Summary
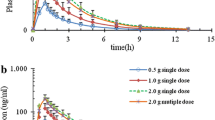
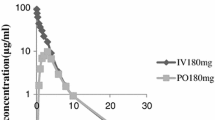
The pharmacokinetics of sulfametopyrazine were studied for seven days after a single oral dose of 2 g. in healthy volunteers in order to establish its chemotherapeutic value. — The appearance and disappearance of the drug in the plasma were evaluated both for compounds with a free amino group and for total sulphonamides. The half-life and absorption, distribution, elimination and excretion coefficients were calculated, as well as the concentrations in plasma water and interstitial fluid. The estimated drug concentrations in the urine agreed with those calculated from the excretion coefficients. — In all subjects at the end of the seventh day the concentrations in all body compartments of active compounds exceeded the minimum required for a therapeutic effect. The highest concentrations found in the urine were always significantly lower than the drug's basal solubility at pH 5, thus excluding any risk of crystalluria.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- β:
-
total binding capacity of plasma proteins for SMP
- ρ:
-
Specific gravity of blood (ρ Bl), and interstitial fluid (ρIF)
- μ:
-
minimum inhibitory concentration for bacterial growth. Evaluation of μ against E. coli or other pathogenic bacteria in a medium free of antagonists [29]
- ε:
-
ratio of dose interval to half-life
- τ:
-
dose interval
- σ:
-
safety factor. Proportionality constant between μ andc min for a therapeutic efficacy of 95 per cent
- δ′:
-
fraction of the administered drug absorbed from the depot (gastrointestinal tract etc.)
- Δ′:
-
distribution coefficient with respect to the drug concentration in blood plasma (ml/g)
- D*:
-
initial dose of the drug
- D :
-
maintenance dose
- M :
-
molecular weight of the drug (280)
- G :
-
weight of subject (kg)
- F :
-
area between time axis and concentration curve (plotted c' values)
- t′ 50% :
-
apparent biological half-life
- w 1 :
-
water content of plasma (ml/ml)
- p :
-
protein concentration of plasma (pBl), or interstitial fluid (pIF) (g/l)
- c′ IF :
-
concentration in the interstitial fluid
- C′ 0 :
-
concentration in plasma at zero time after i.v. administration
- c′ 01 :
-
concentration in plasma after oral absorption extrapolated to zero time
- c 1 :
-
concentration in plasma water of the drug with free amino function
- c min :
-
minimum inhibitory concentration needed in plasma water (minimum therapeutic concentration)
- k′ 01 :
-
rate constant for absorption
- k′ 1 :
-
rate constant for absorption determined at timet; (similarlyk′2)
- K :
-
total elimination coefficient
- k′ el :
-
rate constant for elimination
- k F :
-
rate constant for formation of metabolites
- k D :
-
excretion coefficient of SMP with free amino function
- k U :
-
coefficient of metabolite excretion
- D 0 :
-
quantity of SMP in the body at time zero
- D B :
-
quantity of SMP in the body at timet
- D U :
-
quantity of SMP excreted in the urine at timet
- M F :
-
quantity of metabolites formed at timet
- M B :
-
quantity of metabolites present in the body at timet
- M U :
-
quantity of metabolites excreted in the urine at timet
- K′ :
-
dissociation constant for the sulphonamide-protein complex
- ′:
-
notation for quantities related to drug concentrations in plasma, e.g. c′ (corresponding term without ′ refer to plasma water)
References
Berlin, H.: The practical evaluation of Kelfizin, a new longacting sulfonamide, 720–723. III. Intern. Congress Chemotherapy, 22–27 July, 1963. Stuttgart: G. Thieme 1964.
-- Theory and practice in the evaluation of Kelfizin. Research report Kabi, 303, 1963.
Bratton, A.C., Marshall, E.K. jr.: A new coupling component for sulfanilamide determination. J. biol. Chem.128, 537–550 (1939).
Bünger, P., Diller, W., Fuhr, J., Krüger-Thiemer, E.: Vergleichende Untersuchungen an neueren Sulfanilamiden. Ärztl. Forsch.11, 247–255 (1961).
Cummings, A.J., Martin, B.K., Park, G.S.: Kinetic considerations relating to the accrual and elimination of drug metabolites. Brit. J. Pharm. Chem.29, 136–149 (1967).
—— King, M.L., Martin, B.K.: A kinetic study of drug elimination: the excretion of paracetamol and its metabolites in man. Brit. J. Pharm. Chem.29, 150–157 (1967).
Despopoulos, A., Gallahan, P.X.: Molecular features of sulfonamide transport in renal excretory processes. Amer. J. Physiol.203, 19–26 (1962).
Dost, F.H.: Grundlagen der Pharmakokinetik. 2. Auflage. Stuttgart: Thieme 1968.
Gladtke, E.: Ein Sulfonamid mit extrem langsamer Elimination. Elimination, Verteilung, Dosierung und enterale Absorption von 4-Sulfanilamido-5,6-dimethoxypyrimidin beim Kind. Klin. Wschr.43, 1332–1334 (1965).
Koizumi, T., Arita, T., Kakemi, K.: Absorption and excretion of drugs. XXI. Some pharmacokinetic aspects of absorption and excretion of sulfonamides. Excretion from the kidney. Chem. Pharm. Bull.12, 428–432 (1964).
Krüger-Thiemer, E.: Theorie der Wirkung bakteriostatischer Chemotherapeutica. Quantitative Beziehungen zwischen Dosierung,in vitro-Wirkung, Pharmakokinetik und Distribution. Jahresbericht, Borstel. Fünfter Band, S. 316–400. Herausgegeben von Enno Freerksen. Berlin-Göttingen-Heidelberg: Springer 1961.
-- Bünger, P.: Evaluation of the risk of crystalluria with sulfa drugs. Vol. VI of Proceedings of the European Society for the study of drug toxicity. Stockholm, Sweden, June 1965. (Reprinted from Excerpta Med., Intern. Congr. Ser. No. 97, 185–207.)
—— —— The role of the therapeutic regimen in dosage design. Part. I. Chemotherapia10, 61–73 (1965/66). Part II, Ibidem10, 129–144 (1965/66).
—— Diller, W., Bünger, P.: Pharmacokinetic models regarding protein binding of drugs. Antimicrob. agents and Chemother.5, 183–191 (1965).
—— Wempe, E., Töpfer, M.: Die antibakterielle Wirkung des nicht eiweißgebundenen Anteils der Sulfanilamide im menschlichen Plasmawasser. Arzneimittel-Forsch.15, 1309–1317 (1965).
—— Bünger, P., Dettli, L., Spring, P., Wempe, E.: Dosage regimen calculation of chemotherapeutic agents. Part III, Sulfasymazine. Chemotherapia,10, 325–338 (1965/66).
Loo, J.C.K., Riegelman, S.: New method for calculating the intrinsic absorption rate of drugs. J. Pharm. Sc.57, 918–928 (1968).
Macdonald, H., Place, V.A., Falk, H., Darken, M.A.: Sulfasymazine: absorption, excretion, and metabolism in man. Chemotherapy12, 360–368 (1967).
Martin, B.K.: Kinetics of elimination of drugs possessing high affinity for the plasma proteins. Nature207, 959–960 (1965).
—— Drug urinary excretion data; some aspects concerning their interpretation. Brit. J. Pharm. Chem.29, 181–193 (1967).
Meyer, M.C., Guttman, D.E.: The binding of drugs by plasma proteins. J. Pharm. Sc.57, 895–918 (1968).
Nelson, E.: Studies on the crystalluria potential of sulfamethoxydiazine. Chemotherapy10, 145–151 (1965/66).
—— Krüger-Thiemer, E.: Abstract of pharmacokinetic models and symbols. Chemotherapia12, 8–14 (1964).
van Rossum, J.M., Tomey, A.H.M.: Role of accumulation and plateau plasma concentration of drugs after chronic medication. J. Pharm. Pharmac.20, 390–392 (1968).
Sereni, F., Perletti, L., Marubini, E., Mars, G.: Pharmacokinetic studies with a long-acting sulfonamide in subjects of different age. A modern approach to drug dosage problems in developmental pharmacology. Pediat. Res.2, 29–37 (1968).
Wiegand, R.C., Sanders, P.G.: Calculation of kinetic constants from blood levels of drugs. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther.146, 271–275 (1964).
Wiegand, R.G., Buddenhagen, J.D., Endicott, C.J.: Multiple dose excretion kinetics. J. Pharm. Sc.52, 268–273 (1963).
—— Chun, A.H.C., Scherfling, E., Lopez, F., Herting, R.L.: The chemical pharmacology of 2-sulfanilamido-3-methoxypyrazine. Antimicrobiol. agents Chemother.1964, 549–553 (1965).
Yamazaki, M., Aoki, M., Kamada, A.: Biological activities of drugs. III. Physicochemical factors affecting the excretion of sulfonamides in rabbits. Chem. Pharm. Bull.16, 707–714 (1968).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Devriendt, A., Jansen, F.H. & Weemaes, I. Pharmacokinetics of sulfametopyrazine (Kelfizine W) effects of a single oral dose. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 3, 36–42 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00560289
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00560289