Summary
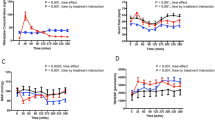
Nifedipine capsules t.d.s. and an extended release formulation of nifedipine, nifedipine-ER tablets, given once daily in corresponding daily doses, have been compared with placebo in a double-blind, three-way crossover study in 24 patients with stable angina pectoris. The objective was to study the influence on the antianginal effect of the different pharmacokinetics of several preparations of nifedipine. All patients received concomitant treatment with β-adrenoceptor blockers. Antianginal efficacy was assessed by a dynamic exercise test at the end of the dosage intervals, i.e. 8 and 24 h after nifedipine capsules and nifedipine-ER, respectively, as well as 6 h after dosing. Six h after dosing the time of onset of chest pain and total excercise time were longer and total work was significantly higher during both nifedipine-ER (plasma concentration 260 nmol/l) and placebo treatment than after nifedipine capsules (plasma concentration 78 nmol/l). Time to 1 mm ST depression was longer during nifedipine-ER than during nifedipine capsule treatment. No significant difference was seen between nifedipine-ER and placebo. At the end of the dosage interval (24 and 8 h after nifedipine-ER and nifedipine capsules, respectively), no significant difference was found between nifedipine-ER (plasma concentration 75 nmol/l) and the other two treatments. However, placebo was superior to nifedipine capsules (plasma concentration 58 nmol/l) both in the time to onset of chest pain and total exercise time. The lack of effect at the end of the dosage interval was probably due to the subtherapeutic plasma nifedipine level. Nifedipine capsules, but not the extended release formulation, were found to be significantly inferior to placebo both after 6 h and at the end of the dosage interval. This unexpected finding may have been induced by the rapid and extensive fluctuation in plasma levels, with a rapid decline from the peak value after the capsule formulation, since a similar deterioration was not seen with nifedipine-ER, despite similar plasma concentrations at the end of the dosage interval. This phenomenon merits further research.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sherman LG, Liang C-S (1983) Nifedipine in chronic stable angina: a double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Am J Cardiol 51: 706–711
Uusitalo A, Arstila M, Bae EA, Härkönen R et al. (1986) Metoprolol, nifedipine and the combination in stable effort angina pectoris. Am J Cardiol 57: 733–737
Nesto RW, White HD, Wynne J, Holman BL, Antman EM (1987) Comparison of nifedipine and isosorbid dinitrate when added to maximal propranolol therapy in stable angina pectoris. Am J Cardiol 60: 256–261
Crake T, Quyyumi AA, Wright C, Mockus L, Fox KM (1987) Treatment of angina pectoris with nifedipine: a double blind comparison of nifedipine and slow-release nifedipine alone and in combination with atenolol. Br Heart J 58: 617–620
Morse JR (1988) Comparison of combination nifedipine-propranolol and diltiazem-propranolol with high dose diltiazem monotherapy for stable angina pectoris. Am J Cardiol 62: 1028–1032
Chaitman BR, Wagniart P, Pasternac A et al. (1984) Improved exercise tolerance after propranolol, diltiazem or nifedipine in angina pectoris: Comparison at 1, 3 and 8 hours and correlation with plasma drug concentration. Am J Cardiol 53: 1–9
Ardissino D, Servi S de, Salerno JA, Specchia G, Previtali M, Mussini A, Bobba P (1983) Efficacy, duration and mechanism of action of nifedipine in stable exercise-induced angina pectoris. Eur Heart J 4: 873–881
Deanfield J, Wright C, Fox K (1983) Treatment of angina pectoris with nifedipine: importance of dose titration. Br Med J 286: 1467–1470
Ahnoff M (1984) Determination of felodipine in plasma by capillary gas chromatography with electron capture detection. J Pharmaceut Biomed Anal 2: 519–526
Åström H, Jonsson B (1976) Design of exercise test, with special reference to heart patients. Br Heart J 38: 289–296
DeMots H, Glasser SP (1989) Intermittent transdermal nitroglycerin therapy in the treatment of chronic stable angina. J Am Coll Cardiol 13: 786–793
Lette J, Gagnon R-M, Lemire JG, Morissette M (1984) Rebound of vasospastic angina after cessation of long-term treatment with nifedipine. Can Med Assoc J 130: 1169–1171
Subramanian VB, Bowles MJ, Khurmi NS, Davies AB, O'Hara MJ, Raftery EB (1983) Calcium antagonist withdrawal syndrome: objective demonstration with frequency-modulated ambulatory ST-segment monitoring, Br Med J 286: 520–521
Emanelsson H, Hjalmarson Å, Holmberg S, Waagstein F, Waldenström A (1984) Effects of nifedipine on arterial concentration and myocardial extraction of catecholamines during pacing-induced angina pectoris. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 6: 224–232
Katzman PL, Hulthén UL, Hökfelt B (1986) The effect of 8 weeks treatment with the calcium antagonist felodipine on blood pressure, heart rate, working capacity, plasma renin activity, plasma angiotensin II, urinary catecholamines and aldosterone in patients with essential hypertension. Br J Clin Pharmacol 21: 633–640
Weisser B, Lieder P, Göbel BO, Vetter H, Düsing R (1989) Effect of the calcium antagonist felodipine on baroreflex-setpoint, sympathetic counterregulation and cardiac beta-1 receptor sensitivity. Am J Hypertens 2: 70A
Parker JO, Fung HL (1984) Transdermal nitroglycerin in angina pectoris. Am J Cardiol 54: 8–13
Parker JO, Farell B, Lakey KA, Moe G (1987) Effect of intervals between doses on the development of tolerance to isosorbid dinitrate. N Engl J Med 316: 1440–1444
Martsevich SYU, Metelitsa VI, Rumiantsev DO, Piotrovskii VK, Slastnikova ID, Egorov LV, Vygodin VA (1990) Development of tolerance to nifedipine in patients with stable angina pectoris. Br J Clin Pharmacol 29: 339–346
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karlson, B.W., Emanuelsson, H., Herlitz, J. et al. Evaluation of the antianginal effect of nifedipine: influence of formulation dependent pharmacokinetics. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 40, 501–506 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00315230
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00315230