Summary
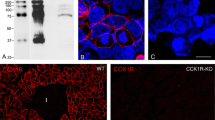
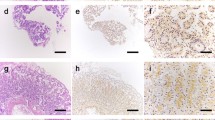
Human prostatic-type of acid phosphatase has been demonstrated by biochemical methods to be expressed in a number of cells and tissues in addition to the prostate gland. However, the function of this activity is unknown, nor has the enzyme been convincingly localized at the cellular level in any non-prostatic tissues. Using biochemical and immunocytochemical methods, we demonstrate that human intestinal epithelium contains both a lysosomal and prostatic type of acid phosphatase. The prostatic-type enzyme is present only in the epithelium of the crypts and to a lesser extent in the transitional zone at the base of the villi, in contrast to the widely-distributed lysosomal type. The prostatic enzyme is contained in granules that do not react with anti-lysosomal acid phosphatase and are probably secretory in nature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aumüller G (1979) Prostate gland and seminal vesicle. In: Oksche A, Vollrath L (eds) Handbuch der mikroskopischen Anatomie des Menschen, vol. VII/6. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, p 380
Aumüller G, Seitz J (1985) Cytochemistry and biochemistry of acid phosphatases VI: Immunoelectron microscopic studies on human prostatic and leucocytic acid phosphatases. Prostate 7:161–169
Bodansky O (1972) Acid phosphatase. Adv Clin Chem 15:43–147
Burnette WN (1981) “Western Blotting”: Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem 112:195–203
Cheng H, Leblond CP (1974) Origin, differentiation and renewal of the four main epithelial cell types in the mouse small intestine. V. Unitarian theory of the origin of the four epithelial cell types. Am J Anat 141:503–520
Choe BK, Dong MK, Walz D, Rose NR (1981) Antibody restores catalytic activity of a small molecular weight fragment of human prostatic acid phosphatase. Mol. Immunol. 18:451–454
DeDuve C, Pressman BC, Gianetto R, Wattiaux R, Appleman F (1958) Tissue fractionation studies. 6. Intracellular distribution patterns of enzymes in rat liver tissue. Biochem J 60:604–617
Drenckhahn D, Wagner J (1986) Stress fibres in the splenic sinus endothelium in situ: Molecular structure, relationship to the extracellular matrix, and contractility. J Cell Biol 102:1738–1747
Gieselmann V, Lemansky P, Hasilik A, von Figura K, Waheed A, Van Etten RL (1986) Human tartrate-inhibitable acid phosphatase. Purification, characterization, biosynthesis and intracellular transport. Acta Biochim Pol 33:119–126
Knecht DA, Dimond RL (1984) Visualization of antigenic proteins on Western blots. Anal Biochem 136:180–184
Kutscher W, Wolbergs H (1935) Prostataphosphatase. Hoppe Seyler's Z Physiol Chem 236:237–240
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Li CY, Lam KW, Yam LT (1980) Immunohistochemical diagnosis of prostatic cancer with metastasis. Cancer 46:706–712
Montero C, Erlandsen SL (1978) Immunocytochemical and histochemical studies on intestinal epithelial cells producing both lysozyme and mucosubstances. Anat Rec 190:127–142
Moss DW (1982) Lysosomal isoenzymes. In: Moss DW (ed) Isoenzymes. Chapman and Hall, New York, pp 98–103
Naritoku WY, Taylor CR (1982) A comparative study of the use of monoclonal antibodies using three different immunohistochemical methods: An evaluation of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies against human prostatic acid phosphatase. J Histochem Cytochem 30:253–260
Ouchterlony O (1958) Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunologic analysis. Prog Allergy 5:1–78
Parenti G, Willemsen R, Hoogeveen AT, Verleun-Mooyman M, van Dongen JM (1987) Immunocytochemical localization of lysosomal acid phosphatase in normal and I-cell fibroblasts. Eur J Cell Biol 43:121–127
Rehkop DM, Van Etten RL (1975) Human liver acid phosphatases. Hoppe Seyler's Z Physiol Chem 356:1775–1782
Saini MS, Van Etten RL (1978a) A homogeneous human liver acid phosphatase isoenzyme. Arch Biochem Biophys 191:613–624
Saini MS, Van Etten RL (1978b) Dimeric nature and amino acid compositions of homogeneous canine prostatic, human liver and rat liver acid phosphatase isoenzymes. Specificity and pH dependence of the canine enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta 526:468–478
Saini MS, Van Etten RL (1981) A clinical assay for prostatic acid phosphatase using choline as a substrate: Comparison with thymolphthalein phosphate. Prostate 2:359–368
Shaw LM, Yang N, Brooks JJ, Neat M, Marsh E, Seamonds B (1981) Immunochemical evaluation of the organ specificity of prostatic acid phosphatase. Clin Chem 27:1505–1512
Skinningsrud A (1983) Acid phosphatases of the human placenta, characterization and immunological comparison with prostatic acid phosphatase. Enzyme 29:250–259
Van Etten RL, Saini MS (1978) Selective purification of tartrateinhibitable acid phosphatases: Rapid and efficient purification (to homogeneity) of human and canine prostatic acid phosphatases. Clin Chem 24:1525–1530
Van Etten RL, Waheed A (1985) Biosynthesis of prostatic acid phosphatase in a normal human cell line. Arch Biochem Biophys 243:264–273
Waheed A, Van Etten RL (1985) Biosynthesis and processing lysosomal acid phosphatase in cultured human cells. Arch Biochem Biophys 243:274–283
Waheed A, Van Etten RL (1986) Biosynthesis and processing of prostatic and lysosomal acid phosphatases in a prostate carcinoma cell line PC-3SF12. Cancer Res 43:4796–4803
Waheed A, Van Etten RL, Gieselmann V, von Figura K (1985) Immunological characterization of human acid phosphatase gene products. Biochem Genet 23:307–317
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Drenckhahn, D., Waheed, A. & Van Etten, R. Demonstration of prostatic-type acid phosphatase in non-lysosomal granules in the crypt epithelium of the human duodenum. Histochemistry 88, 47–52 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00490166
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00490166