Abstract
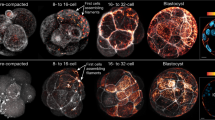
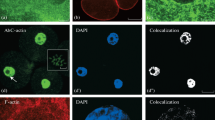
Expression patterns of intermediate filament proteins have been studied during early mouse embryo development. For this purpose, pre-implantation embryos at different stages of development after in vitro fertilization were studied using antibodies to cytokeratins, vimentin and lamins, using the indirect immunofluorescence assay. The levels of expression were quantitated and localization of the protein constituents was assessed by means of confocal scanning laser microscopy. Our studies showed that, although the embryos grew in culture, vimentin could not be detected in a filamentous organization. Immunofluorescence for cytokeratins was only positive from the 8-cell stage onwards. In the morula stage an increased level of cytokeratin expression was observed with a transitional staining pattern, combining a filamentous and a diffuse occurrence. In the blastocyst stages profound cytokeratin filaments were seen in trophoblast cells but not in the inner cell mass. When the cytokeratin subtypes were analysed separately, it became apparent that expression levels of cytokeratins 8 and 18 increased gradually up to a filamentous pattern in the blastocyst stage. Cytokeratins 7 and 19, although elevated in the latter stage and showing a filamentous distribution, were not found as prominently as cytokeratins 8 and 18. A-type as well as B-type lamins could be detected in all developmental stages examined, as a faintly reactive nuclear lamina. In blastocysts both lamin types were detected in trophoblast as well as in inner cell mass.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Battifora H (1988) The biology of the keratins and their diagnostic applications. In: DeLellis RA (ed) Advances in immunohistochemistry. Raven Press, New York, pp 191–221
Brûlet P, Babinet C, Kemler R, Jacob F (1980) Monoclonal antibodies against trophectoderm-specific markers during mouse blastocyst formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:4113–4117
Burke B, Tooze J, Warren G (1983) A monoclonal antibody which recognizes each of the nuclear lamin polypeptides in mammalian cells. EMBO J 2:361–367
Chisholm JC, Houliston E (1987) Cytokeratin filament assembly in the preimplantation mouse embryo. Development 101:565–582
Czernobilsky B, Moll R, Levy R, Franke WW (1985) Co-expression of cytokeratin and vimentin filaments in mesothelial, granulosa and rete ovarii cells of the human ovary. Eur J Cell Biol 37:175–190
Dumoulin JCM, Evers JLH, Bras M, Pieters MHEC, Geraedts JPM (1992) Positive effect of taurine on preimplantation development of mouse embryos in vitro. J Reprod Fertil 94:371–378
Emerson JA (1988) Disruption of the cytokeratin filament network in the preimplantation mouse embryo. Development 104:219–234
Franke WW, Schmid E, Winter S, Osborn M, Weber K (1979) Widespread occurrence of intermediate-sized filaments of the vimentin-type in cultured cells from diverse vertebrates. Exp Cell Res 123:25–46
Franke WW, Grund C, Kuhn C, Jackson BW, Illmensee K (1980) Formation of cytoskeletal elements during mouse embryogenesis. III. Primary mesenchymal cells and the first appearance of vimentin filaments. Differentiation 23:43–59
Höger TH, Zatloukal K, Waizenegger I, Krohne G (1990) Characterization of a second highly conserved B-type lamin present in cells previously thought to contain only a single B-type lamin. Chromosoma 99:379–390
Houliston E, Guilly M, Courvalin J, Maro B (1988) Expression of nuclear lamins during mouse preimplantation development. Development 102:271–278
Jackson BW, Grund C, Schmid E, Bürki K, Franke WW, Illmensee K (1980) Formation of cytoskeletal elements during mouse embryogenesis: intermediate filaments of the cytokeratin type and desmosomes in preimplantation embryos. Differentiation 17:161–179
Jackson BW, Grund C, Winter S, Franke WW, Illmensee K (1981) Formation of cytoskeletal elements during mouse embryogenesis. II. Epithelial differentiation and intermediate-sized filaments in early postimplantation embryos. Differentiation 20:203–216
Kemler R, Brûlet P, Schnebelen M, Gaillard J, Jacob F (1981) Reactivity of monoclonal antibodies against intermediate filament proteins during embryonic development. J Embryol Exp Morphol 64:45–60
Lane EB, Hogan BLM, Kurkinen M, Garrels JI (1983) Co-expression of vimentin and cytokeratins in parietal endoderm cells of early mouse embryo. Nature 303:701–703
Lane EB, Bartek J, Purkis PE, Leigh IM (1985) Keratin antigens in differentiating skin. Ann NY Acad Sci 455:241–258
Lehtonen E (1985) A monoclonal antibody against mouse oocyte cytoskeleton recognizing cytokeratin-type filaments. J Embryol Exp Morphol 90:197–209
Lehtonen E, Virtanen I (1985) Evidence for the presence of cytokeratin-like protein in preimplantation mouse embryos. Ann NY Acad Sci 455:744–747
Lehtonen E, Lehto V-P, Vartio T, Badley RA, Virtanen I (1983) Expression of cytokeratin polypeptides in mouse oocytes and preimplantation embryos. Dev Biol 100:158–165
Oshima RG, Howe WE, Klier FG, Adamson ED, Shevinsky LH (1983) Intermediate filament protein synthesis in preimplantation murine embryos. Dev Biol 99:447–455
Paulin D, Babinet C, Weber K, Osborn M (1980) Antibodies as probes of cellular differentiation and cytoskeletal organization in the mouse blastocyst. Exp Cell Res 130:297–304
Quinn P, Kerin JF, Warnes GM (1985) Improved pregnancy rate in human in vitro fertilization with the use of a medium based on the composition of human tubal fluid. Fertil Steril 44:493–498
Ramaekers FCS, Puts JJG, Moesker O, Kant A, Huijsmans A, Haag D, Jap PHK, Herman CJ, Vooijs GP (1983a) Antibodies to IF proteins in the immunohistochemical identification of human tumours: an overview. Histochem J 15:691–713
Ramaekers FCS, Huijsmans A, Moesker O, Kant A, Jap P, Herman C, Vooijs GP (1983b) Monoclonal antibody to keratin filaments, specific for glandularepithelia and their tumors: use in surgical pathology. Lab Invest 49:353–361
Ramaekers FCS, Haag D, Kant A, Moesker O, Jap PHK, Vooijs GP (1983c) Coexpression of keratin and vimentin-type intermediate filaments in human metastatic carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:2618–2622
Ramaekers FCS, Huijsmans A, Schaart G, Moesker O, Vooijs GP (1987) Tissue distribution of keratin 7 as monitored by a monoclonal antibody. Exp Cell Res 170:235–249
Rheinwald JG, O'Connell TM, Connell ND, Rybak SM, Allen-Hoffmann BL, LaRocca PJ, Wu Y-J, Rehwoldt SM (1984) Expression of specific keratin subsets and vimentin in normal human epithelial cells: a function of cell type and conditions of a growth during serial culture. Cancer Cells 1:217–227
Röber RA, Weber K, Osborn M (1989) Differential timing of nuclear lamin A/C expression in the various organs of the mouse embryo and the young animal: a developmental study. Development 105:365–378
Schatten G, Maul GG, Schatten H, Chaly N, Simerly C, Balczon R, Brown DL (1985) Nuclear lamins and peripheral nuclear antigens during fertilization and embryogenesis in mice and sea urchins. Cell Biol 82:4727–4731
Skalli O, Goldman RD (1991) Recent insights into the assembly, dynamics, and function of intermediate filament networks. Cell Motil Cytoskel 19:67–79
Speel EJM, Schutte B, Wiegant J, Ramaekers FCS, Hopman AHN (1992) A novel fluorescence detection method for in situ hybridisation, based on the alkaline phosphatase-Fast Red reaction. J Histochem Cytochem 40:1299–1308
Stewart C, Burke B (1987) Teratocarcinoma stem cells and early mouse embryos contain only a single major lamin polypeptide closely resembling lamin B. Cell 51:383–392
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coonen, E., Dumoulin, J.C.M. & Ramaekers, F.C.S. Intermediate filament protein expression in early developmental stages of the mouse. Histochemistry 99, 141–149 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00571875
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00571875