Summary
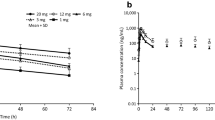
Human calcitonin (hCT) injected into the lumen of the descending colon of normal human subjects was absorbed within minutes and could be recognized intact in plasma as shown by RIA in combination with reverse-phase HPLC.
The absorption was low and variable, with bioavailabilities ranging from 0.01% to 2.7% relative to intravenously administered hCT (area under the concentrationtime curve). With intravenous hCT serum calcium was lowered and the fractional urinary excretion of calcium, phosphorus, sodium and chloride was significantly stimulated. With the intracolonic hCT, the fractional urinary excretions of calcium, sodium and chloride were also marginally stimulated relative to intracolonic vehicle (placebo).
In conclusion, hCT is absorbed intact from the colon, but the bioavailability is low and highly variable.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amoss M, Rivier J, Guillemin R (1972) Release of gonadotropins by oral administration of synthetic LRF or a tripeptide fragment of LRF. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 35:175–177
Austin LA, Heath III IH (1981) Calcitonin. Physiology and pathophysiology. N Engl J Med 304:269–278
Bijvoet OLM, Van der Sluys Veer J, De Vries HR, Van Koppen ATJ (1971) Natriuretic effect of calcitonin in man. N Engl J Med 284:681–688
Buclin T, Randin JP, Jacquet AF, Azria M, Attinger M, Gomez F, Burckhardt P (1987) The effect of rectal and nasal administration of salmon calcitonin in normal subjects. Calcif Tissue Int 41:252–258
Danforth E, Moore RO (1959) Intestinal absorption of insulin in the rat. Endocrinology 65:118–123
Dietrich FM, Hunziker WH, Fischer JA (1975) Synthetic human calcitonin: analysis of antibodies obtained from various animal species and determination of immunoreactive hormone in human sera. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 80: 465–486
Fricker G, Bruns C, Munzer J, Briner U, Albert R, Kissel T, Vonderscher J (1991) Intestinal absorption of the octapeptide SMS 201995 visualized by fluorescence derivatization. Gastroenterology 100:1544–1552
Friend DR (1991) Colon-specific drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 7:149–199
Gnaedinger MP Uehlinger DE, Weidmann P, Sha SG, Muff R, Born W, Rascher W Fischer JA (1989) Distinct hemodynamic and renal effects of calcitonin gene-related peptide and calcitonin in men. Am J Physiol 257: E848-E854
Goverde BC, Veenkamp FJN (1972) Routine assay of total urinary hydroxyproline based on resin-catalysed hydrolysis. Clin Chim Acta 41: 29–40
Haas HG, Dambacher MA, Guncaga J, Lauffenburger T (1971) Renal effects of calcitonin and parathyroid extract in man. Studies in hypoparathyroidism. J Clin Invest 50:2689–2702
Hastewell J, Lynch S, Williamson I, Fox R, Mackay M (1992) Absorption of human calcitonin across the rat colon in vivo. Clin Sci: 82:589–594
Huwyler R, Born W, Ohnhaus EE, Fischer JA (1979) Plasma kinetics and urinary excretion of exogenous human and salmon calcitonin in man. Am J Physiol 236: E15-E19
Kidron M, Bar-On H, Berry EM, Ziv E (1982) The absorption of insulin from various regions of the rat intestine. Life Sci 31: 2837–2841
Köhler E, Duberow-Drewe M, Drewe J, Ribes G, Loubatiéres-Mariani MM, Mazer N, Gyr K, Beglinger C (1987) Absorption of an aqueous solution of a new synthetic somatostatin analogue administered to man by gavage. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 33: 167–171
Lundin S, Vilhardt H (1986) Absorption of 1-deamino-8-D-arginine vasopressin from different regions of the gastrointestinal tract in rabbits. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 112: 457–460
Mackay M (1990) Delivery of recombinant peptide and protein drugs. Biotechnology Genetic Engineering Rev 8:251–278
Moore JA, Pletcher SA, Ross MJ (1986) Absorption enhancement of growth hormone from the gastrointestinal tract of rats. Int J Pharm 34:35–43
Muff R, Dambacher MA, Perrenoud A, Simon C, Fischer JA (1990) Efficacy of intranasal human calcitonin in patients with Paget's disease refractory to salmon calcitonin. Am J Med 89:181–184
Petermann JB, Born W Chang J-Y, Fischer JA (1987) Identification in the human central nervous system, pituitary, and thyroid of a novel calcitonin gene-related peptide, and partial amino acid sequence in the spinal cord. J Biol Chem 262: 542–545
Saffran M, Kumar GS, Savariar C, Burnham JC, Williams F, Neckers DC (1986) A new approach to the oral administration of insulin and other peptide drugs. Science (Wash) 233: 1081–1084
Touitou E, Rubinstein A (1986) Targeted enteral delivery of insulin to rats. Int J Pharm 30: 95–99
Ziegler R, Holz G, Raue F, Streibl W (1979) Nasal application of human calcitonin in Paget's disease of bone. In: MacIntyre I, Szelke M (eds) Molecular Endocrinology. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 293–300
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beglinger, C., Born, W., Muff, R. et al. Intracolonic bioavailability of human calcitonin in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 43, 527–531 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02285096
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02285096