Abstract
Extracellular recordings from the vacoule of photoreceptor cells of Hirudo medicinalis L. were performed using microelectrodes. The cells were adapted by white light flashes given at constant intervals (20 s). Response height versus relative intensity curves obtained from the same cell in physiological saline (PS) and in bathing solutions of either a) lowered calcium contents (2 ΜM/1 or less) or b) raised calcium contents (15 mM/1) were compared. The cells' adaptation state in PS was operationally defined by the ratio Q=h A /h S where h A is the response height evoked by the adapting flashes, and h S is the corresponding saturation response height. Sensitivity changes were measured by the half saturation intensity shift. Lowering extracellular calcium resulted in:
-
1.
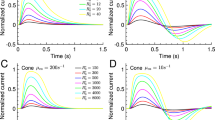
The response height increased and the shape of the response became more rounded and prolonged.
-
2.
The total resistance between the vacuole and outside decreased from 8.2±1.4 MΩ (n=6) in PS to 4.6±0.4 MΩ (n=5). The resistance was independent of the cells' adaptation state.
-
3.
A change of the cells' sensitivity occured either in direction to light adaptation or in direction to dark adaptation. It depended functionally on the ratio Q:
a) if Q was less or equal to about 0.6 the cells' sensitivity increased. b) if Q was greater than 0.6 the cells' sensitivity diminished.
Raising extracellular calcium decreased the sensitivity of all cells tested independent of their adaptation states in PS. The results can be interpreted under the assumptions that 1. the sensitivity of leech photoreceptor cells is inversely proportional to the intracellular free calcium concentration and Z. intracellular calcium can interact with extracellular calcium in relatively dark adapted cells whereas in relatively light adapted cells the raise of intracellular free calcium is mainly effected by a release from intracellular stores. It is assumed that a Q value of about 0.6 separates relatively light adapted cells from relatively dark adapted cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bader JE, Baumann F, Bertrand D (1976) Role of intracellular calcium and sodium in light adaptation in the retina of the honeybee drone (Apis mellifera L.). J Gen Physiol 67: 475–491
Brown JE (1977) Calcium ion, a putative intracellular messenger for light adaptation in Limulus ventral photoreceptors. Biophys Struct Mech 3: 141–143
Brown JE, Brown PK, Pinto LH (1977) Detection of light induced changes of intacellular ionized calcium concentration in Limulus ventral photoreceptors using arsenazo III. J Physiol 267: 299–320
Brown JE, Blinks JR (1974) Changes in intracellular free calcium concentration during illumination of invertebrate photoreceptors: detection with aequorin. J Gen Physiol 64: 643–665
Brown JE, Lisman JE (1975) Intracellular calcium modulates sensitivity and time scale in Limulus ventral photoreceptors. Nature 258: 252–253
Clark RB, Duncan G (1978) Two components of extracellular recorded photoreceptor potentials in the cephalopod retina: differential effects of Na, K and Ca. Biophys Struct Mech 4: 263–300
Duncan G, Pynsent PB (1977) Intracellular and extracellular photoreceptor potentials in the retina of the cephalopod Sepiola atlantica. J Physiol (London) 267: 37–38P
Fein A, Charlton JS (1975) Local membrane current in Limulus photoreceptors. Nature 258: 250–252
Fein A, Charlton JS (1977) A quantitative comparison of the effects of intracellular calcium injection and light adaptationon the photoresponse of Limulus ventral photoreceptors. J Gen Physiol 70: 591–600
Fioravanti R, Fuortes MFG (1972) Analyses of responses in visual cells of the leech. J Physiol (Lond) 227: 173–194
Hanani M, Shaw C (1977) A potassium contribution to the response of the barnacle photoreceptor. J Physiol (Lond) 270: 151–163
Lasanky A, Fuortes MFG (1969) The site of origin of electrical responses in cells of the leech Hirudo medicinalis. J Cell Biol 42: 241–252
Lipton SA, Ostroy SE, Dowling JE (1977) Electrical and adaptive properties of rod photoreceptors in Bufo marinus. J Gen Physiol 70: 747–770
Lisman JE (1976) Effects of removing extracellular calcium on excitation and adaptation in Limulus ventral photoreceptors. Biophys J 16: 1331–1335
Lisman JE, Brown JE (1972) The effects of intracellular injection of calcium and sodium ions on the light response of Limulus ventral photoreceptors. J Gen Physiol 59: 701–719
Maaz G, Stieve H (1980) The correlation of the receptor potential with the light induced transient increase in intracellular calcium concentration measured by absorption change of Arsenazo III injected into Limulus nerve photoreceptor cell. Biophys Struct Mech 6: 191–208
Martinez JM, Srebro R (1976) Calcium and the control of discrete wave latency in the ventral photoreceptors of Limulus. J Physiol (Lond) 261: 535–562
Millecchia R, Mauro A (1969) The central photoreceptor cells of Limulus III. A voltage clamp study. J Gen Physiol 54: 331–351
Naka K, Rushton WAH (1966) S-potential from luminosity units in the retina of the fish (Cyprinidae). J Physiol (Lond) 185: 587–599
O'Day PM, Lisman JE (1979) A component of light adaptation in Limulus ventral photoreceptors is dependent on extracellular calcium ARVO. Sarasota Florida USA, abstract 11, p 179
Perrelet A, Bader CR (1978) Morphological evidence for calcium stores in photoreceptors of the honeybee drone retina. J Ultrastruct Res 63: 237–243
Pinto LH, Brown JE (1977) Intracellular recordings from photoreceptors of the squid (Loligo pealii). J Comp Physiol 122: 241–250
Portzehl H, Caldwell PC, Ruegg JC (1964) The dependence of contraction and relaxation of muscle fibres from the crab Maia Squinado on the internal concentration of free calcium ions. Biochim Biophys Acta 79: 581–591
Sargent PB, Yau KW, Nicholls JG (1977) Extrasynaptic receptors on cell bodies of neurons in central nervous system of the leech. J Neurophysiol 40: 446–452
Schmidt JA, Grossman I, Alkon DL (1978) Effects of external calcium on the photoresponse of a nudibranch mollusc. Biophys J 21: 136a
Schröder W, Frings D, Stieve H (1980) Measuring calcium uptake and release by invertebrate photoreceptor cells by laser microprobe mass spectroscopy. Scanning Electron Microscopy/1980/I1, SEM Inc., AMF O'Hare (Chicago), IL 60666, USA, pp 647–654
Stieve H (1977) On the mechanism of conductance control of the arthropod visual cell membrane. Biophys Struct Mech 3: 145–151
Stieve H, Bruns M (1980) The sensitivity shift of Limulus ventral nerve photoreceptor in light adaptation depending on extracellular calcium concentration. Verh Dtsch Zool Ges 369
Stieve H, Bruns M, Gaube H (1978) Simultaneous recording by extra- and intracellular electrodes of light responses in the crayfish retina. Vision Res 18: 621–628
Walther JB (1970) Widerstandsmessungen an Sehzellen des Blutegels Hirudo medicinalis L. Verh Dtsch Zool Ges 64: 161–164
Walz B (1979) Subcellular calcium localization and ATP-dependent Ca uptake by smooth endoplasmatic reticulum in an invertebrate photoreceptor cell. An ultrastructural, cytochemical and X-ray microanalytical study. Eur J Cell Biol 20: 83–91
White RH, Walter JB (1969) The leech photoreceptor cell: ultrastructure of clefts connecting the phaosomes with extracellular space by lanthanum deposition. Z Zellforsch 95: 102–108
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Part of the data in this communication was presented at the annual meeting of the Deutsche Gesellschaft für Biophysik, held in Konstanz, October 1979
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wulf, J. Sensitivity changes of photoreceptor cells of Hirudo medicinalis caused by changes in extracellular calcium concentration. Biophys. Struct. Mechanism 8, 173–187 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00535458
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00535458