Abstract
Chloroflexus aurantiacus grown in batch culture took up exogenous alcohols and incorporated these into bacteriochlorophyll c as the esterifying alcohol. It was possible to change the distribution of the naturally occurring homologs of bacteriochlorophyll c esterified with phytol, hexadecanol, and octadecanol by adding the appropriate alcohol. The corresponding homolog then made up at least 60% of the cellular bacteriochlorophyll c. It was also possible to obtain novel bacteriochlorophyll homologs not found in detectable amounts in control cells by adding fatty alcohols with short chains (C10, C12) or long chains (C20). These changes in bacteriochlorophyll composition had no detectable effects on the spectral properties of the chlorosomes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
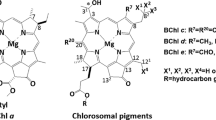
- BChl :
-
Bacteriochlorophyll
References
Amesz J (1991) Green photosynthetic bacteria and heliobacteria. In: Shively JM, Barton LL (eds) Variations in autotrophic life. Academic Press, New York London, pp 99–119
Borrego CM, Garcia-Gil LJ (1994) Separation of bacteriochlorophyll homologues from green photosynthetic sulfur bacteria by reversed-phase HPLC. Photosynthesis Res 41:157–163
Brune DC, Nozawa T, Blankenship RE (1987) Antenna organization in green photosynthetic bacteria. 1. Oligomeric bacteriochlorophyll c as a model for the 740 nm absorbing bacteriochlorophyll c in Chloroflexus aurantiacus chlorosomes. Biochemistry 26:8644–8652
Caple MB, Chow H, Strouse CE (1978) Photosynthetic pigments of green sulfur bacteria. J Biol Chem 19:6730–6737
Fages F, Griebenow N, Griebenow K, Holzwarth AR, Schaffner K (1990) Characterization of light-harvesting pigments of Chloroflexus aurantiacus. Two new chlorophylls: oleyl (octadec-9-enyl) and cetyl (hexadecanyl) bacteriochlorophyllides-c. J Chem Soc (Perkin Trans 1) 1990:2791–2797
Holzwarth AR, Schaffner K (1994) On the structure of bacteriochlorophyll molecular aggregates in the chlorosomes of green bacteria. A molecular modelling study. Photosynthesis Res 41:225–233
Katz JJ, Bowman MK, Michalski TJ, Worcester DL (1991) Chlorophyll aggregation: chlorophyll/water micelles as models for in vivo long-wavelength chlorophyll. In: Scheer H (ed) The chlorophylls, CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 211–235
Larsen KL, Cox RP, Miller M (1994) Effects of illumination intensity on bacteriochlorophyll c homolog distribution in Chloroflexus aurantiacus grown under controlled conditions. Photosynthesis Res 41:151–156
Matsuura K, Olson JM (1990) Reversible conversion of aggregated bacteriochlorophyll c to the monomeric form by 1-hexanol in chlorosomes from Chlorobium and Chloroflexus. Biochim Biophys Acta 1019:233–238
Miller M, Cox RP, Gillbro T (1991) Energy transfer kinetics in chlorosomes from Chloroflexus aurantiacus: studies using picosecond absorbance and fluorescence spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1057:187–194
Nozawa T, Ohtomo K, Suzuki M, Morishita Y, Madigan MT (1991) Structures of bacteriochlorophylls c in chlorosomes from a new thermophilic bacterium Chlorobium tepidum. Chem Lett 1991:1763–1766
Oelze J, Sontgerath B (1992) Differentiation of the photosynthetic apparatus of Chloroflexus aurantiacus depending on growth with different amino acids Arch Microbiol 157:141–147
Ormerod JG (1992) Physiology of the photosynthetic prokaryotes. In: Mann NH, Carr NG (eds) Photosynthetic prokaryotes, Plenum Press, New York, pp 93–119
Otte SCM, Meent EJ van de, Veelen PA van, Pundsnes AS, Amesz J (1993) Identification of the major chlorosomal bacteriochlorophylls of the green sulfur bacteria Chlorobium vibrioforme and Chlorobium phaeovibrioides: their function in lateral energy transfer. Photosynthesis Res 35:159–169
Pierson BK, Castenholz RW (1991) The family Chloroflexaceae. In: Balows A, Truper HG, Dworkin M, Harder W, Schleifer K-H (eds) The prokaryotes: a handbook on the biology of bacteria. Ecophysiology, isolation, identification, application. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 3754–3774
Press WH, Teukolsky SA, Vetterling WT, Flannery BP (1992) Numerical recipes in C. The art of scientific computing. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Risch N, Brockmann H, Gloe A (1979) Structuraufklarung von neuartigen Bacteriochlorophyllen aus Chloroflexus aurantiacus. Liebigs Ann Chem 1979:408–418
Roepstorff P (1993) 252-Californium plasma desorption time-of-flight mass spectrometry of peptides and proteins. In: Jones C, Mulloy B, Thomas AH (eds) Methods in molecular biology: spectroscopic methods and analysis: NMR, mass spectrometry, and metalloprotein techniques. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 229–235
Savitsky A, Golay MJE (1964) Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least-squares procedures. Anal Chem 36:1627–1639
Scheer H (1991) Structure and occurrence of chlorophylls. In: Scheer H (ed) The chlorophylls. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 3–30
Schmidt K (1980) A comparative study on the composition of chlorosomes (Chlorobium vesicles) and cytoplasmic membranes from Chloroflexus aurantiacus strain Ok-70-fl and Chlorobium limicola f. thiosulfatophilum strain 6230. Arch Microbiol 124:21–31
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Larsen, K.L., Miller, M. & Cox, R.P. Incorporation of exogenous long-chain alcohols into bacteriochlorophyll c homologs by Chloroflexus aurantiacus. Arch. Microbiol. 163, 119–123 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00381785
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00381785