Abstract
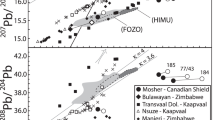
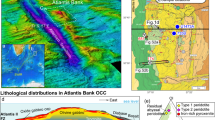
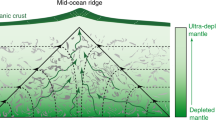
Basalts from 5 Deep Sea Drilling Project (DSDP) sites in the northwest Indian Ocean (Somali Basin and Arabian Sea) have general geochemical features consistent with a spreading origin at the ancient Carlsberg Ridge. However, compared to most MORBS from other oceans they have low normative olivine, TiO2, and Zr contents. There is no evidence that the mantle source of these northwest Indian Ocean basalts was enriched in incompatible elements relative to the Atlantic and Pacific ocean mantles. In detail, incompatible element abundances in these DSDP basalts establish that they evolved from several compositionally distinct parental magmas. In particular, basalts from site 236 in the Somali Basin have relatively high SiO2 and low Na, P, Ti, and Zr contents. These compositional features along with low normative olivine contents are similar to those proposed for melts derived by two-stage (or dynamic) melting. Published data also indicate there is no enrichment in incompatible elements at the southwest Indian Ocean triple junction, although southwest Indian Ocean basalts have slightly higher 87Sr/86Sr than “normal” Atlantic MORB. The data suggest that there are significant subtle geochemical variations in the Indian Ocean mantle sources, but are insufficient to show whether these variations have a systematic temporal or geographic distribution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbey S, Gillieson AH, Perrault G (1975) SY-2, SY-3, and MRG-1: a report on the collaborative analyses of three Canadian rock samples for use as certified reference materials. Can Energy, Mines and Resources Publ Cat No 738-10-75, 132, 56 pp
Bender JF, Hodges FN, Bence AE (1978) Petrogenesis of basalts from the Project FAMOUS AREA: experimental study from 0 to 15 kilobars. Earth Planet Sci Lett 41:277–302
Brown GC, Hughes DJ, Esson J (1973) New XRF data and retrieval techniques and application to USGS standard rocks. Chem Geol 11:223–229
Bryan WB (1979) Regional variation and petrogenesis of basalt glasses from the FAMOUS Area, Mid-Atlantic Ridge. J Petrol 20:293–325
Bryan WB, Thompson G, Michael PJ (1979) Compositional variation in a steady-state zoned magma chamber: Mid-Atlantic Ridge at 36°50′N. Tectonophysics 55:63–85
Bryan WB, Moore JG (1977) Compositional variation of young basalts in the Mid-Atlantic rift valley near 36°49′N. Bull Geol Soc Am 88:556–570
Bryan WB, Thompson G, Frey FA, Dickey JS (1976) Inferred geologic settings and differentiation in basalts from the Deep Sea Drilling Project. J Geophys Res 81:4285–4304
Cann JR (1969) Spilites from the Carlsberg Ridge, Indian Ocean. J Petrol 10:1–19
Carlson RW, MacDougall JD, Lugmair GW (1978) Differential Sm/Nd evolution in oceanic basalts. Geophys Res Lett 5:229–232
Coish RA, Church WR (1979) Igneous geochemistry of mafic rocks in the Betts Cove Ophiolite, Newfoundland. Contrib Mineral Petrol 70:24–40
Dickey JS, Frey FA, Bryan WB, Thompson G, Davies H (1978) Clinopyroxene fraction of MOR basalts from DSDP Hole 238, Indian Ocean. GSA Abstr with Progr 10 (7):389
Dmitriev IV (1974) Petrochemical study of the basaltic basement Indian Ridge: leg 24 Djibouti to Mauritius. In: Fisher RL, Bunce ET et al (eds) Initial Report of the Deep Sea Drilling Project, Vol 24, Washington (US Government Printing Office), pp 767–779
Dmitriev IV, Fisher RL (1974) Preliminary observations on the igneous rocks sampled at site 236. In: Fisher RL, Bunce ET et al (eds) Initial Report of the Deep Sea Drilling Project, Vol 24, Washington (US Government Printing Office), pp 338–341
Donaldson CH, Brown RW (1977) Refractory megacrysts and magnesium-rich melt inclusions within spinel in oceanic tholeiites: indicators of magma mixing and parental magma composition. Earth Planet Sci Lett 37:81–89
Duncan RA, Green DH (1980) The role of multi-stage melting in the formation of oceanic crust. Geology 8:22–26
Engel CG, Bingham E, Fisher RL (1974) Trace element compositions of leg 24 basalts and one diabase. In: Fisher RL, Bunce ET et al (eds) Initial Report of the Deep Sea Drilling Project, Vol 24, Washington (US Government Printing Office), pp 781–786
Engel CG, Fisher RL (1975) Granite to ultramafic rock complexes of the Indian Ocean Ridge System, Western Indian Ocean. Geol Soc Am Bull 86:1553–1578
Erlank AJ, Reid DC (1974) Geochemistry mineralogy and petrology of basalts, leg 25 DSDP. In: Schlick R, Simpson ESW et al (eds) Initial Reports of Deep Sea Drilling Project 25:543–551
Fisher RL, Sclater JG, McKenzie DP (1971) Evolution of the central Indian Ridge, Western Indian Ocean. Geol Soc Am Bull 82:553–562
Flanagan FJ (1973) 1972 Values for international geochemical reference samples. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 37:1189–1200
Frey FA, Bryan WB, Thompson G (1974) Atlantic Ocean floor: geochemistry and petrology of basalts from legs 2 and 3 of the Deep Sea Drilling Project. J Geophys Res 79:5507–5527
Frey FA, Dickey JS, Thompson G, Bryan WB (1977) Eastern Indian Ocean DSDP sites: correlations between petrography, geochemistry and tectonic setting. In: Heirtzler JR et al (eds) Indian Ocean Geology and Biostratigraphy. AGU Monograph Series. Washington, DC, pp 189–257
Govindaraju K, de la Roche H (1977) Rapport (1966–76) sur les éléments en traces dans trois standards géochimique du CRPG: Basalte BR et Granites GA et GH. Géostandards. Newsletter 1 (1):67–98
Green DH, Hibberson WO, Jaques AL (1979) Petrogenesis of mid-ocean ridge basalts. In: McElhinny MW (ed) The Earth: Its Origins, Structure, and Evolution. Academic Press, pp 265–269
Hart SR (1971) K, Rb, Cs, Sr, and Ba contents and Sr isotope ratios of ocean floor basalts. Philos Trans R Soc London, Ser A 268:573–587
Hart SR (1976) LIL-element geochemistry, leg 34 basalts. In: Yeats RS, Hart SR et al (eds) Initial Reports of the Deep Sea Drilling Project, Vol 34. Washington (US Goverment Printing Office), pp 283–288
Harvey PK, Taylor DM, Hendry RD, Bancroft F (1973) An accurate fusion method for the analysis of rocks and chemically related materials by X-ray fluorescence spectrometry. X-ray Spectrometry 2:33–44
Hedge CE, Futa K, Engel CG, Fisher RL (1979) Rare earth systematics of basalts, gabbro, anorthosite and minor granitic rocks from the Indian Ocean ridge system, western Indian Ocean. Contrib Mineral Petrol 68:373–376
Hekinian R (1968) Rocks from the mid-oceanic ridge in the Indian Ocean. Deep-Sea Res 15:195–213
Hofmann AW, Hart SR (1978) An assessment of local and regional isotopic equilibrium in the mantle. Earth Planet Sci Lett 38:44–62
Jacobs JW, Korotev RL, Blanchard DP, Haskin LA (1977) A well-tested procedure for instrumental neutron activation analysis of silicate rocks and minerals. J Radioanal Chem 40:93–114
Langmuir CH, Bender JF, Bence AE, Hanson GN, Taylor SR (1977) Petrogenesis of basalts from the FAMOUS area, Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Earth Planet Sci Lett 73:5925–5941
Ludden JN, Thompson G (1978) Behavior of rare earth elements during submarine weathering of tholeiitic basalt. Nature 274:147–149
Ludden JN, Thompson G (1979) An evaluation of the behavior of the rare earth elements during the weathering of seafloor basalt. Earth Planet Sci Lett 43:85–92
McKenzie D, Sclater JG (1971) The evolution of the Indian Ocean since the late Cretaceous. Geophys J R Astr Soc 24:437–528
Melson WG, Thompson G (1971) Petrology of a transform fault zone and adjacent ridge segments. Philos Trans R Soc London, SerA 268:423–441
Melson WG, Vallier TL, Wright TL, Byerly G, Nelen J (1976) Chemical diversity of abyssal volcanic glass erupted along Pacific, Atlantic and Indian Ocean seafloor spreading centers. In: The geophysics of the Pacific Ocean basin and its margin. AGU Monograph Series 19:351–368
Melson WG, O'Hearn T (1979) Basaltic glass erupted along the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between 0–37°N: Relationships between composition and latitude. In: Talwani M, Harrison CG, Hayes DE (eds) Deep-drilling results in the Atlantic Ocean: Ocean Crust. Am Geophys Union, Washington DC, M Ewing Series, Vol 2, pp 249–261
Norrish K, Hutton JT (1969) An accurate X-ray spectrographic method for the analysis of a wide range of geological samples. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 33:431–453
O'Hara MJ (1968) Are ocean floor basalts primary magma? Nature 220:683–686
Reddy VV, Subbarao KV, Reddy GR, Matsuda J, Hekinian R (1978) Geochemistry of volcanics from the Ninety east Ridge and its vicinity in the Indian Ocean. Mar Geol 26:99–117
Rhodes JM, Dungan MA, Blanchard DP, Long PE (1979) Magma mixing at mid-ocean ridges: evidence from basalts drilled near 22°N on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Tectonophysics 55:35–61
Schilling JG (1971) Sea-floor evolution: rare-earth evidence. Philos Trans R Soc London, Ser A 268:663–706
Schilling JG (1975) Azores mantle blob: rare-earth evidence. Earth Planet Sci Lett 25:103–115
Schlich R, Simpson ESW, Vallier TL (1974) Regional aspects of Deep Sea Drilling in the western Indian Ocean, leg 25, DSDP. In: Simpson ESW, Schlich R et al (eds) Initial Reports of the Deep-Sea Drilling Project, Vol 25. Washington (US Government Printing Office), pp 743–759
Schweitzer EL, Papike JJ, Bence AE (1979) Statistical analysis of clinopyroxenes from deep sea basalts. Am Mineral 64:501–513
Sneeringer MR (1979) The geochemistry of coexisting glass, phenocrysts and glass inclusions in basalts dredged from the West Indian Ocean triple junction. MS Thesis, Mass Inst Tech, p 154
Staudigel H (1980) Chemical Analyses of Interlaboratory Standards. In: Donnelly T, Francheteau J, Bryan W, Robinson P, Flower M, Salisbury M et al. (eds) Initial Reports of the DeepSea Drilling Project, Vol 51, 52, 53, Part 2. Washington (US Goverment Printing Office) pp 1331–1333
Subbarao KU, Hedge CE (1973) K, Rb, Sr and Sr87/Sr86 in rocks from the Mid-Indian Ocean Ridge. Earth Planet Sci Lett 18:223–228
Subbarao KU, Hekinian R, Chandresekharam D (1977) Large ion lithophile elements and Sr and Pb isotopic variations in volcanic rocks from the Indian Ocean. In: Indian Ocean Geology and Biostratigraphy. AGU Monograph Series, pp 259–278
Subbarao KV, Kempe DRC, Reddy VV, Reddy GR, Hekinian R (1979) Review of the geochemistry of Indian and other oceanic rocks. In: Ahrens LH (ed) Origin and Distribution of the Elements. Pergamon, New York, pp 367–399
Sun SS, Nesbitt RW (1977) Chemical heterogeneity of the Archaean mantle, composition of the earth and mantle evolution, Earth Planet Sci Lett 35:429–448
Sun SS, Nesbitt RW, Sharaskin AY (1979) Geochemical characteristics of mid-ocean ridge basalts. Earth Planet Sci Lett 44:118–138
Tatsumoto M (1978) Isotopic composition of lead in oceanic basalt and its implication to mantle evolution. Earth Planet Sci Lett 38:63–87
Thompson G (1973) A geochemical study of the low temperature interaction of seawater and oceanic igneous rock. EOS, Trans Am Geophys Union 54:1015–1019
Thompson G, Bankston DC (1969) A technique for trace element analysis of powdered material using the d.c. arc and photoelectric spectrometer. Spectrochim Acta 24B:335–350
White WM, Schilling JG (1978) The nature and origin of geochemical variation in Mid-Atlantic ridge basalts from central North Atlantic. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 42:1501–1516
Whitmarsh RB (1974) Summary of general features of Arabian Sea and Red Sea Cenozoic history based on Leg 23 cores. In: Whitmarsh RB, Weser OE, Ross DA et al. (eds) Initial Reports of the Deep Sea Drilling Project, Vol 23. Washington (US Government Printing Office), pp 1115–1123
Wiseman JDH (1937) Geological and mineralogical investigations. 1. Basalts from the Carlsberg Ridge, Indian Ocean. Sci Rep J Murray Exped Br Museum (Nat Hist) 3:1–128
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frey, F.A., Dickey, J.S., Thompson, G. et al. Evidence for heterogenes primary MORB and mantle sources, NW Indian Ocean. Contr. Mineral. and Petrol. 74, 387–402 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00518119
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00518119