Abstract
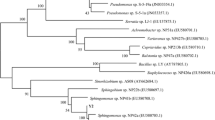
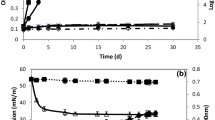
A marine bacterium isolated from a coastal hydrocarbon-polluted sediment has been described and attributed on the basis of its phenotypic and genotypic characteristics to the genus Sphingomonas sp. This strain was capable of using an alkylated phenanthrene 2-methylphenanthrene, as sole source of carbon and energy. In experiments, 2-methylphenanthrene (0.2 g/l) was added as crystals to the culture medium. After 5 days of aerobic growth at 30 °C, 70% was degraded and the complete dissipation occurred after 20 days. Furthermore, the strain could degrade various kinds of polyaromatic compounds, but failed to grow on aliphatic hydrocarbons.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 27 December 1996 / Received last revision: 10 June 1997 / Accepted: 14 June 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gilewicz, M., Ni'matuzahroh, ., Nadalig, T. et al. Isolation and characterization of a marine bacterium capable of utilizing 2-methylphenanthrene. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 48, 528–533 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530051091
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530051091