormalities, but a 5-bp duplication within exon 2 of the γC-crystallin gene has been found in one allele of each affected family member and is absent from both unaffected family members and unaffected controls. This mutation disrupts the reading frame of the γC-crystallin coding sequence and is predicted to result in the synthesis of an unstable γC-crystallin with 38 amino acids of the first "Greek key" motif followed by 52 random amino acids. This finding suggests that the appropriate association of mutant βγ-crystallins into oligomers is not necessary to cause cataracts and may give us new insights into the genetic mechanism of cataract formation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, Z., Li, A., Shastry, B. et al. A 5-base insertion in the γC-crystallin gene is associated with autosomal dominant variable zonular pulverulent cataract. Hum Genet 106, 531–537 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004390000289
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004390000289