Summary
The effect of submaximal exercise on the pharmacokinetics of low dose intravenous propranolol was studied in 15 healthy human subjects.
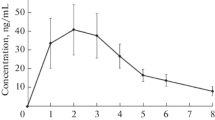
There was a wide individual variation in the results for each subject and a large difference in the degree of changes with exercise. The effect of exercise on the pharmacokinetics of propranolol, a flow limited drug, is marked but variable.
This phenomenon may have profound effects on patients taking the drug regularly who exercise intermittently and drug doses may have to be adjusted.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marshall JM (1982) Antihypertensives. In: Mungall DR (ed) Applied clinical pharmacokinetics. Raven Press, New York
Routledge PA, Shand DG (1979) Clinical pharmacokinetics of propranolol. Clin Pharm 4: 73–90
Shand DG (1976) Pharmacokinetics of propranolol: a review. Postgrad Med J 52 [Suppl 4]: 22–25
Divoll M, Greenblatt DJ, Arendt RM (1984) Propranolol kinetics: use of automated liquid chromatography. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol 22: 457–460
Kopitar Z, Vhrova B, Lenardic A, Cvelbar P, Zorz M, Francetic I (1976) Dose-dependent bioavailability of propranolol. Int J Clin Pharm Ther Toxicol 24: 319–322
Dey M, Brisson J, Davis G, Enever R, Pray K, Zaim B, Dvornik D (1986) Relationship between plasma propranolol concentration and dose in young, healthy volunteers. Biopharm Drug Dispos 7: 103–111
Mayer N, Krumpl G, Schneider W, Raberger G (1986) Propranolol ameliorates exercise induced regional myocardial dysfunction in dogs. Clin Exp Pharm Physiol 13: 791–799
Frisk-Holmberg M, Strom G (1986) Exercise during therapeutic beta-blockade: A two year study in hypertensive patient. Clin Pharm Ther 40: 395–399
Shepherd JT (1985) Circulatory response to beta-adrenergic blockade at rest and during exercise. Am J Cardiol 55: 87D-94D
Ades PA, Gunther PG, Meachem CP, Handy MA, Le-Winter MM (1988) Hypertension in exercise and beta-adrenergic blockade. Ann Intern Med 109: 629–634
Karlsson J (1985) Metabolic adaptations to exercise: a review of potential beta-adrenoceptor antagonist effects. Am J Cardiol 55: 480–550
Vandongen R, Margetts B, Beilin LJ, deKlerk N, Rogers P (1986) Blood pressure and catecholamines following exercise during selective beta-blockade in hypertension. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 30: 283–287
Fletcher GF (1985) Exercise training during chronic beta blockade in cardiovascular disease. Am J Cardiol 55: 110D-113D
Savin WM, Gordon EP, Kaplan SM, Hewitt BF, Harrison DC, Haskell WL (1985) Exercise training during long term betablockade treatment in healthy subjects. Am J Cardiol 55: 101D-109D
Arends BG, Bohm ROB, van Kemenade JE, Rahn KH, van Baak MA (1986) Influence of physical exercise on the pharmacokinetics of propranolol. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 31: 375–377
Shand DB, Kornhauser DM, Wilkinson GR (1975) Effects of route of administration and blood flow on hepatic drug elimination. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 195: 424–432
Shand DG, Cotham RH, Wilkinson GR (1976) Perfusion-Limited effects of plasma drug binding on hepatic drug extraction. Life Sci 19: 125–130
Exercise Testing and Training of Apparently Healthy Individuals: A Handbook for Physicians. The Committee on Exercise, American Heart Association 1972
Nygard G, Shelver WH, Wahba Khalil SK (1979) Sensitive high-pressure liquid chromatographic determination of propranolol in plasma. J Pharm Sci 68: 379–381
Dill DB, Costill DL (1974) Calculation of percentage changes in volumes of blood, plasma and red cells in dehydration. J Appl Physiol 37: 247–248
Swartz RD, Sidell, Cucinell SA (1974) Effects of physical stress on the disposition of drugs eliminated by the liver in man. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 188: 1–7
Mooy J, Arends B, Kaminade JV, Boehm R, Rahn KM, Baak MV (1986) Influence of prolonged submaximal exercise on the pharmacokinetics of verapamil in humans. J Cardiovasc Pharm 8: 940–942
Ylitalo P, Hinkka M (1985) Effect of exercise on plasma levels and urinary excretion of sulfadimidine and procainamide. Int J Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 23: 548–553
Kamimori GH, Somani SM, Knowlton RG, Perkins RM (1987) The effects of obesity and exercise on the pharmacokinetics of caffeine in lean and obese volunteers. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 31: 595–600
Hetzler RK (1988) The effect of prolonged walking on the pharmacokinetics and metabolism of caffeine, Ph.D. Thesis, Southern Illinois University, Carbondale
Rowell LB (1988) Human circulation: Regulation during physical stress. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frank, S., Somani, S.M. & Kohnle, M. Effect of exercise on propranolol pharmacokinetics. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 39, 391–394 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00315416
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00315416