Abstract
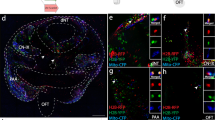
To analyse the proliferative abilities of cells within particular regions of the zebrafish neural plate, injections of fluorescein-dextran were made into single cells at either medial or intermediary positions in the neural plate region of two-somite stage embryos. The resulting cell clones were analysed in 3.5-day-old embryos. Clones with similar compositions were found among those derived from injections in both regions, and these were grouped into classes. 78 clones 29 obtained following injections in the medial region, and 22 of 59 cell clones derived from injections in the intermediary region, were classifiable into 9 and 10 different classes, respectively, each comprising a variable number of clones. Several identified cell types, as well as each of the clone classes themselves, were specific for the regions of the neural plate from which they derived, i.e. they were not represented among the clones derived from the other region. These results suggest that the composition of the lineages derived from particular cells is constant in different animals.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 13 July 1998 / Accepted: 20 October 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Papan, C., Campos-Ortega, J. Region-specific cell clones in the developing spinal cord of the zebrafish. Dev Gene Evol 209, 135–144 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004270050237
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004270050237