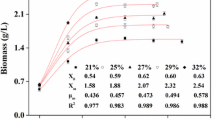
Abstract
The influence of increased dissolved O2 concentrations (DOC) on cell growth and production of the secondary metabolite manumycin by a strain of Streptomyces parvulus (Tü 64) was investigated in a stirred tank fermentor. DOC is given as the O2 partial pressure (po 2) in the gas phase in an equilibrium state with the liquid phase. Growth of S. parvulus was not influenced up to DOC equivalent to po 2 = 1260 mbar. At po 2 = 2205 mbar the maximum biomass concentration was lowered by 40%. Production of manumycin was markedly influenced by DOC and reached the maximal concentration at po 2 = 315 mbar. At increased DOC three new metabolites were observed. Two of them, 64p-A and 64p-B, were identified as carboxamides, which represent the branched side chain of the manumycin molecule and a derivative with a shorter chain length. The third metabolite, 64p-C, was a manumycin derivative containing an aromatic ring system. Feeding of glycerol during the production phase increased the total yield and showed a similar effect of DOC. Since DOC has significant regulation effects on product formation and selectivity, it should be used as a major parameter in development strategies of aerobic microbial processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bylinkina ES, Birukov VV (1972) The problem of scale-up in antibiotic biosynthesis. In: Terui G (ed) Proceedings of the 4th International Fermentation Symposium: Fermentation Technology Today, Kyoto, 19–25 March 1972. Yamada-Kami, Suita-Shi, Osaka, Japan, pp 105–115
Ceriotti G (1952) A microchemical determination of desoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem 198:297–303
Clark DS, Lentz CP (1961) Submerged citric acid fermentation of sugar beet molasses: effect of pressure and recirculation of oxygen. Can J Microbiol 7:447–453
Gräfe U, Bocker H, Reinhardt G, Thrum H (1975) Induzierbare Akkumulation von α-Ketoglutarsäure in Kulturen eines Makrolidantibioticum-bildenden Stammes von Streptomyces hygroscopicus JA 6599. Z Allg Mikrobiol 15:575–583
Khan AH, Ghose TK (1973) Kinetics of citric acid fermentation by Aspergillus niger. J Ferment Technol 51: 734–741
Liefke E (1988) Kultivierung aerober Bakterien bei erhöhtem Sauerstoffpartialdruck als verfahrenstechnische Möglichkeit zur Beeinflussung von Wachstum und Produktbildung. Doctoral Thesis, University of Dortmund
Liefke E, Onken U (1992) Influence of total and oxygen partial pressure on growth and metabolism of Methylomonas clara. Biotechnol Bioeng 40:719–724
Liefke E, Kaiser D, Onken U (1990) Growth and product infmation of actinomycetes cultivated at increased total pressure and oxygen partial pressure. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 32: 674–679
Okoshi H, Sato S, Mukataka S, Takahashi J (1987) Citric acid production by Candida tropicalis under high dissolved oxygen concentration. Agric Biol Chem 5:257–258
Onken U (1990) Batch and continuous cultivation of Pseudomonas fluorescens at increased pressure. Biotechnol Bioeng 35:983–986
Onken U, Liefke E (1989) Effect of total and partial pressure (oxygen and carbon dioxide) on aerobic microbial processes. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 40:137–169
Onken U, Kiese S, Jostmann T (1984) An airlift fermenter for continuous cultures at elevated pressures. biotechnol Lett 6:283–288
Oosterhuis NMG, Groesbeek NM, Kossen NWF, Schenk ES (1985) Influence of dissolved oxygen concentration on the oxygen kinetics of Gluconobacter oxydans. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 21:42–49
Puhar E, Lorencez I, Fiechter A (1983) Influence of partial pressure of oxygen and carbon dioxide on Methylomonas clara in continuous culture. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 18:131–134
Rozycki H, Strelczyk E (1986) Organic acids production by Streptomycess spp. isolated from soil, rhizosphere and mycorrhizosphere of pine (Pinus sylvestris L.). Plant Soil 96:337–345
Ryu DY, Humphrey AE (1972) A reassessment of oxygen transfer rates in antibiotics fermentations. J Ferment Technol 50:424–431
Sattler I (1992) Vorläufer-dirigierte Biosynthese und Fermentation unter erhöhtem Sauerstoffpartialdruck — Isolierung und Strukturaufklärung neuer Verbindungen der Manumycingruppe. Doctoral thesis, University of Göttingen
Thiericke R, Zeeck A, Robinson JA, Beale JM, Floss HG (1989) The biosynthesis of manumycin; origin of the oxygen and nitrogen atoms. J Chem Soc Chem Commun 402–403
Thiericke R, Zeeck A, Nakagawa A, Omura S, Herrold RE, Wu ST, Beale JM, Floss HG (1990) Biosynthesis of manumycin group antibiotics. J Am Chem Soc 112:3979–3987
Träger M, Müller U, Onken U (1987) Einfluss erhöhter Sauerstoffpartialdrück auf die Bildung von Gluconsäure durch Gluconobacter oxydans. Chem Ing Tech 59:939–940
Vardar F, Lilly MD (1982) Effect of cycling dissolved oxygen concentrations on product formation in penicillin productions. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 14:203–211
Zeeck A, Schröder K, Frobel K, Grobe R, Thiericke R (1987) The structure of manumycin, I. Characterization, structure elucidation and biological activity. J Antibiot 40: 1530–1540
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaiser, D., Onken, U., Sattler, I. et al. Influence of increased dissolved oxygen concentration on the formation of secondary metabolites by manumycin-producing Streptomyces parvulus . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 41, 309–312 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00221224
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00221224