Abstract
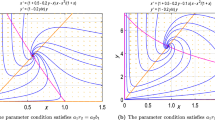
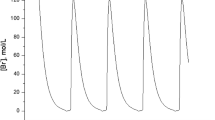
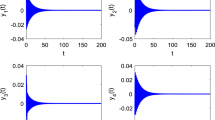
In this paper a mathematical model of AIDS is investigated. The conditions of the existence of equilibria and local stability of equilibria are given. The existences of transcritical bifurcation and Hopf bifurcation are also considered, in particular, the conditions for the existence of Hopf bifurcation can be given in terms of the coefficients of the characteristic equation. The method extends the application of the Hopf bifurcation theorem to higher differential equations which occur in biological models, chemical models, and epidemiological models etc.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, R.M. and May, R.M., Transmission Dynamics of HIV Infection Nature 326,March.,12 (1987), 137–142.
Barre-Sinoussi, F., et al., Isolation of a T-Lymphotropic Retovirus From a Patient at Risk for Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS),Science,220 (1983), 868–870.
Carr, J., Applications of Center Manifold Theory, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1981.
Castillo-Chavez, C., Review of Recent Models of HIV/AIDS Transmission, First Autumn Workshop on Mathematical Ecology, ICTP, Italy, 1988.
Catillo-Chavez, C. and Levin, S.A., The Role of Long Incubation Periods in the Dynamics of Acquired Immunodeflciency Syndrome (AIDS) Single Population Models, First Autumn Workshop on Mathematical Ecology, ICTP, Italy, 1988.
Dietz, K. and Hadeler, K.P., Epidemiological Models for Sexually Transmitted Diseases,J. Math. Biol.,26 (1988), 1–25.
Gallo, R.C., The First Human Retorvirus, Scientific American, December, 1986, 88–98.
Gallo, R.C., The AIDS Virus, Scientific American, January, 1987, 45–56.
Guckenheimer, J. and Holmes, P., Nonlinear Oscillations, Dynamical Systems and Bifurcations of Vector Fields, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1983.
Hassard, B.D. and Kazarinoff, N.D. and Wan, Y-H., Theory and Applications of Hopf Bifurcation, London Mathematical Society Lecture Note Series, 41, 1981.
Knox, E.G., A Transmission Model for AIDS,European Epidemiol.,1 (1986), 1165–1177.
Lancaster, P., Theory of Matrices, Academic, New York, 1969.
Marsden, J.E. and McCracken, M., The Hopf Bifurcation and Its Applications, Springer-verlag, New York, Berlin, 1976.
Wong-Staal, F. and Gallo, R.C., Human T-Lymphotropic Retroviruses,Nature,317 (1985), 395–403.
Coolfont Report., A PHS Plan for Prevention and Control of AIDS and the AIDS Virus,Public Health Rep.,101 (1986), 341–348.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This project is supported by the National Science Foundation “Tian Yuan” Terms and LNM Institute of Mechanics Academy of Science.
This project is supported by the National and Yunnan Province Natural Science Foundation of China.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jing, Z., Liu, Z. Qualitative analysis for a mathematical model of aids. Acta Mathematicae Applicatae Sinica 9, 302–316 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02005919
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02005919