Summary
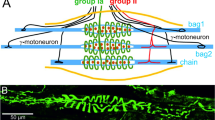
Over 150 complete and 139 incomplete single muscle spindles were examined in serial transverse sections of cat tenuissimus muscles in search for spindles lacking one of the two types of nuclear bag intrafusal fiber. Several histochemical reactions were used to type the intrafusal muscle fibers and assess the spindle motor and sensory innervation. One complete spindle lacked a bag1 fiber, and another spindle lacked a bag2 fiber. Several incomplete spindles also lacked bag1 fibers. In addition, ten double tandem spindles contained one capsular unit each that lacked the bag1 fiber, and one triple tandem spindle had two such capsules. All one-bag-fiber spindles had primary sensory innervation, but none had secondary sensory innervation. Their motor innervation was similar to that of the usual two-bag-fiber spindles in the number and disposition of intrafusal motor endings. It is unclear whether the one-bag fiber spindles, either single or tandem-linked, are products of an aberrant spindle development or represent a true anatomical and functional subcategory of the cat muscle spindle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banks RW (1981) A histological study of the motor innervation of the cat's muscle spindle. J Anat 133:571–591
Banks RW, Harker DW, Stacey MJ (1977) A study of mammalian intrafusal muscle fibers using a combined histochemical and ultrastructural technique. J Anat 123:783–796
Banks RW, Barker D, Stacey MJ (1979) Sensory innervation of cat hind-limb muscle spindles. J Physiol 293:40–41P
Banks RW, Ellaway PH, Scott JJ (1981) Responses of de-efferented muscle spindles of peroneus brevis and tertius muscles in the cat. J Physiol 310:53P
Bakker GJ, Richmond FJR (1981) Two types of muscle spindles in cat neck muscles: a histochemical study of intrafusal fiber compositon. J Neurophysiol 45:973–986
Barker D (1974) The morphology of muscle receptors. In: Hunt CC (ed) Muscle receptors. Handbook of sensory physiology, vol III/2. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 1–90
Barker D, Ip MC (1961) A study of single and tandem types of muscle-spindles in the cat. Proc R Soc London Ser B 154:377–397
Barker D, Banks RW, Harker DW, Milburn A, Stacey MJ (1976) Studies of the histochemistry, ultrastructure, motor innervation, and regeneration of mammalian intrafusal muscle fibers. Prog Brain Res 44:67–87
Boyd IA (1960) The diameter and distribution of the nuclear bag and nuclear chain muscle spindles of the cat. J Physiol 153:23–24P
Boyd IA (1962) The structure and innervation of the nuclear bag auscle fiber system and the nuclear chain muscle fiber system in mammalian muscle spindles. Philos Trans R Soc Lond (Biol) 245:81–136
Boyd IA (1976a) The mechanical properties of dynamic nuclear bag fibers, static nuclear bag fibers and nuclear chain fibers in isolated cat spindles. Prog Brain Res 44:33–49
Boyd IA (1976b) The response of fast and slow nuclear bag fibers and nuclear chain fibers in isolated cat muscle spindles to fusimotor stimulation, and the effect of intrafusal contraction on the sensory endings. QJ Exp Physiol 61:203–254
Boyd IA (1981) The muscle spindle controversy. Sci Prog Oxf 67:205–221
Boyd IA, Gladden MH, McWilliam PN, Ward J (1977) Control of dynamic and static nuclear bag fibers and nuclear chain fibers by gamma and beta axons in siolated cat muscle spindles. J Physiol 265:133–162
Eldred E, Maier A, Bridgman CF (1974) Differences in intrafusal fiber content of spindles in several muscles of the cat. Exp Neurol 45:8–18, 1974
Guth L, Samaha FJ (1970) Procedure for the histochemical demonstration of actomyosin ATPase. Exp Neurol 28:365–367
Jami L, Lan-Couton D, Malmgren K, and Petit J (1978) “Fast” and “slow” skeleto-fusimotor innervation in cat tenuissimus spindles; a study with the glycogen depletion method. Acta Physiol Scand 103:284–298
Kozeka K, Ontell M (1981) The three-dimensional cytoarchitecture of developing murine muscle spindles. Dev Biol 87:133–147
Kucera J (1980a) Motor nerve terminals of cat nuclear chain fibers studied by the cholinesterase technique. Neuroscience 5:403–411
Kucera J (1980b) Histochemical study of long nuclear chain fibers in the cat muscle spindle. Anat Rec 198:567–580
Kucera J (1981a) Histochemical profiles of cat intrafusal muscle fibers and their motor innervation. Histochemistry 73:397–418
Kucera J (1981b) The occurrence of “mixed” nuclear bag intrafusal fibers in the cat muscle spindle. Histochemistry 72:123–131
Kucera J (1982a) Morphometric studies on tenuissimus muscle spindles in the cat. J Morphol 171:137–150
Kucera J (1982b) A study of motor nerve terminals on cat nuclear bag1 intrafusal muscle fibers using the ChE staining technique. Anat Rec 202:407–418
Kucera J (1982c) Comparison of motor endings of the cat's muscle spindle stained for NADH-tetrazolium reductase and cholinesterase. Histochemistry 74:95–106
Kucera J (1982d) Appearance of sensory nerve terminals in cat muscle spindles stained for NADH-tetrazolium reductase. Histochemistry 74:493–503
Kucera J (1982e) Histological study of an unusual cat muscle spindle deficient in motor innervation. Anat Embryol 165:39–49
Kucera J, Hughes R (1982f) Ultrastructural study of motor endings on long chain intrafusal fibers in the cat muscle spindle. Brain Res (in press)
Kucera J, Dorovini-Zis K, Engel WK (1978) Histochemistry of rat intrafusal muscle fibers and their motor innervation. J Histochem Cytochem 26:973–988
Landon DN (1972) The fine structure of developing muscle spindles in the rat. J Anat 111:512–513
Lehrer GM, Ornstein LC (1959) A diazo coupling method for the electron microscope localization of cholinesterase. J Biophys Biochem Cytol 6:399–406
Milburn A (1973) The early development of muscle spindles in the rat. J Cell Sci 12:175–195
Novikoff AB, Shin W, Drucker JC (1961) Mitochondrial localization of oxidative enzymes: staining results with two tetrazolium salts. J Biophys Biochem Cytol 9:47–61
Ovalle WK, Smith RS (1972) Histochemical identification of three types of intrafusal muscle fibers in the cat and monkey based on the myosin ATPase reaction. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 50:195–202
Zelená J (1957) The morphogenetic influence of innervation on the ontogenetic development of muscle spindles. J Embryol Exp Morphol 5:283–292
Zelená J, Soukup T (1974) The differentiation of intrafusal fiber types in rat muscle spindles after motor denervation. Cell Tissue Res 153:115–136
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kucera, J. One-bag-fiber muscle spindles in tenuissimus muscles of the cat. Histochemistry 76, 315–328 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00543954
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00543954