Summary
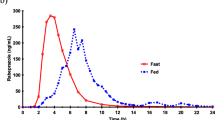
The influence of food intake on the absorption of phenytoin was examined in eight healthy volunteers, by study of single-dose kinetics following ingestion of phenytoin 300 mg either with a standardized breakfast or on an empty stomach. Blood samples were collected at regular intervals from 0 to 48 h, and serum concentrations of unmetabolized phenytoin were determined by gas chromatography. Serum concentrations of the major metabolite of phenytoin, 4-hydroxyphenytoin, were measured by mass fragmentography. Concurrent intake of food and phenytoin appeared to accelerate absorption of the drug from the formulation used, and the peak concentrations were significantly higher (mean increase 40%) in the postprandial than in the preprandial state. As reflected by the AUC (area under the curve), the amount of drug absorbed was increased during postprandial conditions, although the difference only reached borderline significance. It is suggested that phenytoin should always be taken in a defined relation to meals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Melander, A., Wåhlin, E., Danielson, K., Rerup, C.: On the influence of concomitant food intake on sulfonamide bioavailability. Acta Med. Scand.200, 497–500 (1976)
Melander, A., Wåhlin, E., Danielson, K., Hanson A.: Bioavailability of propylthiouracil: interindividual variation and influence of food intake. Acta Med. Scand.201, 41–44 (1977)
Melander, A., Danielson, K., Vessman, J., Wåhlin, E.: Bioavailability of oxazepam: absence of influence of food intake. Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol.40, 584–588 (1977)
Melander, A., Kahlmeter, G., Kamme, C., Ursing, B.: Bioavailability of metronidazole in fasting and non-fasting healthy subjects and in patients with Crohn's disease. Europ. J. clin. Pharmacol.12, 69–72 (1977)
Kamme, C., Kahlmeter, G., Melander, A.: Evaluation of spiramycin as a therapeutic agent for elimination of nasopharyngeal pathogens. Scand. J. Infect. Dis.10, 135–139, 1978.
Melander, A., Berlin-Wahjlén, A., Bodin, N.-O., Danielson, K., Gustafsson, B., Lindgren, S., Westerlund, D.: Bioavailability of d-propoxyphene, acetyl salicylic acid, and phenazone in a combination tablet (Doleron): interindividual variation and influence of food intake. Acta Med. Scand.202, 119–124 (1977)
Melander, A., Hanson, A., Rudell, B., Scherstén, B., Thulin, T., Wåhlin, E.: Enhancement of hydralazine bioavailability by food. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.22, 104–107 (1977)
Melander, A., Danielson, K., Scherstén, B., Wåhlin, E.: Enhancement of the bioavailability of propranolol and metoprolol by food. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.22, 108–112 (1977)
Melander, A., Danielson, K., Scherstén, B., Thulin, T., Wåhlin, E.: Enhancement by food of canrenone bioavailability from spironolactone. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.22, 100–103 (1977)
Melander, A., Wåhlin, E.: Enhancement of dicoumarol bioavailability by concomitant food intake. Europ. J. clin. Pharmacol.14, 441–444 (1978)
Melander, A., Danielson, K., Hanson, A., Jansson, L., Rerup, C., Scherstén, B., Thulin, T., Wåhlin, E.: Reduction of isoniazid bioavailability in normal men by concomitant intake of food. Acta Med. Scand.200, 93–97, 1976
Conney, A. H., Pantuck, E. J., Hsiao, K.-C., Carland, W. A., Anderson K. E., Alvares, A. P. and Kappas, A.: Enhanced phenacetin metabolism in human subjects fed charcoalbroiled beef. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.20, 633–642 (1976)
Melander, A.: Influence of food on the bioavailability of drugs. Clin. Pharmacokinet.2, 337–51 (1978)
Kappas, A., Anderson, K. E., Conney, A. H., Alvares, A. P.: Influence of dietary protein and carbohydrate on antipyrine and theophylline metabolism in man. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.20, 643–653 (1976)
Berlin, A., Agurell, S., Borgå, O., Lund, L., Sjöqvist, F.: Micromethod for the determination of diphenylhydantoin in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid — a comparison between a gas chromatographic and a spectrophotometric method. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest.29, 281–287 (1972)
Hoppel, C., Garle, M., Elander, M.: Mass fragmentographic determination of diphenylhydantoin and its main metabolite 4-(hydroxyphenyl)-5-phenylhydantoin in human plasma. J. Chromatogr.116, 53–61 (1976)
Lund, L., Alvan, G., Berlin, A., Alexandersson, B.: Pharmacokinetics of single and multiple dose of phenytoin in man. Europ. J. clin. Pharmacol.7, 81–86 (1974)
Alván, G., Bertler, Å., Eeg-Olofsson, O., Karlsson, E., Sjöqvist, F., Tomson, G.: Biologic availability — a comparison of three phenytoin preparations. Läkartidningen72, 2621–2623 (1975)
Fredholm, B., Lund, L., Olsson, B., Plym-Forshell, C. G.: Differences in biological availability of phenytoin in different oral preparations. Paper given at Pharmaceutic Annual Congress, Sweden, 1974
Wilson, J., Höjer, B., Rane, A.: Loading and conventional dose therapy with phenytoin in children: Kinetic profile of parent drug and main metabolite in plasma. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.20, 48–58 (1976)
Levy, R. H., Pitlick, W. H., Troupin, A. S., Green, J. R., Neal, J. M.: Pharmacokinetics of carbamazepine in normal man. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.17, 657–664 (1975)
Lund, L.: Clinical significance of generic inequivalence of three different pharmaceutical preparations of phenytoin. Europ. J. clin. Pharmacol.7, 119–124 (1974)
Stewart, M. J., Ballinger, B. R., Devlin, E.-J., Miller, A. Y., Ramway, A. C.: Bioavailability of phenytoin: a comparison of two preparations. Europ. J. clin. Pharmacol.9, 209–12 (1975)
Glazko, A. J.: Diphenylhydantoin. Pharmacology (Basel)8, 163–177 (1972)
LaDu, B. N., Mandel, H. G., Way, E. L. (Eds): Fundamentals of drug metabolism and drug disposition p. 36. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins 1971
Johannesen, S. I., Strandjord, R. E.: Absorption and protein binding in serum of several anti-epileptic drugs. In: Clinical Pharmacology of anti-epileptic drugs. Schneider, H., Janz, D., Gardner-Thorpe, C., Meinard, H., Sherwin, A. L. (eds.), pp. 262–273, discussion contribution, pp. 103–104. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer 1975
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Melander, A., Brante, G., Johansson, Ö. et al. Influence of food on the absorption of phenytoin in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 15, 269–274 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00618516
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00618516