Abstract
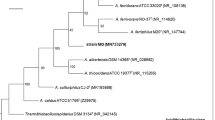
Total base sequences of the 16S rRNA genes ofThiobacillus halophilus andThiobacillus aquaesulis show that these bacteria fall into the gamma- and beta-subdivisions, respectively of the Proteobacteria. The closest relative ofT. halophilus isThiobacillus hydrothermalis (with 98.7% similarity), and the closest relative ofT. aquaesulis isThiobacillus thioparus (93.2% similarity). Physiological properties and mol% G+C content of their DNA serve to confirm that these four organisms are all distinct species. It is reiterated that the species currently assigned to the genusThiobacillus are clearly so diverse that they need reclassification into several genera. The type species,T. thioparus, is unequivocally placed in the beta-subdivision of the Proteobacteria, thus requiring that the use of the genus nameThiobacillus be restricted to the chemolithoautotrophic species falling into that group.T. aquaesulis andT. thioparus may thus be regarded as true species ofThiobacillus. The relatively large number of obligately chemolithoautotrophicThiobacillus species falling in the gamma-subdivision of the Proteobacteria need further study in order to assess the case for reclassification into one or more new or different genera.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beijerinck MW (1904a) Ueber die Bakterien, welche sich im Dunkeln mit Kohlensäure als Kohlenstoffquelle ernähren können. Centralbl Bakteriol. Abt II 11:593–599
Beijerinck MW (1904b) Phénomènes de réduction par les microbes. Arch Neer Sci (Sect 2) 9:131–157
Beijerinck MW, Minkman DC (1910) Bildung und Verbrauch von Stickoxydul durch Bakterien. Centralbl Bakteriol Abt II 25: 30–63
Drobner E, Huber H, Rachel R, Stetter KO (1992)Thiobacillus plumbophilus spec. nov., a novel galena and hydrogen oxidizer. Arch Microbiol 157:213–217
Durand P, Reysenbach A-L, Prieur D, Pace N (1993) Isolation and characterization ofThiobacillus hydrothermalis sp. nov., a mesophilic obligately chmolithotrophic bacterium isolated from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent in Fiji Basin. Arch Microbiol 159:39–44
Felsenstein J (1988) Phylogenies from the molecular sequences: inference and reliability. Annu Rev Genet 22:521–565
Friedrich CG, Mitrenga G (1981) Oxidation of thiosulfate byParacoccus denitrificans and other hydrogen bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett 10:209–212
Giovannoni SJ (1991) The polymerase chain reaction. In: Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics. Wiley, Chichester, pp 177–203
Goebel BM, Stackebrandt E (1994) Cultural and phylogenetic analysis of mixed microbial populations found in natural and commercial bioleaching environments. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:1614–1621
Gutell RR, Larsen N, Woese CR (1994) Lessons from an evolving rRNA: 16S and 23S rRNA structures from a comparative perspective. Microbiol Rev 58:10–26
Katayama-Fujimura Y, Tsuzaki N, Kuraishi H (1982) Ubiquinone, fatty acid and DNA base composition determination as a guide to the taxonomy of the genusThiobacillus. J Gen Microbiol 128:1599–1611
Katayama Y, Hiraishi A, Kuraishi H (1995)Paracoccus thiocyanatus sp. nov., a new species of thiocyanate-utilizing facultative chemolithotroph, and transfer ofThiobacillus versutus to the genusParacoccus asParacoccus versutus comb. nov. with emendation of the genus. Microbiology (UK) 141:1469–1477
Kelly DP (1982) Biochemistry of the chemolithotrophic oxidation of inorganic sulphur. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B298:499–528
Kelly DP (1985) Physiology of the thiobacilli: elucidating the sulphur oxidation pathway. Microbiol Sci 2:105–109
Kelly DP (1988) Oxidation of sulphur compounds. Soc Gen Microbiol Symp 42:65–98
Kelly DP (1989) Physiology and biochemistry of unicellular sulfur bacteria. In: Schlegel HG, Bowien B (eds) Biology of autotrophic bacteria. Science Tech Publishers, Madison, pp 193–217
Kelly DP (1990) Energetics of chemolithotrophic bacteria. In: Krulwich TA (ed) Bacterial energetics. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 479–503
Kelly DP, Harrison AP (1989) GenusThiobacillus Beijerinck. In: Staley JT (ed) Bergey's manual of systematic bacteriology, vol 3. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 1842–1858
Kuenen JG, Robertson LA, Tuovinen OH (1992) The generaThiobacillus, Thiomicrospira, andThiosphaera. In: Balows A, Trüper HG, Dworkin M, Harder W, Schleifer K-H (eds) The prokarytotes. A handbook on the biology of bacteria: ecophysiology, isolation, identification, application, 2nd edn. Springer Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 2638–2657
Lane DJ (1991) 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In: Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics. Wiley, Chichester, pp 177–203
Lane DJ, Harrison AP, Stahl D, Pace B, Giovannoni SJ, Olsen GJ, Pace NP (1992) Evolutionary relationships among sulfur- and iron-oxidizing eubacteria. J Bacteriol 174:269–278
Ludwig W, Mittenhuber G, Friedrich CG (1993) Transfer ofThiosphaera pantotropha toParacoccus denitrificans. Int J Syst Bacteriol 43:363–367
Ludwig W, Schleifer K-H (1994) Bacterial phylogeny based on 16S and 23S rRNA sequence analysis. FEMS Microbiol Rev 15:155–173
Maidak BL, Larsen N, McCaughey MJ, Overbeek R, Olsen GJ, Fogel K, Blandy J, Woese CR (1994) The ribosomal database project. Nucleic Acids Res 22:3485–3487
Marmur J (1961) A procedure for the isolation of deoxyribonucleic acid from microorganisms. J Mol Biol 3:208–218
Neefs J-M, Van de Peer Y, De Rijk P, Goris A, De Wachter R (1991) Compilation of small ribosomal subunit RNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 19:1987–2015
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Saunders SE, Burke JF (1990) Rapid isolation of miniprep DNA for double strand sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res 18:4948
Wiegel J (1992) The genusXanthobacter. In: Balows A, Trüper HG, Dworkin M, Harder W, Schleifer K-H (eds) The prokaryotes. A handbook on the biology of bacteria: ecophysiology, isolation, identification, applications, 2nd edn. Springer Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 2365–2383
Woese CR, Weisburg WG, Paster BJ, Hahn CM, Tanner RS, Krieg NR, Koops H-P, Harms H, Stackebrandt E (1984) The phylogeny of purple bacteria: the beta subdivision. Syst Appl Microbiol 5:327–336
Wood AP, Kelly DP (1988) Isolation and physiological characterisation ofThiobacillus aquaesulis sp. nov., a novel facultatively autotrophic moderate thermophile. Arch Microbiol 149: 339–343
Wood AP, Kelly DP (1991) Isolation and characterisation ofThiobacillus halophilus sp. nov., a sulphur-oxidising autotrophic eubacterium from a Western Australian hypersaline lake. Arch Microbiol 156:277–280
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McDonald, I.R., Kelly, D.P., Murrell, J.C. et al. Taxonomic relationships ofThiobacillus halophilus, T. aquaesulis, and other species ofThiobacillus, as determined using 16S rDNA sequencing. Arch. Microbiol. 166, 394–398 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01682985
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01682985