Abstract
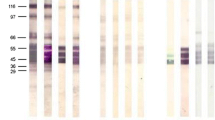
The isolation and purification of a neutral glycolipid fraction fromTaenia crassiceps metacestodes (KBS strain), harvested from both male and female NMRI mice at 70–80 days following intraperitoneal infection, revealed 24 thin-layer chromatography-designated glycolipid bands. The glycolipids were defined as ceramide mono-(n=3), di-(n=3), tri-(n=4), tetra-(n=5), and >tetrasaccharides (n=9) according to their running properties as defined by thin-layer chromatography against standards of known structure. The defined glycolipids were tested for immunoreactivity with sera from noninfected andT. crassiceps-infected NMRI mice (intraperitoneal injection or implantation of 15 larvae/animal) using the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) until day 33 p.i. (IgM and IgG reaction) and high-performance thin-layer chromatography (HPTLC) combined with immunostaining (IgG reaction) until day 7 p.i. ELISA-determined IgM and IgG titres were significantly elevated from day 5 p.i. Immunostaining revealed early reactivity for certain ceramide tetra- and >tetrasaccharides (n=6) on day 3 p.i. From day 5 p.i. onwards, nearly all glycolipids, including ceramide mono-and disaccharides, were recognized by the sera from metacestode-challenged mice. On day 7 p.i., a total of 22 bands were serologically active; of these, a considerable number (n=10) showed increased staining intensity. Remarkably, in many cases (10 of 20), 3 glycolipids (tetra-and >tetrasaccharides) were weakly recognized by mouse sera taken before infection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avila JS, Rojas M (1990) Elevated cerebroside antibody levels in human visceral and cutaneous leishmaniasis,Trypanosoma rangeli infection, and chronic Chagas' disease. Am J Trop Med Hyg 43:52–60
Avramas S, Dighiero G, Lymberi P, Guilbert P (1983) Studies on natural antibodies and autoantibodies. Ann Immunol (Paris) 135D:103–113
Baumeister S, Witteler H, Geyer E (1990) Chemical properties of in vitro released products ofTaenia crassiceps metacestodes strongly inhibiting in vitro mast cell degranulation. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg [A] 317:15
Dennis RD, Geyer R, Egge H, Menges H, Stirm S, Wiegandt H (1985) Glycosphingolipids in insects. Chemical structures of ceramide monosaccharide, disaccharide, and trisaccharide from pupae ofCalliphora vicina (Insecta: Diptera). Eur J Biochem 146:51–58
Feizi T (1985) Demonstration by monoclonal antibodies that carbohydrate structures of glycoproteins and glycolipids are oncodevelopmental antigens. Nature 314:53–57
Galili U (1988) The two antibody specificities within human antiblood group B antibodies. Transfusion Med Rev 2:112–121
Galili U, Buehler J, Shohet SB, Macher BA (1987) The human natural anti-Gal IgG: III. The subtlety of immune tolerance in man as demonstrated by cross-reactivity between natural anti-Gal and anti-B antibodies. J Exp Med 165:693–704
Guilbert B, Dighiero G, Avramas S (1982) Naturally occurring antibodies against nine common antigens in human sera: I. Detection, isolation and characterization. J Immunol 128:2779–2787
Kalinna B, Becker M, Geyer E (1989) Immunoelectrophoretic analysis of antigens shared by the vesicular fluid and cyst wall ofTaenia crassiceps andTaenia saginata metacestodes. Parasitol Res 75:568–574
Kunz J, Baumeister S, Geyer E (1990)Taenia crassiceps: glycolipid antigens of the metacestode cyst wall recognized by sera of patients with cerebralTaenia solium cysticercosis. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg [A] 317:22–23
Ledeen RW, Yu RK, Eng LF (1973) Gangliosides of human myelin: sialogalactosylceramide (G7) as a major component. J Neurochem 21:829–839
Magnani IL, Brockhaus M, Smith DF, Ginsburg V (1982) Detection of glycolipid ligands by direct binding of carbodydrate-binding proteins to thin-layer chromatograms. Methods Enzymol 83:235–240
Petry K, Eisen H (1989) Methods for the determination of glycolipids as parasite antigens. Parasitol Today 5:196–197
Quarles RH (1989) Human monoclonal antibodies associated with neuropathy. Methods Enzymol 179:291–299
Rosen G, Londner MV, Sevlever D, Greenblatt CL (1988)Leish mania major: glycolipid antigens recognized by immune human sera. Mol Biochem Parasitol 27:93–100
Saito T, Hakomori S (1971) Quantitative isolation of total glycosphingolipids from animal cells. J Lipid Res 12:257–259
Weiss JB, Magnani JL, Strand M (1986) Identification ofSchistosoma mansoni glycolipids that share immunogenic carbohydrate epitopes with glycoproteins J Immunol 136:4275–4282
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedicated to Prof. Dr. J. Eckert (Zürich) on the occasion of his 60th birthday
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kunz, J., Baumeister, S., Dennis, R.D. et al. Immunological recognition of larvalTaenia crassiceps glycolipids by sera from parasite-infected mice. Parasitol Res 77, 443–447 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00931642
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00931642