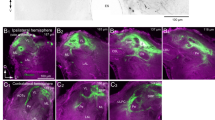
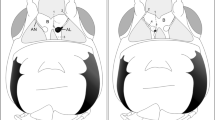
Abstract
Neurons in the brain of the spiny lobster that respond to chemical and mechanical stimulation of the antennule (antenna I) were recorded and stained intracellularly. Described here are neurons that do not arborize in the olfactory and accessory lobes of the deutocerebrum, but rather primarily target the lateral and/or the median antennular neuropils of the deutocerebrum. Some of the neurons also extend into the antennal and tegumentary neuropils of the tritocerebrum and the neuropils of the median protocerebrum. Included are antennular sensory afferents, antennular motoneurons, projection neurons descending from the central brain, projection neurons ascending from the central brain and projection neurons descending from the eyestalk ganglia. Collectively, these neurons consitutute a novel antennular sensory pathway that is parallel to and independent of the antennular olfactory pathway. The novel pathway integrates mechanosensory and non-olfactory chemosensory information in the lateral and/or the median antennular neuropils, which also serve as lower motor centers of the antennule. Division of the arthropod deutocerebrum into two, functionally distinct chemosensory pathways may reflect differences in how chemosensory information is processed that is fundamental to understanding the origin of the sense of smell.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AC :
-
anterior cluster (cluster 6, 7)
- AL :
-
ccessory lobe
- aMC :
-
anterior subcluster of medial cluster (cluster 9)
- AnN :
-
antenna II (antennal) neuropil
- A INv:
-
main antenna I (antennular) nerve
- A INM:
-
antenna I (antennular) motor nerve
- A IINv:
-
main antenna II (antennal) nerve
- A IINM:
-
antenna II (antennal) motor nerve
- DCN :
-
deutocerbral commissure neuropil
- dDLC :
-
dorsal subcluster of dorsal lateral cluster (cluster 15)
- dDUMC :
-
dorsal subcluster of dorsal unpaired median cluster (cluster 17)
- DUGC :
-
dorsal unpaired globuli cell cluster
- LAN :
-
lateral antenna I (antennular) neuropil
- IDUMC :
-
lateral subcluster of dorsal unpaired median cluster (cluster 16)
- LF :
-
lateral flagellum of antenna I (antennule)
- MAN :
-
median antenna I (antennular) neuropil
- mDUMC :
-
median subcluster of dorsal unpaired median cluster (cluster 17)
- MF :
-
medial flagellum of antenna I (antennule)
- MPN :
-
anterior and posterior median protocerebral neuropils
- OC :
-
oesophageal connective
- OCM :
-
oculomotor nerve
- OL :
-
olfactory lobe
- PT :
-
protocerebral tract
- TN :
-
tegumentary neuropil
- TNv :
-
tegumentary nerve
- vDLC :
-
ventral subcluster of dorsal lateral cluster (cluster 14)
- VPALC :
-
ventral paired anterolateral cluster (cluster 8)
- VUMC :
-
ventral unpaired median cluster (cluster 13)
- AMP :
-
adenosine monophosphate
- ASC :
-
L-ascorbic acid
- ASW :
-
artificial sea water
- BET :
-
betaine HCl
- M1 :
-
mixture 1 (TAU, BET, ASC, NH4)
- M2 :
-
mixture 2 (SUC, NIC, AMP, TMA)
- M3 :
-
mixture 3 (M1, M2, PRO)
- NH 4 :
-
NH4Cl
- NIC :
-
nicotinic acid
- PRO :
-
L-proline
- SUC :
-
sucrose
- TAU :
-
taurine
- TM :
-
TetraMarin extract
- TMA :
-
trimethylamine HCl
References
Ache BW, Fuzessery ZM (1979) Chemosensory integration in the spiny lobster: Ascending activity in the olfactory-globular tract. J Comp Physiol 130: 63–69
Arbas EA, Humphreys CJ, Ache BW (1988) Morphology and physiological properties of interneurons in the olfactory midbrain of the crayfish. J Comp Physiol A 164: 231–241
Blaustein DN, Derby CD, Simmons RB, Beall AC (1988) Structure of the brain and medulla terminalis of the spiny lobster Panulirus argus and the crayfish Procambarus clarkii, with an emphasis on olfactory centers. J Crust Biol 8: 493–519
Derby CD, Ache BW (1984) Quality coding of a complex odorant in an invertebrate. J Neurophysiol 51(5): 906–924
Derby CD, Blaustein DN (1988) Morphological and physiological characterization of individual olfactory interneurons connecting the brain and eyestalk ganglia of the crayfish. J Comp Physiol A 163: 777–794
Derby CD, Hamilton KA, Ache BW (1984) Processing of olfactory information at three neuronal levels in the spiny lobster. Brain Res 300: 311–319
Derby CD, Ache BW, Kennel EW (1985) Mixture suppression in olfaction: electrophysiological evaluation of the contribution of peripheral and central neural components. Chem Senses 10: 301–316
Fraser PJ (1974) Interneurones in crab connectives (Carcinus maenas (L.)): directional statocyst fibres. J Exp Biol 61: 615–628
Fraser PJ, Sandeman DC (1975) Effects of angular and linear accelerations on semicircular canal interneurons of the crab Scylla serrata. J Comp Physiol 96: 205–221
Fuzessery ZM (1978) Quantitative stimulation of antennular chemoreceptors of the spiny lobster, Panulirus argus. Comp Biochem Physiol 60: 303–308
Glantz RM, Kirk M, Viancour T (1981) Interneurons in the crayfish brain: The relationship between dendrite location and afferent input. J Neurobiol 12: 311–328
Gleeson RA (1982) Morphological and behavioral identification of the sensory structures mediating pheromone reception in the blue crab, Callinectes sapidus. Biol Bull 163: 162–171
Grünert U, Ache BW (1988) Ultrastructure of the aesthetasc (olfactory) sensilla of the spiny lobster, Panulirus argus. Cell Tissue Res 251: 95–103
Hamilton KA, Ache BW (1983) Olfactory excitation of interneurons in the brain of the spiny lobster. J Comp Physiol 150: 129–140
Helm F (1928) Vergleichend-anatomische Untersuchungen über das Gehirn, insbesondere das “Antennalganglion” der Dekapoden. Z Morph Ökol Tiere 12: 70–134
Horikawa K, Armstrong WE (1988) A versatile means of intracellular labeling: injection of biocytin and its detection with avidin conjugates. J Neurosci Methods 25: 1–11
Kouyama N, Shimozawa T (1982) The structure of a hair mechanoreceptor in the antennule of crayfish (Crustacea). Cell Tissue Res 226: 565–578
Laverack MS (1964) The antennular sense organs of Panulirus argus. Comp Biochem Physiol 13: 301–321
Masson C, Mustaparta H (1990) Chemical information processing in the olfactory system of insects. Physiol Rev 70: 199–245
Maynard DM (1965) Integration in crustacean ganglia. Symp Soc Exp Biol 20: 111–149
Maynard DM, Dingle H (1963) An effect of eyestalk ablation on the antennular function in the spiny lobster, Panulirus argus. Z Vergl Physiol 46: 515–540
Mellon D Jr (1977) Central and peripheral features of crayfish oculomotor organization. In: Hoyle G (ed) Identified neurons and behavior of arthropods. Plenum Press, New York London, pp 149–166
Mellon D Jr, Alones V (1993) Cellular organization and growthrelated plasticity of the crayfish olfactory midbrain. Microsc Res Tech 24: 231–259
Mellon D Jr, Munger SD (1990) Nontopographic projection of olfactory sensory neurons in the crayfish brain. J Comp Neurol 296: 253–262
Mellon D Jr, Alones V, Lawrence MD (1992) Anatomy and fine structure of neurons in the deutocerebral projection pathway of the crayfish olfactory system. J Comp Neurol 321: 93–111
Michel WC, Trapido-Rosenthal HG, Chao ET, Wachowiak M (1993) Stereoselective detection of amino acids by lobster olfactory receptor neurons. J Comp Physiol A 171: 705–712
Nakagawa H, Hisada M (1989) Morphology of descending statocyst interneurons in the crayfish Procambarus clarkii Girard. Cell Tissue Res 255: 539–551
Nakagawa H, Hisada M (1990) A vibration-sensitive descending statocyst interneurone in the crayfish Procambarus clarkii. J Exp Biol 149: 361–378
Nakagawa H, Hisada M (1991) Inhibitory connections underlying the directional sensitivity of the equilibrium system in the crayfish Procambarus clarkii. J Exp Biol 152: 305–312
Nakagawa H, Hisada M (1992) Local spiking interneurons controlling the equilibrium response in the crayfish Procambarus clarkii. J Comp Physiol A 170: 291–302
Neil DM (1982) Compensatory eye movements. In: Sandeman DC, Atwood HL (eds) The biology of Crustacea, vol. 4. Neural integration and behavior. Acad Press, New York London, pp 133–163
Patton ML, Grove RF (1992) The response of statocyst receptors of the lobster, Homarus americanus, to movements of statolith hairs. Comp Biochem Physiol 101A: 249–257
Rospars JP (1988) Structure and development of the insect antennodeutocerebral system. Int J Insect Morphol Embryol 17: 243–294
Roye DB (1975) The physiological basis for pitch-induced antennule movements in the blue crab, Callinectes sapidus. Comp Biochem Physiol 62A: 475–484
Roye DB (1986) The central distribution of movement sensitive afferent fibers from the antennular short hair sensilla of Callinectes sapidus. Mar Behav Physiol 12: 181–196
Roye DB, Dillaman RM (1982) Morphological and physiological characteristics of the antennular short hair sensilla of the blue crab, Callinectes sapidus. Mar Behav Physiol 9: 59–71
Sandeman DC, Denburg JL (1976) The central projections of chemoreceptor axons in the crayfish revealed by axoplasmic transport. Brain Res 115: 492–496
Sandeman DC, Luff SE (1973) The structural organization of glomerular neuropile in the olfactory and accessory lobes of an Australian freshwater crayfish, Cherax destructor. Z Zellforsch 142: 37–61
Sandeman DC, Okajima A (1972) Statocyst-induced eye movements in the crab Scylla serrata. I. The sensory input from the statocyst. J Exp Biol 57: 187–204
Sandeman DC, Okajima A (1973) Statocyst-induced eye movements in the crab Scylla serrata. III. The anatomical projections of sensory and motor neurones and the responses of the motor neurones. J Exp Biol 59: 17–38
Sandeman DC, Sandeman RE (1994) Electrical responses and synaptic connections of giant serotonin-immunoreactive neurons in crayfish olfactory and accessory lobes. J Comp Neurol 341: 130–144
Sandeman D, Sandeman R, Derby C, Schmidt M (1992) Morphology of the brain of crayfish, crabs, and spiny lobsters: A common nomenclature for homologous structures. Biol Bull 183: 304–326
Schmidt M, Ache BW (1992) Antennular projections to the midbrain of the spiny lopbster. II. Sensory innervation of the olfactory lobe. J Comp Neurol 318: 291–303
Schmidt M, Ache BW (1993) Antennular projections to the midbrain of the spiny lopbster. III. Central arborizations of motoneurons. J Comp Neurol 336: 583–594
Schmidt M, Ache BW (1996) Processing of antennular input in the brain of the spiny lobster, Panulirus argus. II. The olfactory pathway. J Comp Physiol A
Schmidt M, Orona E, Ache BW (1991) Parallel processing of chemosensory input in the brain of the spiny lobster. Soc Neurosci Abstr 17: 1018
Schmidt M, Van Ekeris L, Ache BW (1992) Antennular projections to the midbrain of the spiny lobster. I. Sensory innervation of the lateral and medial antennular neuropils. J Comp Neurol 318: 277–290
Silvey GE, Sandeman DC (1976) Integration between statocyst sensory neurons and oculomotor neurons in the crab Scylla serrata. III. The sensory to motor synapse. J Comp Physiol 108: 53–65
Silvey GE, Dunn PA, Sandeman DC (1976) Integration between statocyst sensory neurons and oculomotor neurons in the crab Scylla serrata. II. The thread hair sensory receptors. J Comp Physiol 108: 45–52
Snow PJ (1973) The antennular activities of the hermit crab, Pagurus a/askensis (Benedikt). J Exp Biol 58: 745–765
Snow PJ (1974) Surface structures of the antennular flagella of the hermit crab Pagurus alaskensis (Benedict): A light and scanning electron microscopy study. J Morphol 144: 195–216
Spencer M (1986) The innervation and chemical sensitivity of single aesthetasc hairs. J Comp Physiol A 158: 59–68
Spencer M, Linberg KA (1986) Ultrastructure of aesthetasc innervation and external morphology of the lateral antennule setae of the spiny lobster Panulirus interruptus (Randall). Cell Tissue Res 245: 69–80
Tautz J (1987) Interneurons in the tritocerebrum of the crayfish. Brain Res 407: 230–239
Tautz J, Erber J, Ache B (1986) Chemosensitive interneurons ascend in the optic nerve in the crayfish. Naturwissenschaften 73: 154–155
Tierney AJ, Voigt R, Atema J (1988) Response properties of chemoreceptors from the medial antennular filament of the lobster Homarus americanus. Biol Bull 174: 364–372
Wachowiak M, Ache BW (1994) Morphology and physiology of olfactory projection neurons in the spiny lobster: J Comp Physiol A 175: 35–48
Wyse GA, Maynard DM (1965) Joint receptors in the antennule of Panulirus argus Latreille. J Exp Biol 42: 521–535
Yoshino M, Kondoh Y, Hisada M (1983) Projection of statocyst sensory neurons associated with crescent hairs in the crayfish Procambarus clarkii Girard. Cell Tissue Res 230: 37–48
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmidt, M., Ache, B.W. Processing of antennular input in the brain of the spiny lobster, Panulirus argus . J Comp Physiol A 178, 579–604 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00227374
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00227374