Summary
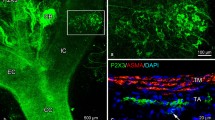
The overall distribution of substance P (SP) immunoreactive (IR) nerves surrounding the cerebral arteries of the bent-winged bat were investigated immunohistochemically. In this microchiropteran species, the walls from the vertebral artery to the caudal part of the basilar artery have considerably well-developed plexuses of SP-IR nerves, whereas no demonstrable SP-IR fibers were found in the crostral part of the basilar artery, and in more rostrally located arteries the nerve supply was very sparse or occasionally lacking. This innervation pattern has not yet been established for the cerebral arterial systems of other mammals that have been studied under normal conditions, but it is very similar to the pattern of SP-IR innervation observed in the guinea pig and cat of which the trigeminal ganglia have been destroyed. From the combination of this and other immunohistochemical findings, it is suggested that SP-IR nerves innervating the vertebral and basilar arteries of the bent-winged bat originate from the upper cervical dorsal root ganglia (DRG) and enter the cranial cavity along the vertebral artery and through the meninges.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BA:
-
basilar artery
- CSN:
-
cervical spinal nerves
- ICS:
-
internal carotid system
- SCG:
-
superior cervical ganglion
- SNB:
-
sympathetic nerve bundle
- VA:
-
vertebral artery
- VBS:
-
vertebro-basilar system
References
Andö K (1981) A histochemical study on the innervation of the cerebral blood vessels in bats. Cell Tissue Res 217:55–64
Andö K (1988) Distribution and origin of VIP-IR, acetylcholinesterase (AChE)-positive and adrenergic nerves of the cerebral arteries in the bent-winged bat (Mammalia: Chiroptera). Cell Tissue Res 251:345–351
Arbab MAR, Wiklund L, Svendgaad NAA (1986) Origin and distribution of cerebral vascular innervation from superior and cervical, trigeminal and spinal ganglia investigated with retrograde and anterograde WGA-HRP tracing in the rat. Neuroscience 19:695–708
Chan-Palay V (1977) Innervation of cerebral blood vessels by norepinephrine, indoleamine, substance P and neurotensin fibers and the leptomeningeal indoleamine axons: Their roles in vasomotor activity and local alterations of brain blood composition. In: Owman C, Edvinsson L (eds) Neurogenic control of brain circulation. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 39–53
Costa M, Buffa R, Furness JB, Solcia EL (1980) Immunohistochemical localization of polypeptides in peripheral autonomic nerves using whole mount preparations. Histochemistry 65:157–165
Duckles SP, Buck SH (1982) Substance P in the cerebral vasculature: Depletion by capsaicin suggests a sensory role. Brain Res 245:171–174
Edvinsson L, Uddman R (1982) Immunohistochemical localization and dilatory effect of substance P on human cerebral vessels. Brain Res 232:466–471
Edvinsson L, McCulloch J, Uddman R (1981) Perivascular localization and cerebrovascular effects of substance P. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1:S319–329
Edvinsson, L, Rosendal-Helgesen S, Uddman R (1983) Substance P: localization, concentration and release in cerebral arteries, choroid plexus and dura mater. Cell Tissue Res 234:1–7
Furness JB, Papka RE, Della NG, Costa M, Eskay RL (1982) Substance P-like immunoreactivity in nerves associated with the vascular system of guinea-pigs. Neuroscience 7:447–459
Graham RC, Karnowsky MJ (1966) The early stages of absorption of injected horseradish peroxidase in the proximal tubules of mouse kidney. Ultrastructural cytochemistry by a new technique. J Histochem Cytochem 14:291–302
Hanko J, Hardebo JE, Owaman CH (1981) Effect of various neuropeptides on the cerebral blood vessels. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1:S346–347
Hasegawa K, Kawano T, Oishi M, Sunagawa G, Nishimura T (1960) The angio-architecture in the brain of bat. Fukuoka Acta Med 51:1251–1266
Helke CJ, O'Donohue TL, Jacobowitz DM (1980), Substance P as a baro- and chemoreceptor afferent neurotransmitter: Immunocytochemical and neurochemical evidence in the rat. Peptides 1:1–9
Kallen FC (1978) The cardiovascular system of bats: Structure and function. In: Wimsatt WA (ed) Biology of bats, III. Academic Press, New York, pp 286–483
Kawano T (1959) On the vascular supply in a bat's brain. Report I. Pial vessels. Fukuoka Acta Med 50:3414–3429
Liu-Chen LY, Han DH, Moskowitz MA (1983a) Pial arachnoid contains substance P originating from trigeminal neurons. Neuroscience 9:803–808
Liu-Chen LY, Mayberg M, Moskowitz M (1983b) Immunohistochemical evidence for a substance P-containing trigeminovascular pathway to pial arteries in cats. Brain Res 268:162–166
Liu-Chen LY, Gillespie SA, Norregaard TN, Moskowitz M (1984) Co-localization of retrogradely transported wheat germ agglutinin and the putative neurotransmitter substance P within trigeminal ganglion cells projecting to cat middle cerebral artery. J Comp Neurol 223:187–192
Takano Y, Nagashima Y, Masui H, Kurimizu K, Kamiya HO (1986) Distribution of substance K (neurokinin A) in the brain and peripheral tissues of rats. Brain Res 369:400–404
Takeuchi Y, Kimura H, Sano Y (1982) Immunohistochemical demonstration of serotonin neurons in the brain stem of the rat and cat. Cell Tissue Res 224:247–267
Uddman R, Edvinsson L, Owman C, Sundler F (1981) Perivascular substance P: Occurrence and distribution in mammalian pial vessels. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1:227–232
Wanaka A, Matsuyama I, Yoneda S, Kimura K, Kamada T, Girgis S, MacIntyre I, Emson P, Tohyama M (1986) Origin and distribution of calcitonin gene-related peptide-containing nerves in the wall of the cerebral arteries of the guinea pig with special reference to the coexistence with substance P. Brain Res 369:185–192
Yamamoto K, Matsuyama T, Shiosaka S, Inagaki, S, Senba E, Shimizu Y, Ishimoto I, Hayakawa T, Matsumoto M, Tohyama M (1983) Overall distribution of substance P-containing nerves in the wall of the cerebral arteries of the guinea pig and its origins. J Comp Neurol 215:421–426
Zamboni L, Martino C de (1967) Buffered picric-acid formaldehyde: a new rapid fixative for electron microscopy. J Cel Biol 35:148A
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andö, K., Ishikawa, A., Kawamura, K. et al. An immunohistochemical study on the innervation of SP-IR nerves in the cerebral arteries of the bent-winged bat. Histochemistry 90, 459–463 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00494357
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00494357