Abstract
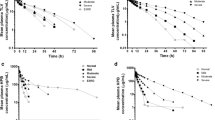
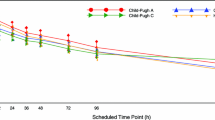
The single dose and steady-state pharmacokinetics of buspirone and its metabolite 1-pyrimidinyl piperazine (1-PP) have been evaluated in normal volunteers and patients with renal or hepatic impairment, using a parallel group design, with assignment of patients to study group on the basis of the degree of renal (mild, moderate, severe) or hepatic (compensated or decompensated) impairment. Each healthy volunteer or patient received a single dose of 10 mg buspirone on Day 1 of the study, and starting 36 h after the first dose, healthy volunteers and patients received 10 mg doses of buspirone every 12 hours for 9 days. On the morning of Day 10 they received the last dose. Serial blood samples were collected on Days 1, 5 and 10 and plasma was analysed for buspirone and 1-PP. The plasma concentrations of buspirone and 1-PP were highly variable regardless of the renal or hepatic function. The peak concentrations (Cmax) and area under the curves (AUC) of buspirone and 1-PP on Days D 5 and 10 were higher than on Day D 1. The trough levels (Cmin) and AUCs (D 5 and 10) of buspirone and 1-PP indicated, that, regardless of renal or hepatic function, steady state was reached after 3 to 5 days of dosing. At steady-state, patients with renal or hepatic impairment had significantly higher Cmax and AUC values of buspirone than in normal volunteers. However, the intensity and frequency of adverse experiences in patients with renal or hepatic impairment were not significantly different from those observed in normal volunteers. There was no correlation between the average plasma concentrations of buspirone (\(\bar C\)) and the degree of renal impairment judged by creatinine clearance. An excellent correlation was observed between \(\bar C\) of buspirone and serum albumin (r=0.862, and P<0.0001) as well as between \(\bar C\) and bromsulphalein clearance (r=0.678, P<0.0003).
In view of high intra-and inter-subject variability in buspirone concentrations, definitive dosing recommendations for patients with compromised renal or hepatic function could not be made, but such patients should initially be dosed cautiously with buspirone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goldberg HL, Finnerty RJ (1979) The comparative efficacy of buspirone and diazepam in the treatment of anxiety. Am J Psychiatry 136: 1184–1187
Rickels K, Weisman K, Norstad M, et al (1982) Buspirone and diazepam in anxiety: controlled study. J Clin Psychiat 43: 80–86
Rickels K, Schweizer E, Csanalosi I et al (1988) Long-term treatment of anxiety and risk of withdrawal. Prospective study of clorazepate and buspirone. Arch Gen Psychiatry 45: 444–450
Oritz A, Pohl R, Gershen S (1987) Azaspirodecanediones in general anxiety disorder: buspirone. J Affect Disord 13: 131–143
Gammans RE, Mayol RF and Labudde JA (1986) Metabolism and disposition of buspirone. Am J Med 80 [Suppl 3B]: 41–51
Caccia S, Vigano GL, Mingardi G, Garattini S, Gammans RE, Placchi M, Mayol RF, Pfeffer M (1988) Clinical pharmacokinetics of oral buspirone in patients with impaired renal function. Clin Pharmacokinet 14: 171–177
Dalhoff K, Poulsen HE, Garred P, Placchi M, Gammans RE, Mayol RF, Pfeffer M (1987) Buspirone pharmacokinetics in patients with cirrhosis. Br J Clin Pharmacol 24: 547–550
Lavers GD, Cole WH, Keeton RW, Gephardt MC, Dyniewicz M (1949) Bromsulphthalein clearnace. J Lab Clin Med 34: 965–972
Tovey JE (1967) Bromsulphalein clearance test of liver function Clin Chem Acta 15: 149–154
Simko V, Kelley RE, Dinesoy HP (1985) Predicting severity of liver disease:twelve laboratory tests evaluated by multiple regression. J Int Med Res 13: 249–254
Sciacca MA, Duncan GF, Shea JP, Faulkner III HC, Farmen RH, Pittman KA (1988) Simultaneous quantitation of buspirone and 1-(2-pyrimidinyl) piperazine in human plasma and urine by capillary gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr 428: 265–274
Gibaldi M, Perrier D (1982) Pharacokinetics, 2nd edn. Dekker, New York, pp 409–417
Conover WJ, Iman RL (1981) Rank transformations as a bridge between parametric and nonparametric statistics. Am Stat 35: 124–133
Branch RA, Herbert CM, Read AE (1973) Determinants of serum antipyrine half-lives in patients with liver disease. Gut 14: 569–573
Zilly W, Breimer DD, Richter E (1978) Hexobarbitol disposition in compensated and decompensated cirrhosis of the liver. Clin Pharmacol Ther 23: 525–534
Blaschke TF, Rubin PC (1979) Hepatic first-pass metabolism in liver disease. Clin Pharmacokinet 4: 423–432
Williams RL, Mamelok RD (1980) Hepatic disease and drug pharmacokinetics. Clin Pharmacokinet 5: 528–547
Bass NM, William RL (1988) Guide to drug dosage in hepatic disease. Clin Pharmacokinet 15: 396–420
McLean AJ, Morgan DJ (1991) Clinical pharmacokinetics in patients with liver disease. Clin Pharmacokinet 21: 42–69
Olsen GD, Bennet WM, Porter GA (1975) Morphine and phenytoin binding to plasma proteins in renal and hepatic failure. Clin Pharmacol Ther 17: 677–684
Blaschke TF (1977) Protein binding and kinetics of drugs in liver disease. Clin Pharmacokinet 2: 32–44
Giacomini KM, Massoud N, Wang FM, Giacomini JC (1984) Decreased binding of verapamil to plasma proteins in patients with liver disease. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 6: 924–928
Guechot J, Loric S, Vaubourdolle M, et al (1989) Effect of protein binding on testosterone extraction by human cirrhotic liver: evidence for a dissociation-limited uptake. J Clin Endocrinol Metabol 69: 200–203
Wood AJJ, Kornhauser DM, Wilkinson GR, Shand DG, Branch RA (1978) The influence of Cirrhosis on steady-state blood concentration of unbound propranalol after oral administration. Clin Pharmacokinet 3: 478–487
Colli A, Buccino, G, Cocciolo M, Parravicini R, Scaltrino G (1988) Disposition of flow-limited (lidocaine) and a metabolic capacity-limited (theophylline) in liver cirrhosis. Clin Pharmacol Ther 44: 642–649
Klotz U, Meltorse TS, Wilkinson GR, Schenker S (1974) The effect of cirrhosis on the disposition and elimination of meperidine in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther 16: 667–675
Branch RA, James JA, Read AE (1978) The clearance of anti-pyrine and indocyanine green in normal subjects and patients with chronic liver disease. Clin Pharmacol Ther 20: 81–89
Forrest JAH, Andrigenssens P, Finlayson NDC, Prescott LF (1979) Paracetamol metabolism in chronic liver disease. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 15: 427–431
Greenblatt DJ, Harmatz JS, Shader RI (1978) Factors influencing diazepam pharmacokinetics: age, sex and liver disease. Int J Clin Pharmacol 15: 341–347
Williams RL, Upton RA, Cello JP, et al (1984) Naproxen disposition in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 27: 291–296
Schoene B, Fleischmann RA, Remmer H, von Oldershausen HF (1972) Determination of drug metabolizing enzymes in needle biopsies of human liver. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 4: 65–73
Alvin J, Mettorse TS, Hoyumpa A, Bush MT, Schenker S (1975) The effect of liver disease in man on disposition of phenobarbital. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 192: 224–235
Hacki W, Bircher J, Preisig R (1976) A new look at the plasma disappearance of sulfobromophthalein (BSP): correlation with the BSP transport maximum and the hepatic plasma flow in man. J Lab Clin Med 88: 1019–1031
Molino G, Milanese M, Villa A, Caranna A, Gaidano GP (1978) Discrimination of hepatobiliary diseases by the evaluation of bromsulfophthalein blood kinetics. J Lab Clin Med 91: 396–408
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barbhaiya, R.H., Shukla, U.A., Pfeffer, M. et al. Disposition kinetics of buspirone in patients with renal or hepatic impairment after administration of single and multiple doses. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 46, 41–47 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00195914
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00195914