Summary
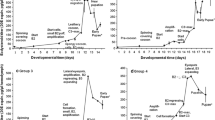
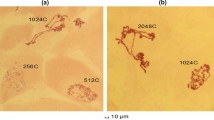
Changes in polytene chromosome 3 L puffing patterns in the fat body ofDrosophila melanogaster larvae and prepupae are compared to those in the salivary gland. While some general features are common to the two tissues, there are differences which reflect their different developmental roles. In vitro experiments with fat body chromosomes show that they have a distinct response to ecdysteroids which is different from that of salivary gland chromosomes, and which does not,in this culture system, reproduce the changes observed in normal development. In short term culture experiments, the fat body chromosomes appear more sensitive to ecdysteroids than the salivary gland chromosomes and, although 20-OH ecdysone is more active than ecdysone in these assays, the possibility is not excluded that ecdysone has a role in normal development as it appears to alter gene activity at physiological levels in these cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashburner M (1972a) Patterns of puffing activity in the salivary gland chromosomes ofDrosophila. VI. Induction by ecdysone in salivary glands ofD. melanogaster cultured in vitro. Chromosoma (Berl) 38:255–281
Ashburner M (1972b) Puffing patterns inDrosophila melanogaster and related species. In: Beermann W (ed) Results and problems in cell differentiation, vol 4. Developmental studies with giant chromosomes. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 101–151
Ashburner M (1973) Sequential gene activation by ecdysone in polytene chromosomes ofDrosophila melanogaster. I. Dependence upon ecdysone concentration. Dev Biol35:47–61
Ashburner M (1977) Happy Birthday — Puffs. In: De la Chapelle A, Sorsa M (eds). Chromosomes Today vol 6. Elsevier/North Holland, Amsterdam, pp 213–222
Ashburner M, Garcia-Bellido A (1973) Ecdysone induction of puffing activity in salivary glands ofDrosophila melanogaster grown in adult abdomens. Wilhelm Roux's Arch172:166–170
Ashburner M, Richards G (1976) Sequential gene activation by ecdysone in polytene chromosomes ofDrosophila melanogaster. III. Consequences of ecdysone withdrawal. Dev Biol54: 241–255
Bainbridge SP, Bownes M (1981) Staging the metamorphosis ofDrosophila melanogaster. J Embryol Exp Morphol (in press)
Becker HJ (1962) Die Puffs der Speicheldrüsenchromosomen vonDrosophila melanogaster. II. Die Auslösung der Puffbildung, ihre Spezifität und ihre Beziehung zur Funktion der Ringdrüse. Chromosoma (Berl)13:341–384
Belyaeva ES, Vlassova IE, Biyasheva ZM, Kakpakov VT, Richards G, Zhimulev IF (1981) Cytogenetic analysis of the 2B3.4-2B11 region of the X chromosome ofDrosophila melanogaster. II. Changes in 20-OH ecdysone puffing caused by genetic defects of puff 2B5. Chromosoma (Berl)84: 207–219
Berendes HD (1967) The hormone ecdysone as effector of specific changes in the pattern of gene activities ofDrosophila hydei. Chromosoma (Berl)22:274–293
Bodenstein D (1950) The postembryonic development ofDrosophila. In: Demerec M (ed) The biology ofDrosophila. J Wiley, New York, pp 275–367
Bonner JJ, Pardue ML (1976) Ecdysone-stimulated RNA synthesis in imaginal discs ofDrosophila melanogaster. Assay byin situ hibridisation. Chromosoma (Berl)58:87–99
Bonner JJ, Pardue ML (1977) Ecdysone-stimulated RNA synthesis in salivary glands ofDrosophila melanogaster. Assay by in situ hybridisation. Cell12:219–225
Bridges PN (1941) A revised map of the left limb of the third chromosome ofDrosophila melanogaster. J Hered32:64–65
Hodgetts RB, Sage B, O'Connor JD (1977) Ecdysone titres during post-embryonic development ofDrosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol60:310–317
Holden JJ, Ashburner M (1978) Patterns of puffing activity in the salivary gland chromosomes ofDrosophila. IX. The salivary and prothoracic gland chromosomes of a dominant temperature sensitive lethal ofD. melanogaster. Chromosoma (Berl)68:205–227
Lepesant JA, Kejzlarova-Lepesant J, Garen A (1978) Ecdysone inductible functions of larval fat bodies inDrosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA75:5570–5574
Richards G (1978) The relative biological activities of α-and β-ecdysone and their 3 dehydro derivatives in the chromosomal puffing assay. J Insect Physiol24:329–335
Richards G (1980a) Ecdysteroids and puffing inDrosophila melanogaster. In: Hoffmann J (ed) Developments in endocrinology, Vol 7. Progress in ecdysone research. Elsevier/North Holland, Amsterdam, pp 363–378
Richards G (1980b) The polytene chromosomes in the fat body nuclei ofDrosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma (Berl)79:241–250
Richards G (1981a) The radioimmune assay of ecdysteroid titers inDrosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Endocrinol21:181–197
Richards G (1981b) Insect hormones in development. Biol Rev56:501–549
Rizki TM (1978a) Fat body. In: Ashburner M, Wright TRF (eds) The Genetics and Biology ofDrosophila vol 2b. Academic Press, London New York, pp 561–601
Rizki TM (1978b) The circulatory system and associated cells and tissues. In: Ashburner M, Wright TRF (eds) The genetics and biology ofDrosophila, vol 2b. Academic Press, London New York, pp 397–452
Roberts DB, Brock HW (1981) The major serum proteins of Dipteran larvae. Experientia37:103–110
Whitten JM (1964) Connective tissue membranes and their apparent role in transporting neurosecretory and other secretory products in insects. Gen Comp Endocrinol4:176–192
Zhimulev IF (1974) Comparative study of the function of polytene chromosomes in laboratory stocks ofDrosophila melanogaster and the l(3)tl mutant (lethal tumorous larvae). I. Analysis of puffing patterns in autosomes of the laboratory stock Batumi-L. Chromosoma (Berl)46:59–76
Zhimulev IF, Belyaeva ES, Semeshin VF (1981) Informational content of polytene chromosome bands and puffs. CRC Critical Rev Biochem11:303–340
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Richards, G. Sequential gene activation by ecdysteroids in polytene chromosomes ofDrosophila melanogaster . Wilhelm Roux' Archiv 191, 103–111 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00848447
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00848447