Abstract
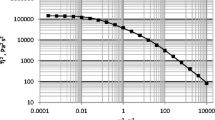
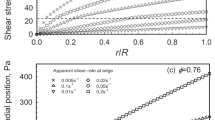
In the present work the measurement and description of the second normal stress difference in pure viscoelastic fluids and in suspensions of these fluids is discussed. The various measurement methods implemented to date are described briefly. Following this, the cone-and-plate distance method, which was introduced by Jackson and Kaye, is discussed. The analysis method of this experimentally relative simply implemented technique is modified. This is done by assuming that the ratio ψ* of the second normal stress difference to the first is independent of shear rate. This permits the precalculation of the measured function with ψ* as a curve parameter. The best possible fit of the measurement leads to the determination of ψ*. This method is used to measure the normal stress ratio of pure polyisobutene and of a 34.5% suspension of the same fluid. The result for the pure fluid matches literature values; ψ* of the suspension was found to have negative sign, as for the pure fluid, but to be of much greater magnitude.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baird DG (1975) A possible method for determining normal stress differences from hole pressure error data. Trans Soc Rheol 19:307–335
Bird RB, Armstrog RC, Hassager O (1987) Dymamics of polymeric liquids. Vol 1, J. Wiley & Sons, New York
Böhme G (1974) Eine Theorie für sekundäre Strömungserscheinungen in nichtnewtonischen Fluiden. DLR FB 74–24
Broadbent JM, Kaye A, Lodge AS, Vale DG (1968) Possible systematic error in the measurement of normal stress differences in polymer solutions in steady shear flow. Nature 217:55–56
Carreau PJ (1968) PhD Thesis; University of Wisconsin, Madison
Christiansen EB, Leppard WR (1974) Steady-state and oscillatory flow properties of polymer solutions. Trans Soc Rheol 18:65–86
Demarmels A, Meissner J (1986) Multiaxial elongations of polyisobutylene and the predictions of several network theories. Colloid Polym Sci 264:829
Ehrmann G (1976) Bestimmung der zweiten Normalspannungsdifferenz von Polymerschmelzen. Rheol Acta 15:8–14
Eitelberg G (1983) Weissenberg effect and its dependence upon the experimental geometry. Rheol Acta 22:131–136
Es HE van (1974) A new method for determining the second normal stress difference in viscoelastic fluids. Rheol Acta 13:905–909
Gao HW, Ramachandran S, Christiansen EB (1981) Dependency of the steady-state and transient viscosity and first and second normal stress difference functions on molecular weight for linear mono polydisperse polystyrene solutions. J Rheol 25:213–235
Ginn RF, Metzner AB (1963) Normal stress in polymeric solutions. Proc 4. Congr Rheol, Ed EH Lee Interscience Publishers pt 2; 533–600
Ginn RF, Metzner AB (1969) Measurement of stresses developed in steady laminar shearing flows of viscoelastic media. Trans Soc Rheol 13:429–453
Gleißle W (1978 a) Ein Kegel-Platte-Rheometer für sehr zähe viscoelastische Flüssigkeiten bei hohen Schergeschwindigkeiten, Untersuchung des Fließverhaltens von hochmolekularem Siliconöl und Polyisobutylen. Dissertation Universität Karlsruhe (TH)
Gleißle W (1978b) Interner Bericht; Institut für mechanische Verfahrenstechnik; Universität Karlsruhe (TH)
Harris J (1968) Measurement of normal stress differences in solutions of macromolecules. Nature 217:1248–1249
Higashitani K, Iwamoto K (1976) Estimation of second normal stress difference by falling film method. In: Klason C, Kubat J (eds) Proc 7 Int Congr Rheol, Gothenburg, pp 222–223
Higashitani K, Pritchard WG (1972) A kinematic calculation of intrinsic errors in pressure measurements made with holes. Trans Soc Rheol 16:687–696
Higashitani KO, Lodge AS (1975) Trans Soc Rheol 19:307–335
Jackson R, Kaye A (1966) The measurement of the normal stress differences in a liquid undergoing simple shear flow using a cone and plate total thrust apparatus only. Brit Appl Phys 17:1355–1360
Janeschitz-Kriegel (1983) Polymer melt rheology and flow birefringence. Springer Verlag, Berlin New York
Joseph DD, Beavers GS (1977) Rheol Acta 16:167–189
Keentok M, Georgescu AG, Sherwood AA, Tanner RI (1980) The measurement of second normal stress difference for some polymer solutions. J Non-Newt Fl Mech 6:303–324
Kotaka T, Kurata M, Tamura M (1959) Normal stress effect in polymer solutions. J Appl Phys 30:1750
Kuo Y, Tanner RI (1974) On the use of open-channel flows to measure the second normal stress difference. Rheol Acta 13:443–456
Lodge AS (1985) Low shear-rate rheometry and pol quality control. Chem Eng Comm 32:1/60
Lodge AS, Al-Hadithi TSR, Walters K (1987) Measurement of the first normal-stress difference at high shear rates for a PIB/decalin solution “D2”. Rheol Acta 26:516–521
Lodge AS, Ko YS (1989) Slit die viscometry at shear rates up to 5e+06 〈1/s〉: an analytical correction for small viscous heating errors. Rheol Acta 28:464–472
Marsh BD, Pearson JRA (1968) The measurement of normal-stress differences using cone-and-plate total thrust apparatus. Rheol Acta 4:326–331
Meissner J, Garbella RW, Hostetter J (1989) Measuring normal stress differences in polymer melt shear flow. J Rheol 33:843–864
Petersen JF (1974) Zur Bestimmung der Normalspannungsfunktionen von Hochpolymeren mittels der Kegel-Platte-Abstands-Anordnung. Ph D Thesis, Aachen
Pipkin AC, Tanner RI (1972) A survey of theory and experiment in viscometric flows of viscoelastic liquids. In: Nemat-Nasser S (ed) Mechanics today. Pergamon Press, Oxford; Vol 1, pp 262–321
Pollett WFO (1955) Rheological behavior of continuously sheared polythene. Brit J Appl Phys 6:199–206
Pritchard WG (1971) Measurements of the viscometric functions for a fluid in steady shear flow. Phil Trans Roy Soc Lond A 270:507–556
Ramachandran S, Gao HW, Christiansen EB (1985) Dependence of viscoelastic flow functions on molecular structure for linear and branched polymers. Macromolecules 18:695–699
Sturges LD, Joseph DD (1975) Slow motion and viscometric motion pt. 5: The free surface on a simple fluid flowing down a titled trough. Arch Rational Mech Anal 59:359–387
Sturges LD, Joseph DD (1980) A normal stress amplifier for the second normal stress difference. J Non-Newt Fl Mech 6:325–331
Tanner RI (1970) Some methods for estimating the normal stress functions in viscometric flows. Trans Soc Rheol 14:483–507
Wagner MH, Demarmels A (1990) A constitutive analysis of extensional flows of polyisobutylene. J Rheol 34:943–958
Wales JLS (1976) The application of flow birefringence measurements to rheological studies of polymer melts. Delft University Press
Wales JLS, Philippoff W (1973) Rheol Acta 12:25
Weissenberg K (1947) Cont Theory of Rheol Phen. Nature 159:310
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohl, N., Gleissle, W. The second normal stress difference for pure and highly filled viscoelastic fluids. Rheola Acta 31, 294–305 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00366508
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00366508