Abstract
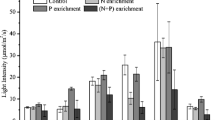
We report nutrient addition bioassays at 18 stations in Chesapeake Bay (USA) to assess resources limiting phytoplankton growth. Data were pooled from several sampling programs conducted from 1989 to 1994. Spatially, light and P limitation declined from low salinity regions to high salinity regions, as N limitation increased. This spatial pattern was driven primarily by freshwater inflows with high N/P and seawater inflows with low N/P. Seasonally, there was a marked progression of winter light limitation, spring P limitation, and summer N limitation at mesohaline and polyhaline stations. The seasonal pattern appeared to be caused by temperature, mixing, river discharge, and sediment P fluxes. At high salinity stations, we also observed winter N limitation (caused by DIN depletion prior to spring nitrate delivery), and at lower salinity stations there was fall P limitation (caused by reaeration of bottom sediments). At tidal fresh stations, turbidity and nutrient concentrations resulted in continuous light limitation, except at some stations in summer. Interannual decreases in light limitation and increases in N and P limitation appear to represent improvements in water quality.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 31 October 1997 / Accepted: 18 December 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fisher, T., Gustafson, A., Sellner, K. et al. Spatial and temporal variation of resource limitation in Chesapeake Bay. Marine Biology 133, 763–778 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002270050518
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002270050518