Abstract
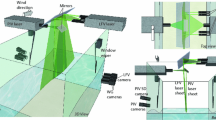
With a cw visible laser, the method of photon-burst correlation is used measure atmospheric crosswinds. A scaling law, including the effects of atmospheric turbulence, for performance evaluation of both laser Doppler (LDV) and laser time-of-flight (LTV) velocimeters, is introduced theoretically and established experimentally with field experiments. Crosswind measurements in the night at a range of 500 m with a low-power argon-ion laser are reported. The measured signal particle arrival rate is consistent with the predicted arrival rate based on the scaling law. In addition to the use of higher laser power, it is suggested that with proper inclusion of signal photon bursts resulting from the simultaneous arrival of several particles, routine operation of this type of laser velocimeter for long ranges, up to 1000m, should be feasible.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Yeh, H.Z. Cummins: Appl. Phys. Lett.4, 176 (1964)
L. Danielsson, E.R. Pike: J. Phys. E16, 107 (1983), and references therein
2nd Topical Meeting on Coherent Laser Radar: Technology and Applications, Technical Digest (Optical Society of America, 1983). The meeting was held in Aspen, Colorado, August 1–4, 1983; the concept of WINDSAT and its hardware developments were discussed extensively
M.J. Post, F.F. Hall, R.A. Richter, T.R. Lawrence: Appl. Opt.21, 2442 (1982)
E.O. Schulz-DuBois (ed.):Photon Correlation Techniques in Fluid Mechanics. Springer Ser. Opt. Sci.38 (Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York 1983). This is the proceedings of the 5th international conference held at Kiel-Damp, FRG, May 23–26, 1982; most of the active research groups in atmospheric crosswind sensing using photon-correlation techniques were represented. On p. 30 is the paper by J. B. Abbiss
K.G. Bartlett, C.Y. She: Appl. Opt.15, 1980 (1976)
K.G. Bartlett, C.Y. She: Opt. Lett.1, 175 (1977)
C.Y. She: Opt. Acta.26, 645 (1979)
K.G. Bartlett, C.Y. She: J. Opt. Soc. Am.69, 455 (1979)
C.Y. She, R.F. Kelley: J. Opt. Soc. Am.72, 365 (1982)
P.J. Bourke, C.G. Brown: Opt. Laser Tech.4, 23 (1971)
W.M. Farmer, J.O. Hornkohl: Appl. Opt.12, 2636 (1973)
L. Danielsson: InProceedings of the Symposium on Long Range and Short Range Optical Velocity Measurements, ed. by H.J. Pfeiffer, Report ISLR 117/80, paper XII (1980)
F. Durst, B. Howe, G. Richter: InPhoton Correlation Techniques in Fluid Mechanics, ed. by W.T. Mayo, Jr. and A.E. Smart, (Stanford Joint Institute for Aeronautics and Acoustics publication 1980) paper 3
L. Lading, A. Skov-Jensen, C. Fog, H. Andersen: Appl. Opt.17, 1486 (1978)
F. Durst, B.M. Howe, G. Richter: Appl. Opt.21, 2596 (1982)
W.H. Marlow (ed.):Aerosol Microphysics I and II, Topics Current Phys.16 and29 (Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York 1980 and 1982)
M. Kerker,The Scattering of Light and Other Electromagnetic Radiation (Academic Press, New York 1969)
S. Twomey:Atmospheric Aerosols (Elsevier, Amsterdam 1977) p. 9
R.L. Fante: Proc. IEEE63, 1669 (1975)
H.J. Pfeifer, M. Kömg, B. Koch: J. Opt. Soc. Am.70, 163 (1980)
D.L. Fried: J. Opt. Soc. Am.56, 1372 (1966)
R.F. Lutomirski, W.L. Woodie, R.G. Buser: Appl. Opt.16, 665 (1977)
M.B. Richardson:A General Algorithm for the Calculation of Laser Beam Spreading, ASL-TR-0116 (U.S. Army Atmospheric Sciences Laboratory, White Sands Missle Range, NM 1982)
R.F. Kelley, L.S. Hsu, C.Y. She: J. Opt. Soc. Am. to be published
G.R. Ochs, W.D. Cartwright, D.D. Russell:Optical C n2 Instrument Model II, NOAA Technical Memorandum ERL WPL-51 (1979)
R.F. Kelley: Performance Evaluation and Estimation of a Laser Time-of-Flight Velocimeter, Ph.D. thesis (Colorado State University, 1983) (unpublished) R.F. Kelley, L.S. Hsu, H. Shimizu, C.Y. She: In [Ref. 5, p. 205]
H.J. Nussbaumer:Fast Fourier Transform, and Convolution Algorithms, Springer Ser. Inform. Sci.2 (Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York 1982)
H.J. Pfeifer, E. Sommer: Private communication
E. Sommer, H.J. Pfeifer: In2nd Topical Meeting on Coherent Laser Radar: Technology and Applications. Technical Digest, Paper WAII (Optical Society of America, 1983)