Abstract
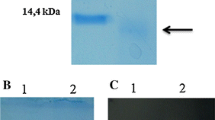
Two electrophoretically different forms of superoxide dismutase, one of them containing manganese-protein and the other iron-protein, were detected in eleven different strains of the genus Flavobacterium. The activities of the different strains were similar to those described for other bacteria. The two molecular forms of the enzyme differed clearly with regard to activity, electrophoretic behaviour, sensitivity to cyanide and peroxide, and NaCl requirement. Both molecular forms were isolated from Flavobacterium halmephilum. Molecular mass absorption spectra, metal content, optimum pH, heat-sensitivity and stability were described.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews P (1965) The gel-filtration behaviour of protein related to the their molecular weight over a wide range. Biochem J 96:595–606
Austin FF, Barbieri JT, Cori RE, Grigas KE, Cox CD (1981) Distribution of superoxide dismutase, catalase and peroxidase activities among Treponema pallidum and other spirochetes. Infect Inmun 33:372–379
Borders CL, Fridovich I (1985) A comparison of the effects of cyanide, hydrogen peroxide and phenyglyoxal on eukaryotic and prokaryotic Cu, Zn superoxide dismutase. Arch Biochem Biophys 241:472–476
Bull CH, Fee JA (1985) Steady-state kinetic studies of superoxide dismutases: properties of the iron containing protein from Escherichia coli. J Am Chem Soc 107:3295–3304
Daily OP, Debell RM, Joseph SW (1978) Superoxide dismutase and catalase levels in halophilic vibrios. J Bacteriol 134:375–380
Kanematsu S, Asada K (1979) Ferric and manganic superoxide dismutase in Euglena gracilis. Arch Biochem Biophys 195:535–545
Kirby TW, Lancaster JR, Fridovich I (1981) Isolation and characterization of the iron-containing superoxide dismutase of Methanobacterium bryantii. Arch Biochem Biophys 210:140–148
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
McCord JM, Fridovich I (1969) Superoxide dismutase: on enzymic function for erythrocuprein (hemocuprein). J Biol Chem 244:6049–6055
Moody CS, Hassan HM (1984) Anaerobic biosynthesis of the manganese-containing superoxide dismutase in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 259:12821–12825
Selander RK, Smith MH, Yang SV, Johnson WE, Gentry JB (1971) Biochemical polymorphism in the genus Peromyscus. I. Variation in the old field mouse (Peromycus polionotus). Studied in Genetics 6. University of Texas Publication 7103:49–90
Ventosa A, Quesada E, Rodriguez-Valera F, Ruiz-Berraquero F, Ramos-Cormenzana A (1982) Numerical taxonomy of moderately halophilic Gram negative rods. J Gen Microbiol 128:1959–1968
Yost FJ, Fridovich I (1973) An iron-containing superoxide dismutase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 248:4905–4908
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sanchez-Moreno, M., Monteoliva-Sanchez, M., Ortega, F. et al. Superoxide dismutase in strains of the genus Flavobacterium: isolation and characterization. Arch. Microbiol. 152, 407–410 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00425182
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00425182