Summary
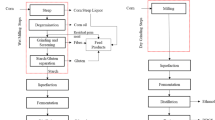
It is well known that molasses stillage is difficult to dry because of its high hygroscopicity. This investigation was made to try to affect the drying capability of beet molasses stillage by the addition of gelling agents. Increase in crude protein and essential amino acid content of beet molasses was obtained by growing Brevibacterium flavum and Candida utilis. The results obtained showed that drying performance is probably due to an “optimum” combination of the chemico-physical properties of the raw material.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang CT, Yang WL (1973) Study on feed yeast production from molasses distillery stillage. Taiwan Sugar 20:200–205
Klose RE, Glicksmann M (1968) Gums. In: Fura TE (ed) Handbook of food additives. The Chemical Rubber Co., Cleveland Ohio, p 325
Kujala P, Hull R, Engstrom F, Jackman E (1976) Alcohol from molasses as a possible fuel and the economics of distillery effluent treatment: Sugar y Azuc March: 28–39
Manfredini M, Cavani C (1980) Distillery effluents as animal feed: the use of condensed beet molasses stillage (CBMS) in broiler feeding. Anim Feed Sci Technol 5:233–239
Robertiello A (1982) Upgrading of agricultural and agoindustrial wastes: the treatment of distillery effluents (vinasses) in Italy. Agric Wastes 4:387–395
Sheenan GJ, Greenfield PF (1980) Utilization treatment and disposal of distillery wastewater. Water Res 14:257–277
Tauk SM (1982) Culture of Candida in vinasse and molasses: effect of acid and salt addition on biomass and raw protein production. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 16:223–227
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matteuzzi, D., Rosa, M.D., Brigidi, P. et al. Drying trials and protein enrichment by microbial growth on cane and beet molasses distillery stillage. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 21, 187–188 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00295118
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00295118