Abstract
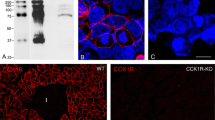
The histological localization was investigated of adrenomedullin (AM), a novel vasorelaxant peptide originally isolated from human pheochromocytoma. The immunohistological distribution was examined of AM in human, rat, and procine tissues using a polyclonal antibody to a fragment comprising C-terminal amino acids 40–52 of human adrenomedullin [AM(40–52)NH2]. Almost all of the human pheochromocytoma and normal adrenal medullary cells of all three species were immunostained and found to be intensely positive for AM. Furthermore, AM-immunoreactive cells were present in the pancreatic islets, gastrointestinal neuroendocrine system, anterior pituitary, and choroid plexus with some degree of interspecies heterogeneity. These findings indicate that AM-immunoreactive cells are widely distributed in the endocrine and neuroendocrine system, suggesting that AM plays some important role in the control of systemic and local circulation and also of humoral secretion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ichiki Y, Kitamura K, Kangawa K, Kawamoto M, Matsuo H, Eto T (1994) Distribution and characterization of immunoreactive adrenomedullin in human tissue and plasma. FEBS Lett 338:6–10
Ishiyama Y, Kitamura K, Ichiki Y, Nakamura B, Kida O, Kangawa K, Eto T (1993) Hemodynamic effects of a novel hypotensive peptide, human adrenomedullin, in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 241:271–273
Kitamura K, Kangawa K, Kawamoto M, Ichiki Y, Nakamura S, Matsuo H, Eto T (1993a) Adrenomedullin: a novel hypotensive peptide isolated from human pheochromocytoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 192:553–560
Kitamura K, Sakata J, Kangawa K, Kojima M, Matsuo H, Eto T (1993b) Cloning and characterization of cDNA encoding a precursor for human adrenomedullin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 194:720–725
Kitamura K, Kangawa K, Kojima M, Ichiki Y, Matsuo H, Eto T (1994) Complete amino acid sequence of porcine adrenomedullin and cloning of cDNA encoding its precursor. FEBS Lett 338:306–310
Sakata J, Shimokubo T, Kitamura K, Nakamura S, Kangawa K, Matsuo H, Eto T (1993) Molecular cloning and biological activities of rat adrenomedullin, a hypotensive peptide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 195:921–927
Takahashi H, Watanabe T, Nishimura M, Nakanishi T, Sakamoto M, Yoshimura M, Komiyama Y, Masuda M, Murakami T (1994) Centrally induced vasopressor and sympathetic responses to a novel endogenous peptide, adrenomedullin, in anesthetized rats. Am J Hypertens 7:478–482
Washimine H, Kitamura K, Ichiki Y, Yamamoto Y, Kangawa K, Matsuo H, Eto T (1994) Immunoreactive proadrenomedullin N-terminal 20 peptide in human tissue, plasma and urine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 202:1081–1087
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Washimine, H., Asada, Y., Kitamura, K. et al. Immunohistochemical identification of adrenomedullin in human, rat, and porcine tissue. Histochem Cell Biol 103, 251–254 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01457408
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01457408